The Latest News
FCC | Broadband | Congress | Wireless | State Regulation
Mergers & Acquisitions: Goldman Sachs Purchasing ImOn Communications
February 17, 2022 – Global investment firm Goldman Sachs has entered into an agreement to purchase ImOn Communications, a communications service provider based in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Goldman Sachs’s asset management division is making the acquisition. ImOn was originally created as a cable TV provider, but today operates a fiber-to-the-premises network that covers over 60,000 homes and businesses in Cedar Rapids, Marion, Hiawatha, Iowa City, and Dubuque, Iowa. The parties have not disclosed the purchase price or other financial terms of the agreement.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Authorizes RDOF Support For 2,576 Winning Bids (6th RDOF Authorization)
February 14, 2022 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced it has authorized Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction support for 2,576 winning bids. This is the sixth Public Notice authorizing RDOF support. A list of the authorized winning bids is available as Attachment A to the Bureau’s Public Notice. The authorizations were granted after the Bureau reviewed long-form application information for each authorized winning bidder, including letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters, and concluded the submissions were acceptable. Consequently, the Bureau has directed and authorized the Universal Service Administrative Company to obligate and disburse Universal Service Fund support to each winning bidder. Support will be disbursed in 120 monthly payments, beginning at the end of February 2022.
FCC Releases Information on Applications For Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program – 161 Applications Accepted – Roughly $5.6 Billion In Funding Requested
February 9, 2022 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released further details on the applications filed for participation in the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program. A total of 181 applications were filed to participate in the program, and of those, 162 have been initially found eligible and acceptable. Applicants whose applications are found materially deficient will have a 15-day opportunity to cure the deficiency before their application is denied.
Of the 162 acceptable filings, the gross cost estimate demand for support for the removal, replacement, and disposal of Huawei and ZTE equipment is approximately $5.6 billion. The gross demand for requested funding in the submitted applications exceeds the $1.9 billion appropriated for the program. Also, the Bureau has determined that “the cost estimates submitted with applications appear to be significantly higher than the estimated amounts reported to the Commission in the 2019 data collection.”
The Wireline Competition Bureau and Reimbursement Program Fund Administrator will now carefully evaluate all cost estimates and “closely scrutinize Reimbursement Claim Requests to ensure that reimbursement is limited to reasonable expenses that are actually incurred.” However, because of the amount and complexity of filed applications, the Wireline Competition Bureau has announced it will extend the application review period by an additional 45 days, moving the deadline to approve or deny submitted applications from May 1, 2022, to Wednesday, June 15, 2022.
Annual CPNI Certifications Due March 1, 2022
February 7, 2022 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has released an Enforcement Advisory reminding telecommunications carriers that they must file an annual Customer Proprietary Network Information (CPNI) certification by March 1, 2022. The annual certification documents a telecommunications carrier’s compliance with the FCC’s CPNI rules, and must be filed in EB Docket No. 06-36. The telecommunications carriers that must file an annual CPNI certification include, but are not limited to, local exchange carriers, interexchange carriers, commercial mobile radio services providers, resellers, prepaid telecommunications providers, and calling card providers. Failure to comply with the FCC’s CPNI rules, including failing to file an annual certification, may result in an enforcement action, including monetary forfeitures of up to $220,213 for each violation or each day of a continuing violation, up to a maximum of $2,202,123. Additional information on the annual CPNI certification is available from the Bureau’s Enforcement Advisory.
Comments On FCC’s Proposed Broadband Consumer Label Requirements Due March 9th
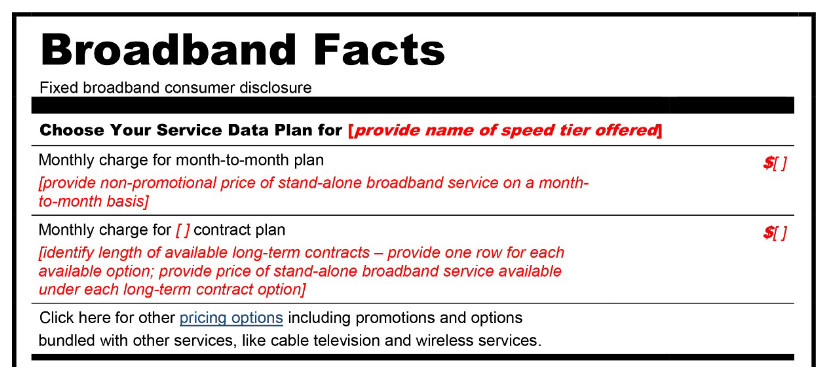
February 7, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) broadband consumer labels Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) has been published in the Federal Register. As a result, comments on the NPRM are due on or before March 9, 2022, and reply comments are due on or before March 24, 2022. In the NPRM, the FCC proposes to “require that broadband Internet access service providers (ISPs) display, at the point of sale, labels to disclose to consumers certain information about prices, introductory rates, data allowances, broadband speeds, and management practices, among other things.” Among other things, the FCC’s NPRM seeks comment on the following issues:
In order to allow sufficient time for providers to implement the measures necessary to
comply with these requirements, the FCC proposes to make these rules effective six months following publication in the Federal Register of the Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB’s) approval of the adopted rules. Is six months sufficient for both large and smaller providers?Should the FCC adopt a different implementation timeline or temporary exemption for smaller providers to allow them more time to come into compliance with the labels’ requirements, and does the FCC have the discretion to do so?
Are there alternative ways, other than different implementation timeframes, to minimize the economic impact on smaller service providers while achieving the FCC’s transparency objectives?
Have broadband service offerings and consumers’ use of broadband services changed sufficiently since the release of the 2016 labels to necessitate modifications to the labels’ content and/or format, or are there any other reasons to change the content or format of the labels?
Where should the labels be displayed to best inform consumers?
Are there enforcement issues related to the label requirement, including how the FCC should ensure the accuracy of label content?
Are there any implementation issues, including the time by which broadband providers should be required to display the labels?
What is needed to ensure that any required labels are accessible to persons with disabilities and that any broadband consumer label advances equity in the provision of and access to digital communications services and products for all people of the United States, without discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, or disability?
NTIA Receives Public Comments On Implementing Infrastructure Act’s Broadband Funding Programs
February 5, 2022 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has posted the comments it has received in response to a Notice and Request for Comment concerning implementation of the broadband funding programs created by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. NTIA’s Notice and Request for Comment was released on January 10, 2022, and public input was due no later than 5 p.m. on February 4, 2022. The Infrastructure Act directs NTIA to distribute over $48 billion in funding through the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program, the Enabling Middle Mile Broadband Infrastructure Program, and the State Digital Equity Planning Grant Program. NTIA sought public comment on 36 specific topics related to the three broadband funding programs.
FCC Receives 181 Applications For Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program – Roughly $5.6 Billion In Funding Requested
February 4, 2022 – FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has notified Congress that the FCC has received over 181 applications from U.S. communications service providers requesting approximately $5.6 billion from the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program. Funding will be used to “reimburse providers of advanced communications services for costs reasonably incurred for removing, replacing, and disposing of communications equipment and services produced or provided by Huawei Technologies Company and ZTE Corporation.” Applications to participate in the Program, which was allocated $1.9 billion, were due January 28, 2022. The FCC is now reviewing each application to, among other things, confirm the eligibility of the applicant, identify reimbursable network equipment and services, and analyze cost estimates.
FCC Announces Online Portal For Submitting Supply Chain Annual Report – Providers Of Advanced Communications Services Must File By May 5, 2022
February 4, 2022 – The FCC’s Office of Economics and Analytics and Wireline Competition Bureau have announced the creation of an online portal for use by providers of advanced communications services to file Supply Chain Annual Reports detailing whether their networks contain or use “covered” communications equipment or services. The Supply Chain Annual Report must be submitted to the online portal no later than May 5, 2022.
“Covered” equipment or services are prohibited from U.S. communications networks because they have been “deemed to pose an unacceptable risk to the national security of the U.S. or the security and safety of U.S. persons.” Providers of advanced communications services must file a Supply Chain Annual Report, regardless of whether they have covered equipment or services or whether they are eligible to participate in the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program. The FCC has explained that “as this is a new information collection, past participation in the 2019 Supply Chain Information Collection does not constitute compliance with this reporting requirement.” Thus, a provider of advanced communications service that does not have any covered communications equipment or services must file a report and certify as such through the online reporting portal by May 5, 2022.
If a provider certifies its network does not contain or use “covered” communications equipment or services, it will not be required to file again, unless there is a change in its status. A subsequent annual report is not needed “unless the provider purchases, rents, leases, or obtains covered communications equipment or services at a later date, or if additional equipment or services are added to the Covered List that would mean that the provider can no longer certify that it does not have any covered communications equipment or services to report.” However, according to the Public Notice, after this year’s Supply Chain Annual Report, any provider that has previously certified that it had purchased, rented, leased, or otherwise obtained covered communications equipment and services on the Covered List must continue to submit a report once per year on or before March 31 with respect to information as of December 31 of the previous year until such covered communications equipment and services are removed. Additional information on the online reporting portal, reporting requirements, and filing instructions are available from the FCC’s Supply Chain website at https://www.fcc.gov/supplychain.
The FCC’s Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau has published a list of the prohibited equipment and services, which is periodically reviewed and updated. Currently, this Covered List contains equipment or services produced by five entities, which extends both to subsidiaries and affiliates of the entities, as well as to telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entities or using such equipment:
Huawei Technologies Company – Telecommunications equipment, including telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entity or using such equipment.
ZTE Corporation – Telecommunications equipment, including telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entity or using such equipment.
Hytera Communications Corporation – Video surveillance and telecommunications equipment, to the extent it is used for the purpose of public safety, security of government facilities, physical security surveillance of critical infrastructure, and other national security purposes, including telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entity or using such equipment.
Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Company – Video surveillance and telecommunications equipment, to the extent it is used for the purpose of public safety, security of government facilities, physical security surveillance of critical infrastructure, and other national security purposes, including telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entity or using such equipment.
Dahua Technology Company – Video surveillance and telecommunications equipment, to the extent it is used for the purpose of public safety, security of government facilities, physical security surveillance of critical infrastructure, and other national security purposes, including telecommunications or video surveillance services provided by such entity or using such equipment.
Broadband Industry Groups Urge Federal Agencies To Waive “Buy American” Provisions For Infrastructure Act Broadband Funding
February 1, 2022 – Broadband industry advocacy groups TIA, CCA, CTIA, NCTA, NTCA, TechNet, and US Telecom have sent a letter to Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo, Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, and Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack urging the agency leaders to consider a waiver of the “Buy American” provisions in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act for information and communication technology products. Those provisions generally require that materials and products included in infrastructure projects funded by the Act be produced in the U.S., and they apply to the Infrastructure Act’s broadband funding programs. The Infrastructure Act provides for exceptions to or waiver of Buy American provisions under certain conditions. The broadband associations maintain that “the waiver would allow better investment in broadband infrastructure to ensure Americans are connected.” They claim “the limited waiver would be in line with previous waivers from the NTIA and other agencies implemented in the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, and it is a vital and necessary step toward the goal of ensuring that every American has access to high-speed broadband.”
USAC Files Estimated 2Q 2022 Universal Service Funding Requirements
February 1, 2022 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed the Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections For Second Quarter 2022. USAC’s filing shows the following total projected 2Q 2022 funding requirements for each Universal Service Fund (USF) support mechanism:
High Cost Support Mechanism – $880.14 million (The 1Q 2022 funding requirement was $1.04452 billion). The 2Q 2022 total funding requirement for the High Cost Support Mechanism was initially projected at $999.62 million, but was adjusted as follows: decreased by prior period adjustments of $134.73 million and increased by administrative costs of $15.25 million; resulting in a total projected 2Q 2022 funding requirement of $880.14 million.
Low Income Support Mechanism – $220.47 million (The 1Q 2022 funding requirement was $137.51million). The 2Q 2022 total funding requirement for the Low Income Support Mechanism was initially projected at $277.76 million, but was adjusted as follows: decreased by prior period adjustment of $72.98 million and increased for administrative costs of $15.69 million; resulting in a total projected 2Q2022 funding requirement of $220.47 million.
Rural Health Care Support Mechanism – negative $7.62 million (The 1Q 2022 funding requirement was $11.72 million). The 2Q 2022 Rural Health Care Support Mechanism collection requirement of $153.01 million represents one quarter of the cap for Funding Year 2021. The amount includes collection requirements for the Telecommunications Program, the Healthcare Connect Fund, and administrative costs. The collection requirement of $153.01 million is adjusted as follows: decreased by funds available for roll forward from prior years of $153.01 million, decreased by prior period adjustment of $7.62 million; resulting in a total projected 2Q 2022 funding requirement for the Rural Health Care Support Mechanism of negative $7.62 million.
Connected Care Pilot Program – $7.81 million (The 1Q 2022 funding requirement was $9.21 million). The 2Q 2022 Connected Care Pilot Program initial collection requirement of $8.33 million was adjusted as follows: decreased by prior period adjustment of $0.59 million and increased by $0.07 million for administrative expenses, resulting in a total projected 2Q 2022 funding requirement of $7.81 million.
E-Rate Schools and Libraries Support Mechanism – $563.22 million (The 1Q 2022 funding requirement was $637.95 million).
For its consolidated budget, USAC projects total administrative costs of $58.09 million for 2Q 2022, which breaks out to $34.02 million in direct costs for all four support mechanisms, and $24.07 million in joint and common costs which include costs associated with billing, collection, and disbursement of universal service funds. This is a slight increase in administrative costs from last quarter (USAC projected a consolidated budget of $55.57 million for 1Q 2022). The FCC will use the of the quarterly funding requirements for the four USF Support Mechanisms, the projected administrative expenses, and the USF contribution base amount, to establish a quarterly USF contribution factor.
January 2022
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Ready To Authorize $1.2 Billion In RDOF Support For 5,254 Winning Bids
January 28, 2022 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced they are ready to authorize support for 5,254 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bids. This is the sixth group of RDOF winning bids that is ready to be authorized – $1.2 billion in ten-year RDOF support for 23 broadband service providers to serve over 1 million locations in 32 states.
A list showing each winning bid ready to be authorized, the corresponding long-form applicant, each winning bid’s total amount of 10-year support, and other details is available as Attachment A to the Public Notice. Attachment B contains a list of default bids. These are bids that RDOF winners or their assignees have notified the FCC that they do not intend to pursue. RDOF support will not be authorized for those bids, and the winning bidders and assignees are in default and may be subject to forfeiture penalties.
For this sixth set of ready-to-be-authorized RDOF winning bids, FCC staff reviewed the long-form applications associated with the winning bids, and determined they met all legal, financial, and technical requirements. To be authorized to receive the listed support amounts, however, each RDOF winning bidder must submit acceptable irrevocable stand-by letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters for each state where they have winning bids that are ready to be authorized prior to 6:00 p.m. ET on February 11, 2022. The FCC will continue to review RDOF long-form applications on a rolling basis, and will announce other approvals of long-forms in future public notices. Additional information on broadband service providers set to receive RDOF Phase I auction support and RDOF funding amounts by state are available from the FCC’s RDOF auction website: https://www.fcc.gov/auction/904.
FCC’s New Rural Broadband Accountability Plan Will Increase USF High-Cost Audits & Promote Transparency Of High-Cost Support Programs
January 28, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has announced the creation of the Rural Broadband Accountability Plan, which is a new FCC effort to ensure compliance with FCC rules for the universal service fund’s (USF) high-cost program. The FCC has released a Fact Sheet containing limited details on the new oversight plan.
Under the Rural Broadband Accountability Plan, the number of USF audits performed by the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) in 2022 will double, as compared to 2021. Audits will include on-site audits, audits and verifications based upon random selection, and increased verifications prior to a program’s first required deployment milestone. Service providers that receive a large amount of USF support “will be subject to an on-site audit in at least one state.” Service providers that are considered higher-risk recipients “will be subject to additional audits and verifications.” Also, in an effort to increase transparency within the high-cost support programs, the results of verifications, audits, and speed and latency performance testing will be made available to the public on USAC’s website.
The new Rural Broadband Accountability Plan efforts will apply to all of the FCC programs that distribute USF high-cost support, such as: Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II Model; Alternative Connect America Cost Model (Original A-CAM) and Revised ACAM; ACAM II; Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS); Rural Broadband Experiments (RBE); Alaska Plan; CAF Phase II Auction; and Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF).
FCC Releases Tentative Agenda For February 18 Open Meeting
January 28, 2022 – Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s February 18, 2022 open meeting:
Promoting Telehealth in Rural America – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would seek comment on reforms to the urban and rural rates determination process for the Rural Health Care Program’s Telecommunications Program, revisions to Rural Health Care Program rules governing the internal funding cap on upfront payments and multi-year contracts, and modifications to the Rural Health Care Program invoicing procedures. (WC Docket No. 17-310)
Aureon Refund Data Order – The Commission will consider an Order requiring Iowa Network Access Division (d/b/a Aureon) to file cost and demand data to enable Commission staff to calculate appropriate refunds due to Aureon’s customers after two investigations into Aureon’s tariffed switched transport rate. (WC Docket No. 18-60)
Updating Technical Rules for Radio Broadcasters – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to eliminate or amend outmoded or unnecessary broadcast technical rules. (MB Docket No. 21-263)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Comments On FCC Proposal To Create E-Rate Bidding Portal Due March 28, 2022
January 27, 2022 – Comments on the FCC’s proposal to require E-Rate bids be submitted to centralized portal are due on or before March 28, 2022. Reply comments are due on or before April 27, 2022. In a December 16, 2021 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, the FCC proposed to create a central document repository – an online bidding portal – through which communications service providers would be required to submit bids to the E-Rate program administrator, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC), instead of directly to E-Rate applicants. The FCC also requested public comment on requiring USAC to temporarily withhold submitted bids from applicants for a stated minimum period of time; whether to revise the FCC’s rules to require applicants to submit competitive bidding documentation that is not captured in the online bidding portal; and whether there are any potential benefits and burdens that the adoption and implementation of a bidding portal and these associated changes would have on E-Rate program participants and the public, as well as any required rule modifications needed to effectuate the proposed changes.
FCC NPRM Proposes Requiring Broadband Consumer Labels
January 27, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that proposes to “require that broadband Internet access service providers (ISPs) display, at the point of sale, labels to disclose to consumers certain information about prices, introductory rates, data allowances, broadband speeds, and management practices, among other things.” Comments are due on or before 30 days after the date the NPRM is published in the Federal Register. Reply comments are due 45 days after Federal Register publication. The FCC has created the following docket for the proceeding: Empowering Broadband Consumers Through Transparency, CG Docket No. 22-2.
The November 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act directs the FCC “to promulgate regulations to require the display of broadband consumer labels…to disclose to consumers information regarding broadband Internet access service plans.” The labels must “include information regarding whether the offered price is an introductory rate and, if so, the price the consumer will be required to pay following the introductory period.” As a starting point, the FCC’s NPRM includes broadband consumer labels for both fixed and mobile broadband that were approved by the FCC’s Consumer and Governmental Affairs, Wireline Competition, and Wireless Telecommunications Bureaus in a 2016 Public Notice.
In the NPRM, the FCC seeks comment on the following issues:
In order to allow sufficient time for providers to implement the measures necessary to
comply with these requirements, the FCC proposes to make these rules effective six months following publication in the Federal Register of the Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB’s) approval of the adopted rules. Is six months sufficient for both large and smaller providers?Should the FCC adopt a different implementation timeline or temporary exemption for smaller providers to allow them more time to come into compliance with the labels’ requirements, and does the FCC have the discretion to do so?
Are there alternative ways, other than different implementation timeframes, to minimize the economic impact on smaller service providers while achieving the FCC’s transparency objectives?
Have broadband service offerings and consumers’ use of broadband services changed sufficiently since the release of the 2016 labels to necessitate modifications to the labels’ content and/or format, or are there any other reasons to change the content or format of the labels?
Where should the labels be displayed to best inform consumers?
Are there enforcement issues related to the label requirement, including how the FCC should ensure the accuracy of label content?
Are there any implementation issues, including the time by which broadband providers should be required to display the labels?
What is needed to ensure that any required labels are accessible to persons with disabilities and that any broadband consumer label advances equity in the provision of and access to digital communications services and products for all people of the United States, without discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, or disability?
Montana Hires LightBox To Create State Broadband Serviceable Location Map
January 24, 2020 – The state of Montana has entered into a contract with LightBox for the creation of a broadband serviceable location map for Montana. LightBox is “a leading information and technology platform for the commercial real estate and location-based analytics industry.” To create the map, LightBox will utilize its recently released SmartFabric product, which integrates data such as “parcel, building footprint, address file, and geocoding with points of interest, cell phone location, and tax assessor details” to produce “a proprietary and flexible modeled fabric.” As described by LightBox’s CEO, the company’s SmartFabric software product “is a commercial off-the-shelf solution that states that can license to meet their serviceable location mapping goals in a timely manner.” LightBox also will handle the collection, cleansing, and geospatial mapping of data submitted by internet service providers in Montana. Two other states – Georgia and Alabama – have previously engaged LightBox to create serviceable location maps detailing the availability of broadband services throughout their states.
FCC Releases Affordable Connectivity Program Rules
January 21, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released a Report And Order And Further Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking containing final rules for the new Affordable Connectivity Program. As part of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, Congress allocated $14.2 billion to create the ACP, which builds on the Emergency Broadband Benefit Program and is intended to be a longer-term broadband affordability program. The new Affordable Connectivity Program rules address provider eligibility, household eligibility, services and devices covered by the program, the reimbursement process, consumer protection, outreach, data reporting, transition of EBB households, audits, enforcement, and program administration. They are set out in a new Subpart R to Part 54 of the FCC’s rules. In the FNPRM, the FCC seeks comment on other aspects of the Infrastructure Act and proposals for increasing awareness of and participation in the Affordable Connectivity Program.
FCC Final Agenda For January 27th Open Meeting
January 20, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the following final agenda for the FCC’s January open meeting scheduled for 10:30 am on Thursday, January 27, 2022:
Empowering Broadband Consumers Through Transparency – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to require that broadband internet access service providers display, at the point of sale, labels to disclose to consumers certain information about their prices, introductory rates, data allowances, broadband speeds, and management practices, among other things. (CG Docket No. 22-2)
Connecting Tribal Libraries – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would amend the definition of library in the Commission’s rules to clarify that Tribal libraries are eligible for support through the E-Rate Program. (CC Docket No. 02-6)
Updating Outmoded Political Programming and Record-Keeping Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to update outmoded political programming rules. (MB Docket No. 21-293)
Facilitating Better Use of ‘White Space’ Spectrum – The Commission will consider a Second Order on Reconsideration and Order resolving pending issues associated with white space devices and the white spaces databases, enabling unlicensed white space devices to continue operating efficiently while protecting other spectrum users. (ET Docket Nos. 04-186, 14-165, 20-36; GN Docket No. 12-268)
Updating Equipment Authorization Rules – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to update existing equipment authorization rules to reflect more recent versions of the technical standards that are incorporated by reference and incorporate by reference a new technical standard so that our equipment authorization system can continue to keep pace with technology developments. (ET Docket Nos. 21-363, 19-48)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
National Security Matter – The Commission will consider a national security matter.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Hawaiian Telecom Completes CAF Phase II Broadband Deployment
January 19, 2022 – Hawaiian Telecom, Inc. has filed a letter notifying the Federal Communications Commission that it has completed 100 percent of its Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II broadband deployment obligations. Hawaiian Telcom accepted CAF Phase II support to deploy broadband service to 11,081 locations within CAF II eligible census blocks in the state of Hawaii. Pursuant to a June 2021 waiver, however, Hawaiian Telcom’s total deployment obligation was reduced from 11,081 to 10,711 locations.
FCC Announces Results Of Auction 110: $22.4 Billion In Net Bids – 23 Bidders Won 4,041 Spectrum Licenses
January 14, 2022 – The FCC’s Office of Economics and Analytics and Wireless Telecommunications Bureau have announced that bidding in Auction 110 has concluded, resulting in a total of $22,418,284,236 in net bids and $22,513,601,811 in gross bids, with 23 bidders winning a total of 4,041 licenses.
Auction 110 offered 4,060 new flexible‐use licenses for spectrum in the 3.45-3.55 GHz band. The 100 megahertz of spectrum will be licensed on an unpaired basis divided into ten 10-megahertz blocks in partial economic areas (PEAs) located in the contiguous 48 states and the District of Columbia.
Of the 23 winning bidders, 13 qualified as small businesses or as entities serving rural communities, and over one-third of the top 100 markets have at least four winning bidders. Together, AT&T and DISH won 2,856 of the 4,041 licenses (just over 70 percent).
Attachment A to the Public Notice summarizes auction results for each bidder. Attachment B lists information about each bidder’s upfront payment and post-auction payments or refund. The biggest winners in terms of total licenses won are:
AT&T: 1,624 Licenses Won (406 PEAs)
Weminuche L.L.C. (DISH): 1,232 Licenses Won (406 PEAs)
U.S. Cellular: 380 Licenses Won (104 PEAs)
Cherry Wireless, LLC: 319 Licenses Won (144 PEAs)
T-Mobile: 199 Licenses Won (79 PEAs)
Skylake Wireless II, LLC: 57 Licenses Won (33 PEAs)
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Authorizes RDOF Support For 2,521 Winning Bids (5th RDOF Authorization)
January 14, 2022 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced it has authorized Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction support for 2,521 winning bids. This is the fifth Public Notice authorizing RDOF support. A list of the authorized winning bids is available as Attachment A to the Bureau’s Public Notice. Many of the winning bids authorized for support belong to Windstream. The authorizations were granted after the Bureau reviewed long-form application information for each authorized winning bidder, including letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters, and concluded the submissions were acceptable. Consequently, the Bureau has directed and authorized the Universal Service Administrative Company to obligate and disburse Universal Service Fund support to each winning bidder. Support will be disbursed in 120 monthly payments, beginning at the end of January 2022.
FCC Announces Telecommunications Interagency Working Group To Focus On Needs Of Telecommunications Industry Workforce
January 14, 2022 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the establishment of the Telecommunications Interagency Working Group, as required by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. This cross-agency working group, formed by the FCC, Department of Labor, Department of Education, and NTIA, “will collaborate to identify the current and future needs of the telecommunications industry workforce, including the safety of that workforce.” The Telecommunications Interagency Working Group is comprised of representatives of Federal agencies (the FCC, OSHA, NTIA, and Department of Education), and member representatives from industry, labor, and other stakeholder organizations. The list of members is included with the FCC’s Public Notice. The group will provide recommendations on telecommunications industry workforce needs in a report to Congress, due no later than January 14, 2023.
FCC Releases 2021 Universal Service Monitoring Report
January 14, 2022 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released the 2021 Universal Service Monitoring Report which details universal service fund (USF) information available as of September 2021. It was compiled using data from numerous sources, including the National Exchange Carrier Association (NECA), the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC), USF contributors, and recipients. Section 1 provides an update on revenues, universal service program funding requirements, and contribution factors. Sections 2 through 5 provide the latest data on the low-income, high-cost, schools and libraries, and rural health care support mechanisms. Section 6 presents recent Census and Bureau of Labor Statistics data on voice telephony subscribership and expenses taken from the Current Population Survey, the American Community Survey and the Consumer Expenditure Survey as well as data on telephone subscribership by income by state. It also includes data on residential Internet subscribership and expenses. Section 7 includes updated Consumer Price Index data.
CenturyLink & Frontier Tell FCC They Have Met Their CAF II Broadband Deployment Obligations
January 14, 2022 –CenturyLink and Frontier have filed letters with the Federal Communications Commission stating they have met their Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II broadband deployment obligations in the states in which they elected to receive support.
According to CenturyLink’s filing, preliminary year-end data shows that CenturyLink has used CAF II support to deploy broadband service at speeds of at least 10/1 Mbps and voice service to approximately 1.2 million customer locations in CAF II Census Blocks in 33 states. CenturyLink will provide, by March 1, 2022, requisite year-end 2021 status data to the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) High Cost Universal Broadband (HUBB) portal.
In its letter, Frontier says year-end data shows that it deployed broadband facilities to more than 740,000 of its 733,627 target homes and met or exceeded the CAF II program’s December 31, 2021, final broadband deployment milestone in 24 of the 25 states it serves and for which it received CAF II funding. In Arizona, data shows Frontier “reached 98% of the 22,768 locations in the state as of December 31, 2021,” and Frontier may elect the FCC’s flexibility option there which permits carriers to deploy to more than 95% but less than 100% of locations.
FCC Considering New CPNI Data Breach Rules
January 12, 2022 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chair Jessica Rosenworcel has circulated a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that would revise the FCC’s rules for notifying customers and federal law enforcement of breaches of customer proprietary network information (CPNI). According to the FCC’s News Release, the new rules are intended to “better align the FCC’s rules with recent developments in federal and state data breach laws covering other sectors.” The NPRM proposes the following revisions to current FCC rules (47 CFR Subpart U - Customer Proprietary Network Information) on telecommunications carriers’ breach notification requirements:
Eliminating the current seven business day mandatory waiting period for notifying
customers of a breach;Expanding customer protections by requiring notification of inadvertent breaches; and
Requiring carriers to notify the FCC of all reportable breaches in addition to the FBI and U.S. Secret Service.
NTIA Requests Public Comment On Broadband Funding Programs Authorized By Infrastructure Investment And Jobs Act
January 10, 2022 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released a Request For Comment Notice which seeks public input on new broadband grant programs authorized and funded by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021. The Infrastructure Act directs NTIA to distribute over $48 billion in funding through the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program, the Enabling Middle Mile Broadband Infrastructure Program, and the State Digital Equity Planning Grant Program.
NTIA is seeking public comment on 36 specific topics related to the three broadband funding programs, which can be found in NTIA’s Request For Comment Notice that was published in the Federal Register. Written comments may be submitted on or before 5 p.m. Eastern Standard Time on February 4, 2022. All comments may be submitted through the Federal e-Rulemaking Portal at http://www.regulations.gov.
FCC To Consider Requiring Broadband “Nutrition Labels”
January 6, 2022 – During its January 27th open meeting, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that proposes to “require that broadband Internet access service providers (ISPs) display, at the point of sale, labels to disclose to consumers certain information about prices, introductory rates, data allowances, broadband speeds, and management practices.” The November 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act directs the FCC “to promulgate regulations to require the display of broadband consumer labels,” within a year. As a starting point, the FCC’s NPRM includes broadband consumer labels for both fixed and mobile broadband that were approved by the FCC’s Consumer and Governmental Affairs, Wireline Competition, and Wireless Telecommunications Bureaus in a 2016 Public Notice. The FCC also seeks comment on the following related issues:
Have broadband service offerings and consumers’ use of broadband services changed sufficiently since the release of the 2016 labels to necessitate modifications to the labels’ content and/or format, or are there any other reasons to change the content or format of the labels;
Where should the labels be displayed to best inform consumers;
Are there enforcement issues related to the label requirement, including how the FCC should ensure the accuracy of label content;
Are there any implementation issues, including the time by which broadband providers should be required to display the labels; and
What is needed to ensure that any required labels are accessible to persons with disabilities and that any broadband consumer label advances equity in the provision of and access to digital communications services and products for all people of the United States, without discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, or disability.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For January 27th Open Meeting
January 6, 2022 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s January open meeting scheduled for Thursday, January 27, 2022:
Empowering Broadband Consumers Through Transparency – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to require that broadband internet access service providers display, at the point of sale, labels to disclose to consumers certain information about their prices, introductory rates, data allowances, broadband speeds, and management practices, among other things. (CG Docket No. 22-2)
Connecting Tribal Libraries – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would amend the definition of library in the Commission’s rules to clarify that Tribal libraries are eligible for support through the E-Rate Program. (CC Docket No. 02-6)
Updating Outmoded Political Programming and Record-Keeping Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to update outmoded political programming rules. (MB Docket No. 21-293)
Facilitating Better Use of ‘White Space’ Spectrum – The Commission will consider a Second Order on Reconsideration and Order resolving pending issues associated with white space devices and the white spaces databases, enabling unlicensed white space devices to continue operating efficiently while protecting other spectrum users. (ET Docket Nos. 04-186, 14-165)
Updating Equipment Authorization Rules – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to update existing equipment authorization rules to reflect more recent versions of the technical standards that are incorporated by reference and incorporate by reference a new technical standard so that our equipment authorization system can continue to keep pace with technology developments. (ET Docket Nos. 21-363, 19-48)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
National Security Matter – The Commission will consider a national security matter.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Consumers’ Research Files Legal Challenge To USF Contribution Factor
January 5, 2022 – Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 11 individuals have filed a Petition For Review with the U.S. Court Of Appeals For The Fifth Circuit challenging the FCC’s approval of the universal service fund contribution factor for the first quarter of 2022. They want the Court to declare the FCC’s action and the 1Q USF contribution factor unlawful, and set them aside. This same group filed comments and objections to the USF contribution factor with the FCC before and after the contribution factor was formally adopted by the FCC. The group also filed a Petition for Review with the Sixth Circuit challenging the FCC’s approval of the proposed fourth quarter 2021 USF contribution factor. In its most recent challenge, Consumers’ Research et al. claims the FCC’s approval of the 1Q USF contribution factor and the contribution factor itself “exceed the FCC’s statutory authority and violate the Constitution and other federal laws,” in the following ways:
(1) Congress’s standardless delegation to the FCC of legislative authority to raise and spend nearly unlimited money via the Universal Service Fund violates Article I, section 1 of the U.S. Constitution.
(2) To the extent Congress permitted the FCC to re-delegate (or de facto re-delegate) to a private company the authority to raise and spend nearly unlimited money via the Universal Service Fund, Congress unconstitutionally delegated its legislative power to a private entity—the Universal Service Administrative Company (“USAC”)—in contravention of Article I, section 1 of the Constitution.
(3) The revenues raised for the Universal Service Fund pursuant to 47 U.S.C. § 254 are taxes and therefore Congress’s standardless delegation to the FCC of authority to raise and spend nearly unlimited taxes violates Article I, section 8 of the U.S. Constitution.
(4) To the extent Congress permitted the FCC to re-delegate (or de facto re-delegate) to USAC the authority to raise and spend nearly unlimited taxes for FCC-defined “universal service,” Congress unconstitutionally delegated its taxing power to a private entity in contravention of Article I, section 8 of the Constitution.
(5) To the extent Congress did not to permit the FCC to delegate to a private company the authority to raise and spend nearly unlimited money for FCC-defined “universal service,” the FCC’s subsequent re-delegation to USAC is beyond the FCC’s lawful statutory authority, regardless of whether the charges are deemed to be “taxes.”
(6) If USAC is determined not to be a private entity, and to the extent Congress permitted the FCC Chair to appoint USAC board directors, Congress violated the Constitution’s Appointments Clause.
(7) To the extent Congress did not statutorily permit the FCC Chair to appoint USAC board directors, the FCC has acted in excess of its statutory authority in doing so.
(8) The USF Tax Factor is a binding legislative rule, but the FCC did not comply with the APA’s requirements for rulemaking, nor with the Federal Register Act’s requirements for publication.
(9) The FCC’s action and inaction are otherwise contrary to law.
FCC Extends Comment Deadlines For Notice Of Inquiry On The Future Of The Universal Service Fund
January 4, 2022 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has extended the comment and reply comment deadlines by 30 and 45 days, respectively, for the FCC’s Notice Of Inquiry (NOI) on the future of the Universal Service Fund (USF). Accordingly, comments are due on or before February 17, 2022, and reply comments are due March 17, 2022.
In the NOI, the FCC seeks comment on issues related to the future of the USF “in light of the broadband investments in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act,” which provides “the largest ever federal investment in broadband, totaling approximately $65 billion.” The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act directed the FCC to: (1) report to Congress on the FCC’s options for improving its effectiveness in achieving universal service goals for broadband; and (2) commence a proceeding to evaluate the implications of the Jobs Act on how the FCC should achieve broadband universal service goals.
First, the FCC is seeking comment on the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act impact on: (1) the FCC’s existing universal service programs; (2) the FCC’s universal service goals; and (3) other federal broadband programs.
Second, the FCC is seeking comment on: (1) potential recommendations for future FCC action related to the USF programs (High-Cost, Lifeline and The Affordable Connectivity Program, E-Rate and The Emergency Connectivity Fund Program, and Rural Health Care); and (2) sustaining the USF programs.
Third, the FCC is seeking comment on potential FCC recommendations for future congressional action related to universal service.
FCC Provides Temporary Waiver Of Broadband Performance Testing Requirements
January 3, 2022 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has provided a set of limited waivers of the broadband performance testing requirements for certain broadband providers receiving universal service support. The Bureau’s Order grants in part, and denies in part, NTCA–The Rural Broadband Association’s waiver request; extends a similar waiver to additional broadband support programs; and grants a petition for waiver filed by Reserve Communications and Computer, L.L.C.
Under the FCC’s Connect America Fund regime, broadband providers that receive high-cost universal service support must offer broadband service that meets certain basic performance requirements – speed and latency – in the areas where they receive that support. Testing is conducted from the premises of active subscribers to a remote test server located at, or reached by passing through, an FCC-designated Internet exchange point. Broadband providers undergo a pre-testing period prior to the actual testing start date in order to familiarize themselves with the process. During actual testing, providers whose broadband service fails to meet the minimum requirements will have universal service support withheld and be subject to additional reporting requirements.
In December 2021, NTCA–The Rural Broadband Association filed a petition requesting the FCC extend, by six months, the relief granted in the Wireline Competition Bureau’s December 2020 waiver Order, which allowed broadband providers that receive Alternative Connect America Cost Model I (A-CAM I) support, Rural Broadband Experiment (RBE) support, and Alaska Plan support to pre-test only 70% of their random sample of subscribers during the four quarters of pre-testing in 2021. To support its request, NTCA explained that broadband provides continue to face challenges to deploying new testing compatible equipment at user locations due to the COVID-19 pandemic and supply chain disruptions continue to interfere with providers’ abilities to source and purchase equipment needed to carry out performance testing.
In the January 2022 waiver Order, the Bureau has granted in part NTCA’s petition for limited waiver of broadband performance testing requirements for recipients of A-CAM I support, RBE support, and Alaska Plan support. These broadband providers must only test 70% of their USAC-selected samples during the first two quarters of 2022.
Second, on its own motion, the Bureau has extended similar relief to broadband providers that receive universal service support from the following programs: Alternative Connect America Cost Model II (A-CAM II), Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS), and Connect America Fund (CAF) II Auction. Accordingly, these broadband providers are only required to pre-test 70% of their required sample size for the first two quarters of 2022.
Third, the Bureau has denied NTCA’s requests to adopt a simplified waiver process and to extend the pre-testing period for A-CAM I, RBE, and Alaska Plan support recipients.
Finally, the Bureau has granted a petition for waiver filed by Reserve Communications and Computer, L.L.C., which provides relief from the pre-testing requirements for the first quarter of 2022.
Filing Requirement Update: High Cost Universal Broadband – HUBB – Portal Filings Due By March 1, 2022
January 3, 2022 – Broadband service providers that receive universal service support and have defined broadband buildout obligations have until March 1, 2022, to file broadband deployment data with the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) High Cost Universal Broadband (HUBB) portal. The filings must show where (by latitude and longitude) broadband providers have built out “mass-market, high-speed Internet service” during calendar year 2021. The submitted data will be used in the Connect America Fund (CAF) Map, and will be the “starting point” for the FCC’s Broadband Performance Testing framework. Additional information is available on the HUBB resource page.
Broadband service providers receiving support from the following funding programs are required to file data by March 1, 2022, for broadband service deployed to all locations using CAF support in 2021 or certify that they have no locations to upload in the HUBB:
Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II Model
Alternative Connect America Cost Model (Original A-CAM) & Revised ACAM
ACAM II
Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS)
Rural Broadband Experiments (RBE)
Alaska Plan (other than carriers with individualized performance plans that only require them to maintain service at existing levels)
CAF Phase II Auction
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF)
Filing Requirement: Lifeline Providers Must File FCC Form 555 By January 31, 2022
January 3, 2022 – All service providers that participate in the FCC’s Lifeline program are required to file FCC Form 555, the “Annual Lifeline Eligible Telecommunications Carrier Certification Form,” by January 31, 2022. FCC Form 555 is used by Lifeline providers to report the results of the annual recertification process and includes data accuracy certifications that must be completed. Lifeline service providers must submit one FCC Form 555 per study area code (SAC) in which they provide Lifeline service. The form must be filed online using the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) One Portal. Lifeline providers may file bulk uploads using the FCC Form 555 Bulk Upload Template. Additionally, Lifeline service providers must file a copy of their Form 555 with the FCC in WC Docket No. 14-171, and with their state regulatory commissions and relevant Tribal governments.
Cox Communications Claims Sony Plaintiffs Lied About Evidence To Obtain $1 Billion DMCA Copyright Infringement Verdict
January 1, 2022 – Cox Communications has filed a motion For Relief From Judgment in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District Of Virginia, which claims the $1 billion judgment against it for copyright infringement in Sony Music Entertainment, et al. v. Cox Communications “was based on evidence that was created years after the alleged infringement occurred.” Cox claims the Sony plaintiffs lied to the court and this helped secure victory:
The bottom line is that Plaintiffs lied. They lied to Cox; they lied to the Court; and they lied to the jury. And they rode those lies to a $1 billion judgment.
In July 2018, Cox was sued by a group of recording companies who claimed Cox “knowingly contributed to, and reaped substantial profits from,” massive copyright infringement committed by thousands of its broadband subscribers. They claimed Cox “deliberately refused to take reasonable measures to curb its customers from using its Internet services to infringe on others’ copyrights – even once Cox became aware of particular customers engaging in specific, repeated acts of infringement.” Cox was sued for both contributory and vicarious copyright infringement. The recording companies sought statutory damages in an amount of up to $150,000 with respect to each work infringed. The jury ultimately returned a guilty verdict on both counts, with total damages of $1 billion awarded to plaintiffs.
Cox Communications filed its Motion For Relief From Judgment after reviewing new evidence produced in a similar copyright lawsuit against another ISP, (Warner Records, Inc. et al. v. Charter Communications, Inc., Case No. 1:19-cv-00874-RBJ-MEH (U.S. District Court For The District Of Colorado)). In general, Cox claims Sony used MarkMonitor to surveil peer-to-peer filesharing networks to identify potentially infringing audio files, download those files, and then generate and send DMCA infringement notices to Cox broadband subscribers that allegedly copied the files. During the trial, Sony presented this data – spreadsheets and a hard drive – as evidence of copyright infringement by Cox subscribers. At trial, Cox challenged “the authenticity, foundation, and provenance of this evidence,” but the Sony plaintiffs “successfully persuaded the Court and the jury that the exhibits were what they were represented to be: an integrated and contemporaneous whole created during or before the 2013–2014 Claims Period.” Now, Cox claims this key piece of evidence was false:
Evidence produced in Charter has revealed that the audio files on the Hard Drive were downloaded by MarkMonitor and subjected to Audible Magic verification years after the notices were sent. Thus, the files on the Hard Drive are not the same files used to generate the infringement notices, and the Audible Magic verifications documented in the MarkMonitor Spreadsheet were not of the files on the Hard Drive. In other words, Plaintiffs’ evidence constituted two mismatched halves created years apart from one another—not the integrated and contemporaneous whole they represented it to be.
Cox is asking the District Court to enter an indicative ruling under Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 62.1 stating that it is inclined to grant Cox’s motion for relief from the judgment, or – at a minimum – that Cox’s motion raises a substantial issue that warrants further consideration by the Court. Upon receipt of such a ruling, Cox will move in the Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit for a limited remand to the District Court to resolve Cox’s motion.
December 2021
FCC Announces Start Of Affordable Connectivity Program
December 31, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission (FC) has announced it has officially launched the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), the $14.2 billion successor program to the Emergency Broadband Benefit program. Under the ACP, eligible households may receive up to a $30 per month discount toward internet service and up to $75 per month if located on qualifying Tribal lands. Eligible households can also receive a one-time discount of up to $100 to purchase a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet from participating providers if they contribute more than $10 and less than $50 toward the purchase price. A household is eligible for the ACP if a member of the household meets at least one of following requirements:
Has an income that is at or below 200% of the federal poverty guidelines;
Participates in certain assistance programs, such as SNAP, Medicaid, Federal Public Housing Assistance, SSI, WIC, or Lifeline;
Participates in Tribal specific programs, such as Bureau of Indian Affairs General Assistance, Tribal TANF, or Food Distribution Program on Indian Reservations;
Is approved to receive benefits under the free and reduced-price school lunch program or the school breakfast program, including through the USDA Community Eligibility Provision in the 2019-2020, 2020-2021, or 2021-2022 school year;
Received a Federal Pell Grant during the current award year; or
Meets the eligibility criteria for a participating provider's existing low-income program.
FCC Extends Covid Waiver Of Certain Lifeline Program Rules Through March 31, 2022
December 30, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has extended prior waivers of certain Lifeline program rules governing documentation requirements for subscribers residing in rural areas on Tribal lands, reverification, recertification, general de-enrollment, and income documentation through March 31, 2022. The prior waivers were set to expire on December 31, 2021. The Bureau once again extended the waivers as a way to provide relief from the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic to low-income households to in the U.S. Pursuant to the Bureau’s Order, the following Lifeline program rules are waived through March 31, 2022: 54.405(e)(1); 54.405(e)(4); 54.410(a); 54.410(b)(1)(i)(B); and 54.410(f).
FCC Submits Robocall Report To Congress
December 22, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has submitted a report to Congress on “Robocalls And Transmission Of Misleading Or Inaccurate Caller Identification Information.” The report was prepared by the FCC’s Enforcement Bureau, Consumer and Governmental Affairs Bureau, and Wireline Competition Bureau, and was conducted pursuant to Sections 3, 11, and 13 of the Pallone-Thune Telephone Robocall Abuse Criminal Enforcement and Deterrence Act (TRACED Act). It provides data regarding informal consumer complaints that the FCC received during the preceding five full calendar years (2016-2020), and FCC enforcement actions during the preceding calendar year (2020), as well as additional informal consumer complaint data and information about FCC enforcement actions through November 30, 2021. Also, Sections 11 and 13 of the report address certain FCC and private industry actions with respect to illegal robocalls, including unsolicited calls using an artificial or prerecorded voice message, often referred to as “robocalls.” Information in Sections 11 and 13 covers the period from December 1, 2020 through November 30, 2021.
Consumers’ Research Files Objection To FCC’s First Quarter 2022 USF Contribution Factor
December 21, 2021 –Nonprofit organization Consumers’ Research, communications provider Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 11 individual consumers have filed comments and objections with the Federal Communications Commission in response to the FCC’s proposed first quarter 2022 Universal Service Fund (USF) contribution factor. On December 13, 2021, the FCC’s Office of Managing Director announced that the proposed USF contribution factor for the first quarter of 2022 will be will be 25.2 percent. In general, Consumers’ Research et al. request that the FC reject the proposed USF contribution factor and instead set it at 0 percent because they claim “it is an unconstitutional tax raised and spent by an unaccountable federal agency.” The group recently filed a petition for review with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit challenging the Federal Communications Commission’s approval of the proposed fourth quarter 2021 universal service contribution factor, claiming the FCC’s approval of the 4Q 2021 contribution factor (and the proposed contribution factor itself) “exceeds the FCC’s statutory authority and violates the Constitution and other federal laws.”
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Ready To Authorize $1.041 Billion In RDOF Support For 7,608 Winning Bids
December 16, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced they are ready to authorize support for 7,608 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bids. A list showing each winning bid ready to be authorized, the corresponding long-form applicant, each winning bid’s total amount of 10-year support, and other details is available as Attachment A to the Public Notice.
This is the fifth set of RDOF winning bids that is ready to be authorized – $1,041,074,000 in ten-year RDOF support for 69 broadband service providers to serve 518,088 locations in 32 states. So far, the FCC has announced over $2.7 billion in funding to RDOF Phase I auction winning bidders for new broadband service deployments. Information on broadband service providers set to receive RDOF Phase I auction support and RDOF funding amounts by state are available from the FCC’s RDOF auction website: https://www.fcc.gov/auction/904.
For this fifth set of ready-to-be-authorized RDOF winning bids, FCC staff reviewed the long-form applications associated with each winning bid, and determined they met all legal, financial, and technical requirements. To be authorized to receive the listed support amounts, however, each RDOF winning bidder must submit acceptable irrevocable stand-by letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters for each state where they have winning bids that are ready to be authorized prior to 6:00 p.m. ET on Friday, January 7, 2022. The FCC will continue to review RDOF long-form applications on a rolling basis, and will announce other approvals of long-forms in future public notices.
FCC Announces Voice & Broadband Benchmarks: Rates & Minimum Usage Allowance
December 16, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced the 2022 reasonable comparability benchmarks for fixed voice and broadband services for eligible telecommunications carriers (ETCs) that are subject to broadband public interest obligations (i.e., incumbent local exchange rate-of-return carriers, incumbent price-cap carriers that are receiving Connect America Fund Phase II support, Rural Broadband Experiment providers, CAF Phase II Auction winners, and Rural Digital Opportunity Fund Auction winners).
Voice Rates. The 2022 urban average monthly rate is $35.05. Therefore, the reasonable comparability benchmark for voice services, two standard deviations above the urban average, is $52.65. Under the FCC’s rules, each ETC, including competitive ETCs providing fixed voice services, must certify in their FCC Form 481 filed no later than July 1, 2022, that the pricing of its basic residential voice services is no more than $52.65.
Broadband Rates. The reasonable comparability broadband benchmark varies, depending upon the supported service’s download and upload bandwidths and usage allowance. To facilitate benchmark calculations, broadband providers can utilize an Excel file calculation tool, available at http://www.fcc.gov/encyclopedia/urban-rate-survey-data. Recipients of high-cost and Connect America Fund support that are subject to broadband performance obligations are required to offer broadband service at rates that are at or below the relevant reasonable comparability benchmark. Carriers subject to the Alaska Plan are required to meet Alaska specific benchmarks and to certify that they are meeting the relevant reasonable comparability benchmark for their broadband service offering in the FCC Form 481 filed no later than July 1, 2022.
Minimum Usage Allowance. The Bureau has adopted a minimum monthly usage allowance of 500 GB for 2022. An explanation of the Bureau’s calculations determining the minimum monthly usage allowance is available from the Bureau’s Public Notice. ETCs subject to broadband public interest obligations must provide broadband with usage allowances reasonably comparable to those available through comparable offerings in urban areas.
Data on fixed voice and broadband services data collected in the most recent urban rate survey, and explanatory notes regarding the data, are available on the FCC’s urban rate survey website at http://www.fcc.gov/encyclopedia/urban-rate-survey-data.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Announces RDOF Defaulted Bids
December 16, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced that several Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bidders have notified the FCC that they do not intend to pursue some or all of their RDOF winning bids. The winning bidders and assignees are considered to be in default for these bids and subject to FCC Enforcement Bureau action, including forfeiture penalties. A list showing these defaulted bids is available as Attachment B to the Public Notice. The census blocks associated with the defaulted bids will be potentially eligible for other broadband funding programs. The FCC expects to announce additional RDOF defaults in future public notices.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Denies Hotwire Communications Waiver Petition – Hotwire Defaults On RDOF Winning Bids In Florida
December 16, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau and Office of Economics and Analytics have denied a petition filed by Hotwire Communications, Ltd. (Hotwire) seeking waiver of the FCC rule that prohibits an RDOF winning bidder from making a major modification to its pending long-form application. Consequently, Hotwire has defaulted on its RDOF winning bids in the state of Florida.
When Hotwire filed its short-form application to participate in the RDOF Phase I auction, it listed one direct owner, Michael Karp, as having 100% ownership interest, and did not disclose any pending or prospective changes in ownership. Hotwire then won $5,150,040 in 10-year RDOF support to serve 3,233 locations in Florida. Hotwire’s RDOF long-form application contained the same ownership information as its short-form application.
Hotwire subsequently amended its RDOF long-form application to disclose that on April 22, 2021, Michael Karp consummated a transaction in which he transferred his ownership interest to a new entity, Hotwire Holdings, LLC, and Hotwire became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hotwire Holdings, LLC, resulting in the following ownership breakdown:
Following the transaction, Mr. Karp holds a 40% equity and voting interest in Hotwire Holdings, LLC, while four funds owned by The Blackstone Group, Inc. hold an aggregate equity and voting interest of 50%, and a company owned solely by Mr. Karp’s wife, Kristen Johnson, holds the remaining 10%. Hotwire’s long-form amendment further reports that a single individual, Stephen Schwarzman, ultimately controls 50% of Hotwire Holdings, LLC, through a chain of Blackstone holding companies. The amendment further explains that Hotwire Holdings, LLC, is controlled by a board of managers comprised of Mr. Karp, Ms. Johnson, and two Blackstone executives.
Concurrently with its RDOF long-form amendment, Hotwire fired a petition for waiver of the major modification prohibition, and argued the transaction was pro forma transfer. The FCC denied the waiver petition. First, the FCC determined the transaction was not a pro forma transfer because “[s]ixty percent of the voting stock and equity ownership of Hotwire…changed hands, with 50% of the equity and voting stock now being controlled by Blackstone.” Second, the FCC “conclude[d] that Hotwire has not demonstrated good cause to grant its requested waiver.” The FCC determined that Hotwire presented a situation that the rule prohibiting major modifications to a long-form application is intended to address:
The purpose of the rule is to foster participation and competition in the auction by ensuring that an auction applicant’s ownership information, real parties in interest, and financial condition can be fully assessed prior to the start of bidding, resulting in a pre-auction process that is transparent for the Commission, auction participants, and other interested parties and that enhances auction competition by leveling the informational playing field. The rule also promotes transparency and competition by limiting the extent to which after the close of bidding and prior to authorization of the award a winning bidder can turn around and “shop” its winning bids to others. Among other things, the prohibition deters bidders from participating with an expectation that, post-auction, they may be able to leverage their winning bids in a late effort to gain financing, and it avoids unfairness to other bidders that comply with the auction rules. Furthermore, the rule promotes competition within the auction by encouraging interested entities to participate in the bidding directly and compete for the desired offered items, rather than subsequently combining their resources with a winning bidder after the auction.
FCC Issues Notice Of Inquiry On The Future Of The Universal Service Fund – Comments Due January 18, 2022
December 15, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice Of Inquiry (NOI) on the future of the Universal Service Fund (USF). Comments are due on or before January 18, 2022. Reply comments are due January 31, 2022.
In the NOI, the FCC seeks comment on issues related to the future of the USF “in light of the broadband investments in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act,” which provides “the largest ever federal investment in broadband, totaling approximately $65 billion.” The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act directed the FCC to: (1) report to Congress on the FCC’s options for improving its effectiveness in achieving universal service goals for broadband; and (2) commence a proceeding to evaluate the implications of the Jobs Act on how the FCC should achieve broadband universal service goals.
First, the FCC is seeking comment on the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act impact on: (1) the FCC’s existing universal service programs; (2) the FCC’s universal service goals; and (3) other federal broadband programs.
Second, the FCC is seeking comment on: (1) potential recommendations for future FCC action related to the USF programs (High-Cost, Lifeline and The Affordable Connectivity Program, E-Rate and The Emergency Connectivity Fund Program, and Rural Health Care); and (2) sustaining the USF programs.
Third, the FCC is seeking comment on potential FCC recommendations for future congressional action related to universal service.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Authorizes RDOF Support For 2,008 Winning Bids (4th RDOF Authorization)
December 14, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced it has authorized Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction support for 2,008 winning bids. This is the fourth RDOF support authorization. A list of the authorized winning bids is available as Attachment A to the Bureau’s Public Notice. The authorizations were granted after the Bureau reviewed long-form application information for each authorized winning bidder, including letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters, and concluded the submissions were acceptable. Consequently, the Bureau has directed and authorized the Universal Service Administrative Company to obligate and disburse Universal Service Fund support to each winning bidder. Support will be disbursed in 120 monthly payments, beginning at the end of December 2021.
First Quarter 2022 USF Contribution Factor: 25.2 Percent
December 13, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission’s Office of Managing Director has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the first quarter of 2022 will be will be 25.2 percent. This is a decrease from the 29.1 percent factor that was used in the fourth quarter of 2021.
For the first quarter of 2022, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $9.235846 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected. (The 4Q 2021 total was $9.517295 billion.)
USAC estimates that $1.84091 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms in the first quarter of 2022. (The 4Q 2021 demand was $2.123870 billion.) Total first quarter 2022 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, and breaks out as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $637.95 million
Rural Health Care: $11.72 million
High-Cost: $1.04452 billion
Lifeline: $137.51 million
Connected Care: $9.21 million
If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. Historical information on quarterly universal service fund contribution factors is available online from the FCC.
Robocall Prevention: FCC Imposes June 30, 2022 STIR/SHAKEN Deadline For Small “Non-Facilities-Based” Voice Providers
December 10, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has approved a Fourth Report And Order which revises the FCC’s robocall prevention rules for small non-facilities-based voice providers. Specifically, “[t]o better protect Americans from illegally spoofed calls,” non-facilities-based small voice providers are now required to implement STIR/SHAKEN in the Internet Protocol (IP) portions of their voice networks by June 30, 2022.
Accordingly, non-facilities-based small voice service providers also must update their filings in the Robocall Mitigation Database within 10 business days of the effective date of the Fourth Report And Order to indicate they are no longer subject to a two-year extension and must implement STIR/SHAKEN by June 30, 2022 in the IP portions of their voice networks.
The existing June 30, 2023, STIR/SHAKEN extension for facilities-based small voice service providers remains in place. Non-facilities-based small voice service providers, as well as other voice service providers, must also update their certifications and associated filings in the Robocall Mitigation Database within 10 business days of completion of STIR/SHAKEN implementation. The FCC also revised Section 64.6305(b)(5) of its rules to require voice service providers to update, within 10 business days of any change, all information originally submitted with its Robocall STIR/SHAKEN certification.
Additionally, the FCC has adopted a new Robocall prevention tool for the FCC’s Enforcement Bureau that applies to small voice service providers:
Any small voice service provider that the FCC’s Enforcement Bureau suspects of originating illegal robocalls and that fails to mitigate such traffic upon Bureau notice or otherwise fails to meet its burden under section 64.1200(n)(2) of the FCC’s rules, must implement STIR/SHAKEN within 90 days of that determination unless sooner implementation is otherwise required.
FCC Announces Re-Chartered Precision Agriculture Task Force Members
December 9, 2021 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has appointed members to serve on the re-chartered Task Force for Reviewing the Connectivity and Technology Needs of Precision Agriculture in the United States. A list of the Precision Ag Connectivity Task Force members is available on the FCC’s Public Notice. The group’s first meeting is set for Thursday, January 13, 2022, at 10:00 am EST. The re-chartered Task Force will continue to provide advice and recommendations to the FCC on accelerating the deployment of broadband service on unserved agricultural land to promote precision agriculture, and will rely on four working groups to carry out its mission: (1) Mapping and Analyzing Connectivity on Agricultural Lands; (2) Examining Current and Future Connectivity Demand for Precision Agriculture; (3) Encouraging Adoption of Precision Agriculture and Availability of High-Quality Jobs on Connected Farms; and (4) Accelerating Broadband Deployment on Unserved Agricultural Lands.
FCC Releases Further Guidance On Transitioning From Emergency Broadband Benefit Program To New Affordable Connectivity Program
December 8, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released an Order which waives certain Emergency Broadband Benefit (EBB) Program rules and provides guidance on transitioning from the EBB Program to the new Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP).
First, the Bureau has waived Sections 54.1600(n) and (s) of the FCC’s rules which requires EBB Program internet service offerings and accompanying standard rates to be offered on the same manner and terms as offerings available on December 1, 2020. This will allow broadband service providers to offer EBB discounts on any of their internet service offerings to participating households (similar to how the ACP will require participating broadband providers to offer the ACP discount on any internet service offering). The waiver is in force until the FCC enacts final rules governing the ACP.
Second, the Bureau has waived Section 54.1601(c)(2) of the FCC’s rules which requires broadband service providers that are participating in the EBB Program to provide the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) with a “statement that, in each state or territory, the provider was a ‘broadband provider’ as of December 1, 2020.” This is consistent with the ACP’s statutory language which does not contain the December 1, 2020, restriction.
Finally, the Bureau’s Order provides the following guidance on transitioning from the EBB Program to the new ACP: (1) the transition of EBB providers to the Affordable Connectivity Program; (2) the timing of the enrollment freeze for the EBB Program and the start of enrollments for the Affordable Connectivity Program; (3) the continued access to the paper and online EBB Program applications; (4) the treatment of pending applications for the EBB Program on and after December 31, 2021; (5) the households that qualify for the 60-day transition period; (6) the reverification process for certain households enrolled in the EBB Program; and (7) the service provider consumer notification responsibilities about the upcoming program changes.
NTIA Announces Virtual Listening Sessions On New Federal Broadband Grant Programs
December 6, 2021 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has announced it will hold broadband grant program public virtual listening sessions for the following broadband grant programs created by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act:
The Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program (BEAD)
The Enabling Middle Mile Broadband Infrastructure Program
The Digital Equity Act Programs (State Digital Equity Planning Grant Program, State Digital Equity Capacity Grant Program, and Digital Equity Competitive Grant Program)
The listening sessions will help collect stakeholder input and inform each program’s development and implementation. Registration information will be available on NTIA’s BroadbandUSA website. NTIA has released the following schedule for the public virtual listening sessions:
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Broadband Programs Public Virtual Listening Session #1: Wednesday, December 15, 2021, from 2:30–4 p.m. Eastern Time (ET);
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Broadband Programs Public Virtual Listening Session #2: Wednesday, January 12, 2022, from 2:30–4 p.m. ET;
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Broadband Programs Public Virtual Listening Session #3: Wednesday, January 26, 2022, from 2:30–4 p.m. ET;
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Broadband Programs Public Virtual Listening Session #4: Wednesday, February 9, 2022, from 2:30–4 p.m. ET; and
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Broadband Programs Public Virtual Listening Session #5: Wednesday, February 23, 2022, from 2:30–4 p.m. ET.
FCC Releases Updated Responses To Frequently Asked Questions For The Secure And Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program
December 3, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has published an updated version of responses to Frequently Asked Questions for the $1.9 billion Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program. The updated FAQs are included as an attachment to the Bureau’s Public Notice announcement. The updated FAQs address how the FCC will handle funding allocations among affiliated Reimbursement Program participants; whether third-party network equipment that is not compatible with replacement equipment can be reimbursable; and provide additional explanation for other pending questions. Other important information and documents related to the Reimbursement Program are available on the FCC’s supply chain website.
LTD Broadband Files Lawsuit Against Iowa Utilities Board To Reverse Decision Denying Expanded ETC Designation
December 3, 2021 – LTD Broadband, LLC has filed a Petition for Judicial Review with the District Court for Polk County, Iowa seeking review of the Iowa Utilities Board’s November 5, 2021 denial of LTD’s amendment to its existing Eligible Telecommunications Carrier (ETC) designation. In its Petition, LTD requests that the Court reverse the decision of the Board.
LTD Broadband, one of the biggest winners in the FCC’s Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction, was awarded $23,184,786.30 in ten-year RDOF support to serve 12,916 locations in Iowa. Pursuant to the FCC’s rules, LTD Broadband was required to demonstrate, by June 7, 2021, that it had been designated as an ETC in each of the geographic areas for which it won RDOF support. LTD Broadband previously had been designated as an ETC by the Iowa Utilities Board in 2019 for areas in Iowa where it won support in the FCC’s Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II auction. In May 2021, LTD filed an application with the Iowa Utilities Board to expand its ETC service area to cover where it won RDOF support. However, in a November 5, 2021, order, the Iowa Utilities Board denied LTD’s application. (In October 2021, the FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau issued an Order denying LTD Broadband’s petition for waiver of the ETC requirement, which resulted in the loss of RDOF support LTD was awarded in Iowa.)
In its Petition For Judicial Review, LTD ultimately requests that the Court reverse the decision of the Board, and makes the following claims for relief:
The Board’s delay and denial of LTD’s request to amend its ETC territory was arbitrary and capricious, and inconsistent with how the Board treated applicants making similar application.
The Board’s delay and denial failed to take into account the magnitude of the loss of potential investment in Iowa’s underserved communities and the public policy interests in timely action to facilitate the implementation of RDOF and the FCC’s decision to award LTD additional territories.
The Board’s apparent application of standards closer to those for an initial ETC application misinterprets the Board’s own rules, and used standards that were wholly subjective in violation of LTD’s due process. Moreover, if the FCC or the Iowa Legislature allowed and intended for the Board to use unclear, subjective standards without notice, such delegation of authority is an unconstitutional delegation beyond the scope of an administrative agency.
LTD Broadband, LLC respectfully requests that the Court reverse the decision of the Board, and enter such other relief as it finds proper on the facts and law before it
NTCA Asks For Waiver Of Broadband Performance Testing Obligations
December 3, 2021 – NTCA–The Rural Broadband Association has filed a petition requesting a waiver of certain aspects of the FCC’s broadband performance testing obligations. NTCA has requested that the FCC extend the relief granted in the Wireline Competition Bureau’s December 2020 waiver Order. In that Order, the Bureau provided a waiver allowing broadband providers that receive Alternative Connect America Cost Model I (A-CAM I) support, Rural Broadband Experiment support, and Alaska Plan support to pre-test only 70% of their random sample of subscribers during the four quarters of pre-testing in 2021. NTCA is asking for “an additional six months for pre-testing at 70% of the locations that would otherwise be required, with the understanding that if supply chain conditions do not ease sufficiently a further extension may be warranted.” In support of its waiver request, NTCA maintains that broadband provides continue to face challenges to deploying new testing compatible equipment at user locations due to the COVID-19 pandemic and supply chain disruptions continue to interfere with providers’ abilities to source and purchase equipment needed to carry out performance testing.
USAC Files First Quarter 2022 USF Contribution Base Data: $9.235 Billion
December 2, 2021 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed projected universal service fund (USF) contribution base data which will be used to determine the USF contribution factor for the first quarter of calendar year 2022. USAC has determined that the total projected interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenue base for the first quarter of 2022 is $9,235,845,776. To provide a comparison, the total USF contribution base amounts for the past eight quarters were as follows:
Fourth Quarter 2021: $9,517,295,012
Third Quarter 2021: $9,665,944,070
Second Quarter 2021: $9,905,669,690
First Quarter 2021: $10,068,712,553
Fourth Quarter 2020: $10,428,377,862
Third Quarter 2020: $10,219,123,520
Second Quarter 2020: $10,865,131,593
First Quarter 2020: $11,129,976,956
USAC’s estimated revenue base for the first quarter of 2022 was derived from projected collected revenue for January to March 2022 reported by telecommunications service providers using FCC Form 499-Q submitted in November 2021 – 4,775 reporting providers, of which 3,112 are USF contributors and 1,663 are non-contributing de minimis service providers. As of November 19, 2021, USAC has yet to receive information from 132 non-de minimis telecommunications service providers that had previously submitted Form 499-Q revenue information to USAC.
After the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approves the total USF contribution base, the quarterly funding requirements for USF support mechanisms, and projected USF administrative costs, the FCC will establish a USF contribution factor for the first quarter of 2022. The new contribution factor will be announced by a Public Notice. USAC will then bill USF contributors on a monthly basis for their individual obligations based on the approved contribution factor.
Members Of The Blackfeet Tribe File Class Action Lawsuit Against 3 Rivers Telephone Cooperative To Recover $8.88 Million In Capital Credits
December 1, 2021 – Native American members of the Blackfeet Tribe have filed a class action lawsuit, on behalf of themselves and all others situated, against 3 Rivers Telephone Cooperative, Inc. to recover patronage capital credits that allegedly belong to the plaintiffs and the class.
In the Class Action Complaint And Demand For Jury Trial, the plaintiffs allege that after 3 Rivers sold its Browning Exchange to Siyeh Communications in December 2020, “3 Rivers failed to retire the capital credits belonging to the Browning Exchange members.” The plaintiffs allege that 3 Rivers retained the capital credits “even though the Browning Exchange members are no longer members of 3 Rivers by virtue of the sale.”
3 Rivers is incorporated and operates as a non-profit entity. Customers that purchase services from the cooperative are considered member-owners. Each year, a cooperative will allocate a percentage of its revenues earned above operating expenses to each member-owner on a pro-rata basis according to the total amount paid or produced for services. These allocations are known as capital credits. They are refunded to cooperative patrons pursuant to individual company policies.
The plaintiffs estimate that “the total membership of 3 Rivers’ Browning Exchange is approximately 2,000, most of whom are Native American.” They estimate that the amount of capital credits that 3 Rivers has retained from the former Browning Exchange members is approximately 8.88 million dollars.
NOVEMBER 2021
USDA Now Accepting ReConnect Program Applications
November 24, 2021 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has announced it is now accepting applications for loans and grants from the $1.15 billion ReConnect Program. Funding will be awarded to expand the availability of high-speed broadband internet access services in rural areas. ReConnect Program applications must be submitted through USDA Rural Development’s online application system. Additional information on ReConnect Program funding requirements can be found in the Funding Opportunity Announcement.
Eligible applicants are state, local or territory governments; corporations; Native American Tribes; limited liability companies and cooperative organizations. To be eligible for ReConnect Program funding, a proposed project must serve a rural area where at least 90 percent of households do not have access to broadband service at speeds of 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload, and commit to building facilities capable of providing broadband service at speeds of 100 Mbps, download and upload, to every location in its proposed service area. USDA will prioritize projects that will serve low-density rural areas with locations lacking internet access services at speeds of at least 25/3Mbps. USDA will also consider, among other things, the economic needs of the community to be served; the extent which a provider will offer affordable service options; a project’s commitment to strong labor standards; and whether a project is serving tribal lands or is submitted by a local government, Tribal Government, non-profit or cooperative.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For December 14th Open Meeting
November 23, 2021 – Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s December 14, 2021, open meeting:
Improving Accessibility and Clarity of Emergency Alerts – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and a Notice of Inquiry to improve clarity and accessibility of Emergency Alert System (EAS) visual messages to the public, including for persons who are deaf or hard of hearing, and others who are unable to access the audio message. (PS Docket No. 15-94)
Facilitating Satellite Broadband Competition – The Commission will consider an Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose revisions to the Commission’s rules for spectrum sharing among low-earth orbit satellite systems. The goal of the proposed revisions is to facilitate the deployment of the new generation of non-geostationary satellite orbit, fixed-satellite service (NGSO FSS) systems, including new competitors. (IB Docket No. 21-456; RM-11855)
Promoting Fair and Open Competitive Bidding in the E-Rate Program – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that proposes to implement a central document repository (i.e, bidding portal) through which service providers would be required to submit their bids to the E-Rate Program Administrator and seeks comment on other changes to the E-Rate competitive bidding rules. (WC Docket 21-455)
LightBox Challenges FCC Decision To Award Broadband Fabric Contract To CostQuest
November 19, 2021 – LightBox Parent, LP has filed a bid protest with the Government Accountability Office challenging the FCC’s decision to award a $44.9 million contract to CostQuest Associates Inc. to create a Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric. A “bid protest” is a challenge to the terms of a solicitation or the award of a federal contract.
The “Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric” will be a common dataset of all locations in the U.S. where fixed broadband internet access service can be installed, and is a key component of the FCC’s new Broadband Data Collection program. Broadband service providers will provide the FCC with granular and detailed coverage data which will be layered on top of the Fabric, thereby giving the FCC an accurate picture of broadband coverage in the U.S. and creating a more accurate national broadband map.
The FCC released a Request for Proposals (RFP) to create the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric on June 1, 2021, with responses due July 1, 2021. However, a pre-award protest was filed with Government Accountability Office following the RFP response deadline, which forced the FCC to issue a revised RFP on August 13, 2021. Revised proposals were due August 26, 2021. The $44.9 million contract to develop the Fabric was then ultimately awarded on November 9, 2021, to CostQuest.
LightBox, who also submitted a proposal in response to the Fabric RFP, filed its bid protest challenging the FCC’s decision pursuant to the Federal Acquisition Regulation process. As a result, “FCC efforts to proceed with the Fabric have been stayed while the GAO has 100 days to issue a decision on the protest.”
Reforming Broadband Connectivity Act of 2021 Introduced In Senate
November 18, 2021 – Senators Amy Klobuchar (D-MN) and John Thune (R-SD) have introduced the Reforming Broadband Connectivity Act of 2021, S.3236, which, if passed, would direct the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to reform the Universal Service Fund (USF). First, the bill directs the FCC to “conduct a study assessing the need to expand the contribution base of the [USF] to ensure that the contribution requirement under section 254(d) of the Communications Act of 1934 (47 U.S.C. 254(d)) is imposed fairly and equitably,” and report the findings to Congress. Second, the bill requires the FCC, not later than one year after enactment, to “complete a rulemaking to reform the contribution system of the [USF], including by expanding the contribution base of the [USF].” The bill has been referred to the Senate’s Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation.
FCC Spectrum Auction 110 Clock Phase Ends: Bidders Win 4,041 Of 4,060 Spectrum Licenses – Gross Proceeds Total Over $21.8 billion
November 16, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has announced that the clock phase of Auction 110 has concluded. Auction 110 bidders won 4,041 of the 4,060 available spectrum blocks, with gross proceeds totaling over $21.8 billion.
Auction 110 offered 4,060 new flexible‐use licenses for spectrum in the 3.45-3.55 GHz band. The 100 megahertz of spectrum will be licensed on an unpaired basis divided into ten 10-megahertz blocks in partial economic areas (PEAs) located in the contiguous 48 states and the District of Columbia.
Auction 110 now moves to the assignment phase, in which winning clock phase winners will have the opportunity to bid for their preferred combinations of frequency-specific license assignments using a series of sealed-bid rounds conducted by PEA.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Authorizes RDOF Support For 311 Winning Bids
November 12, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced it has authorized Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) support for 311 winning bids. This is the third RDOF support authorization. A list of the authorized winning bids is available as Attachment A to the Bureau’s Public Notice. The authorizations were granted after the Bureau reviewed long-form application information for each authorized winning bidder, including letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters, and concluded the submissions were acceptable. Consequently, the Bureau has directed and authorized the Universal Service Administrative Company to obligate and disburse Universal Service Fund support to each winning bidder. Support will be disbursed in 120 monthly payments, beginning at the end of November 2021.
President Biden Signs Secure Equipment Act of 2021 Into Law
November 11, 2021 – President Biden has signed into law the Secure Equipment Act of 2021. The new law will prohibit the Federal Communications Commission (Commission) from reviewing or approving any authorization application for equipment that is on the list of covered communications equipment or services. Specifically, the Secure Equipment Act of 2021 requires the Commission to initiate a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, within one year, in ET Docket No. 21 – 232 (Protecting Against National Security Threats to the Communications Supply Chain through the Equipment Authorization Program). Final rules adopted by the Commission “shall clarify that the Commission will no longer review or approve any application for equipment authorization for equipment that is on the list of covered communications equipment or services published by the Commission under section 2(a) of the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act of 2019 (47 U.S.C. 1601(a)).” “Covered communications equipment or services” are those that the Commission determines pose an unacceptable risk to national security or the security and safety of U.S. persons.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Ready To Authorize $709 Million In RDOF Support For 2,081 Winning Bids
November 10, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced they are ready to authorize support for 2,081 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bids. Funding will eventually go to 50 broadband service providers to deploy broadband services to over 400,000 locations in 26 states. A list showing each winning bid ready to be authorized, the corresponding long-form applicant, each winning bid’s total amount of 10-year support, and other details is available as Attachment A to the Public Notice. Much of the funding in this announcement will be provided to rural electric cooperatives.
The FCC reviewed the long-form applications associated with each winning bid, and determined they met all legal, financial, and technical requirements. To be authorized to receive the listed support amounts, however, each RDOF winning bidder must submit acceptable irrevocable stand-by letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters for each state where they have winning bids that are ready to be authorized prior to 6:00 p.m. ET on November 30, 2021. The FCC will continue to review RDOF long-form applications on a rolling basis, and will announce other approvals of long-forms in future public notices.
This is the fourth group of RDOF winning bids that is ready to be authorized – a total of $709,060,159 in ten-year RDOF support. In total, the FCC has announced over $1.7 billion in funding to RDOF Phase I auction winning bidders for new broadband service deployments. A list of broadband providers and RDOF Phase I auction funding amounts by state, is available from the FCC’s RDOF auction website: https://www.fcc.gov/auction/904.
Final Agenda For FCC November 18 Open Meeting
November 10, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its open meeting scheduled for 10:30 a.m. on Thursday, November 18, 2021. The meeting can be viewed live online via the FCC’s web page at www.fcc.gov/live and on the FCC’s YouTube channel. The open meeting final agenda contains the following items for consideration:
Enabling Text-to-988 (WC Docket No. 18-336) – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order that would require covered text providers to support text messaging to 988 by routing certain text messages sent to 988 to the National Suicide Prevention Hotline by July 16, 2022.
Enhanced Competition Incentive Program for Wireless Radio Services (WT Docket No. 19-38) – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking proposing an Enhanced Competition Incentive Program (ECIP) and other rule changes intended to promote competition, access to spectrum by small carriers and Tribal Nations, and expanded rural wireless coverage.
Updating FM Radio Directional Antenna Verification (MB Docket No. 21-422) – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to allow applicants proposing directional FM antennas the option of verifying the directional antenna pattern through computer modeling.
Kinéis Low-Earth Orbit Satellites Market Access (IBFS File No. SAT-PDR-20191011-00113) – The Commission will consider an Order and Declaratory Ruling on Kinéis’ petition to access the U.S. market using a low-earth orbit satellite system to provide connectivity for Internet of Things devices, as well as enhancements to maritime domain awareness through monitoring of maritime communications.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Hanson Communications Acquiring Consolidated Communications’ Ohio Assets
November 10, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 application filed by Consolidated Communications of Ohio Company, LLC
(Consolidated Ohio) and Hanson Communications of Ohio, LLC (Hanson), requesting consent to transfer substantially all the assets of Consolidated Ohio to Hanson. Comments are due on or before November 24, 2021, and reply comments are due December 1, 2021.
Consolidated Ohio is a wholly-owned, indirect subsidiary of Consolidated Communications Holdings, Inc. Consolidated Ohio operates as an incumbent local exchange carrier (LEC) serving three study areas: Columbus Grove Telephone Company; Germantown Independent Telephone Company; and Orwell Telephone Company. In 2015, Consolidated Ohio’s predecessors in interest – FairPoint – accepted Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II support, which required it to offer voice and broadband service to 1,247 locations in the state over a six-year term, in exchange for annual support of $420,997.00. Consolidated Ohio elected to receive a seventh year of CAF Phase II support. To date, Consolidated Ohio has reported deployment to 1,248 qualifying locations, meeting its CAF Phase II obligations.
Hanson is a privately held Ohio LLC created for the purpose of acquiring and operating the assets of Consolidated Ohio. Hanson is wholly-owned by Hanson Communications, Inc. (HCI), a Minnesota holding company. HCI’s eight incumbent LEC operating companies serve approximately 10,061 access lines and provide broadband connections to approximately 15,357 customers in Minnesota, Nebraska, South Dakota, and Ohio. According to the application, “HCI’s operating companies have deployed approximately 1,500 miles of fiber optic cable, which facilitate high speed internet access, high-definition video services, and will be able to support wireless and wireline service for the delivery of 5G technology in rural America.”
Pursuant to the terms and conditions of an asset purchase agreement, Consolidated Ohio will sell and assign to HCI, substantially all of the assets, property, and rights of Consolidated Ohio. Following the closing of the transaction, the assets, property, and rights currently held by Consolidated Ohio will be owned and operated by Hanson, a subsidiary of HCI created for that purpose.
Consolidated Communications Holdings, Inc. announced the deal to sell its Ohio assets in September 2021. According to the company’s press release, “Consolidated’s Ohio operations contributed approximately $9 million of revenue in fiscal 2020 and includes approximately 4,000 access lines and 3,900 Internet connections.” The deal is expected to be completed by the end of 2021.
FCC Chooses CostQuest To Create Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric
November 10, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has awarded a $44.9 million contract to CostQuest Associates Inc. to create a Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric.
The “Fabric” will be a common dataset of all locations in the U.S. where fixed broadband internet access service can be installed, and is a key component of the FCC’s new Broadband Data Collection program. Broadband service providers will provide the FCC with granular and detailed coverage data which will be layered on top of the Fabric, thereby giving the FCC an accurate picture of broadband coverage in the U.S. and creating a more accurate national broadband map.
CostQuest describes itself as a consulting firm that “builds datasets and custom models to help you make decisions about communications or utilities infrastructure.” The potential value of the awarded Fabric contract is $44,921,200.
The FCC released a Request for Proposals (RFP) to create the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric on June 1, 2021, with responses due July 1, 2021. However, a pre-award protest was filed with Government Accountability Office following the RFP response deadline, which forced the FCC to issue a revised RFP on August 13, 2021. Revised proposals were due August 26, 2021. The contract to develop the Fabric was then ultimately awarded on November 9, 2021, to CostQuest.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Reservation Telephone Cooperative Acquiring Midstate Telephone Company & Midstate Communications
November 10, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 application requesting the transfer of control of Midstate Telephone Company, LLC and Midstate Communications, Inc. to Reservation Telephone Cooperative (RTC). Comments are due on or before November 24, 2021. Reply comments are due December 1, 2021.
Midstate Telephone Company is a rural incumbent local exchange carrier (LEC) serving approximately 2,000 customers in the Stanley, Medora, and Portal exchanges North Dakota. Midstate Communications is a rural incumbent LEC serving approximately 1,000 customers in the Beach exchange in North Dakota.
RTC is a rural incumbent LEC serving approximately 11,000 customers in 20 exchanges in northwestern North Dakota. RTC is a North Dakota cooperative that is owned by its member-subscribers. No single member-subscriber owns or controls more than 10% of the equity interests of RTC.
Pursuant to the terms and conditions of a stock purchase agreement, RTC will acquire all operations and assets of Midstate Telephone Company, LLC, and Midstate Communications, Inc. In their application, the parties claim the transaction: will enable economies of scale; strengthen the combined competitive position of the Midstate companies; allow the Midstate companies to leverage RTC’s financial, technical, and managerial resources; help the Midstate companies compete effectively in the telecommunications marketplace; will be seamless for consumers; and is not expected to result in any discontinuance or impairment of the Midstate companies’ existing services.
FCC Announces Over $421 Million In Emergency Connectivity Fund Support
November 8, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has announced it will commit over $421 million in the latest round of Emergency Connectivity Fund (ECF) allocations. Total EFC program commitments now total over $3.05 billion. ECF funding supports schools and libraries in all U.S states and territories, and can be used to support off-campus learning. According to the FCC’s press release, so far, the ECF program “has committed to supporting 6,954 schools, 613 libraries, and 80 consortia, which are approved to receive over 6.8 million connected devices and over 3.5 million broadband connections.” Further details on the ECF program and the schools and libraries receiving funding are available from the FCC’s ECF program website.
State-by-state breakdown of total ECF committed funding
Congress Passes $1.2 Trillion Infrastructure Bill – $65 Billion For Broadband, Including $42.45 Billion For New Broadband Equity, Access, And Deployment Program
November 6, 2021 – The U.S. House of Representatives has passed the roughly $1.2 trillion infrastructure plan by a 228-206 vote. It was passed by the Senate in August on a 69-30 vote. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act now awaits President Biden’s signature. It allocates federal funding for roads, bridges, ports, rail transit, and other infrastructure. Also, the bill includes $65 billion in federal funding for broadband networks and services, most of which will be made available through grants to states.
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act allocates $42.45 billion for a new Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program which is a grant program that will be run by the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA). Funding will be provided to U.S. states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and U.S. territories. States and territories may use program funding to award grants for the following uses:
deploying broadband service to unserved and underserved areas;
connecting eligible community anchor institutions with broadband service;
broadband data collection, broadband mapping, and planning;
installing internet and Wi-Fi infrastructure or providing reduced-cost broadband within a multi-family residential building, with priority given to a residential building that has a substantial share of unserved households, or is located in an area containing a high percentage of low-income individuals;
broadband adoption, including programs to provide affordable internet-capable devices; and
other uses as determined necessary by NTIA to facilitate the goals of the program.
FCC “Pauses” Two Lifeline Program Changes: Phase-Out Of Support For Voice-Only Services & Increase In Mobile Broadband Data Capacity
November 5, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has paused both the scheduled phase-out of Lifeline support for voice-only services and the scheduled increase in the Lifeline mobile broadband data capacity minimum service standards. The pause will last for one year, until December 1, 2022.
Pursuant to the 2016 Lifeline Order, Lifeline support for voice-only services was reduced from $7.25 to $5.25 on December 1, 2020, and support was scheduled to be eliminated in most areas on December 1, 2021. The minimum service standard for mobile broadband data capacity was set to increase from 4.5 GB per month to 18 GB per month on December 1, 2021.
The Bureau determined there is “good cause” to issue its Order pausing the two Lifeline program changes in light of the creation of the Emergency Benefit Broadband Program, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and new data collected for the State of the Lifeline Marketplace Report. Accordingly, basic Lifeline support of $5.25 remains available to eligible consumers who subscribe to voice-only service on and after December 1, 2021, and the minimum service standard for mobile broadband data capacity will remain at 4.5 GB per month.
Over the next year, the FCC will continue to evaluate whether longer-term modifications to the Lifeline program are needed.
FCC Partially Grants Boeing’s Application To Operate Satellite Broadband System
November 3, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued an Order and Authorization which grants in part and dismisses in part Boeing Company’s application to construct, deploy and operate a proposed non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) fixed-satellite service (FSS) system using frequencies in portions of the V-band, and to operate inter-satellite links (ISLs) using frequencies in portions of the V-band and the Ka-band. Boeing’s NGSO FSS system – referred to as the V-band Constellation – will ultimately consist of 132 low Earth orbit satellites in a circular orbit at an altitude of 1056 kilometers (km) and 15 highly inclined NGSO satellites at an altitude between approximately 27,355 and 44,221 km.
Pursuant to the FCC’s Order and Authorization, Boeing is authorized to provide FSS in parts of the V-band (the 37.5-40, 40-42, 47.2-50.2 and 50.4-51.4 GHz bands), and operate ISLs in the 65-71 GHz part of the V-band. However, the FCC dismissed Boeing’s request to operate ISLs in other portions of the V-band and in the Ka-band that are not allocated internationally for operations of the FSS in the space-to-space direction, and denied certain waivers requested by Boeing. Nevertheless, the authorization will allow Boeing “to provide broadband and communications services to residential, commercial, institutional, governmental and professional users in the United States and globally.”
FCC Terminates China Telecom’s Authority To Provide Service
November 2, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued an Order On Revocation And Termination which revokes China Telecom (Americas) Corporation’s domestic authority to provide service, and revokes and terminates China Telecom’s international authority to provide service. After conducting a public interest analysis under section 214 of the Communications Act and considering the totality of the extensive unclassified record, the FCC concluded “that the present and future public interest, convenience, and necessity is no longer served” by China Telecom’s retention of its Section 214 authority. The FCC provided the following summary of the key decision-making issues:
First, we find that CTA, a U.S. subsidiary of a Chinese state-owned enterprise, is subject to exploitation, influence, and control by the Chinese government and is highly likely to be forced to comply with Chinese government requests without sufficient legal procedures subject to independent judicial oversight.
Second, given the changed national security environment with respect to China since the Commission authorized CTA to provide telecommunications services in the United States, we find that CTA’s ownership and control by the Chinese government raise significant national security and law enforcement risks by providing opportunities for CTA, its parent entities, and the Chinese government to access, store, disrupt, and/or misroute U.S. communications, which in turn allow them to engage in espionage and other harmful activities against the United States.
Third, independent of these concerns, CTA’s conduct and representations to the Commission and other U.S. government agencies demonstrate a lack of candor, trustworthiness, and reliability that erodes the baseline level of trust that the Commission and other U.S. government agencies require of telecommunications carriers given the critical nature of the provision of telecommunications service in the United States.
Fourth, given the record evidence, we find that further mitigation would not address these significant national security and law enforcement concerns. We therefore revoke CTA’s domestic and international section 214 authority.
Fifth, separate and apart from our findings concerning revocation, we terminate CTA’s international section 214 authorizations based on CTA’s willful violation of two of the five provisions of the 2007 Letter of Assurances with the Executive Branch agencies, compliance with which is an express condition of its international section 214 authorizations.
Finally, although it is not necessary to support these findings and conclusions, we find that the classified evidence submitted by the Executive Branch agencies further supports our decisions to revoke the domestic authority and revoke and terminate the international authorizations issued to CTA, and the determination that further mitigation will not address the substantial national security and law enforcement risks.
China Telecom must discontinue any domestic or international services that it provides pursuant to its Section 214 authority no later than 60 days from the release of the FCC’s Order.
Locast & TV Broadcasters Agree To $32 Million Settlement & Permanent Injunction
November 1, 2021 – Defunct online streaming service Locast has agreed to a “Stipulated Consent Judgment and Permanent Injunction” with the U.S. broadcast television networks that successfully brought a lawsuit against it.
The settlement awards statutory damages under the Copyright Act in the amount of $32 million to the lawsuit’s plaintiffs: American Broadcasting Companies, Inc., Disney Enterprises, Inc., Twentieth Century Fox Film Corporation, CBS Broadcasting Inc., CBS Studios Inc., Fox Television Stations LLC, Fox Broadcasting Company LLC, NBCUniversal Media, LLC, Universal Television LLC , and Open 4 Business Productions, LLC.
The settlement also permanently restrains and enjoins Locast owners David R. Goodfriend and Sports Fans Coalition New York from operating the Locast service and “from operating, participating in, assisting or aiding any retransmission service relying on or purporting to rely on Section 111(a)(5) of the Copyright Act.”
On August 31, 2021, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District Of New York ruled in favor of the largest U.S. broadcast television networks in their copyright infringement lawsuit against Locast, a purported “non-profit” streaming service that made local, over-the-air television available for free online.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For November 18th Open Meeting
November 1, 2021 – Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s open meeting scheduled for Thursday, November 18, 2021:
Enabling Text-to-988 – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order that would require covered text providers to support text messaging to 988 by routing certain text messages sent to 988 to the National Suicide Prevention Hotline by July 16, 2022. (WC Docket No. 18-336)
Enhanced Competition Incentive Program for Wireless Radio Services – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking proposing an Enhanced Competition Incentive Program (ECIP) and other rule changes intended to promote competition, access to spectrum by small carriers and Tribal Nations, and expanded rural wireless coverage. (WT Docket No. 19-38)
Updating FM Radio Directional Antenna Verification – The Commission will consider an Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to allow applicants proposing directional FM antennas the option of verifying the directional antenna pattern through computer modeling. (MB Docket No. 21-422)
Kinéis Low-Earth Orbit Satellites Market Access – The Commission will consider an Order and Declaratory Ruling on Kinéis’ petition to access the U.S. market using a low-earth orbit satellite system to provide connectivity for Internet of Things devices, as well as enhancements to maritime domain awareness through monitoring of maritime communications. (IBFS File No. SAT-PDR-20191011-00113)
FCC Releases Fixed & Mobile Broadband Deployment Data As Of December 31, 2020
November 1, 2021 – The FCC has released updated data on fixed broadband deployment, and mobile voice and broadband deployment as of December 31, 2020. The fixed broadband data include revisions made by FCC Form 477 filers through September 30, 2021, while the mobile deployment data include revisions made by filers through April 21, 2021. The information is publicly available at the following websites:
Fixed Deployment Data are available for download at https://www.fcc.gov/general/broadband-deployment-data-fcc-form-477.
Mobile Deployment Data are available at https://www.fcc.gov/mobile-deployment-form-477-data
FCC Denies CAF II Coalition’s Petition To Change CAF II Eligible Locations Adjustment Process
November 1, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has denied a petition filed by the Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II Coalition seeking to modify the FCC’s CAF II Eligible Locations Adjustment Process. The CAF Phase II Coalition is made up of 14 service providers that receive universal service support through the CAF Phase II auction program. In its petition, the group asked the FCC to generally change the process for adjusting CAF II auction deployment obligations “in situations where the number of funded locations is greater than the number of locations qualifying for support.” The Coalition proposed using an end-of-term certification process and requested that CAF II auction support recipients “retain all support awarded so long as the number of actual locations served in the state is at least 65% of the original defined deployment obligation.” Initially, the Wireline Bureau determined that portions of the waiver petition challenge substantive rules and policy decisions, effectively making them a petition for reconsideration. Those portions were dismissed as procedurally defective, but also were independently denied on the merits. The remainder of the petition was denied because the Bureau found “the Coalition has failed to demonstrate good cause for waiver.”
Mergers & Acquisitions: WOW! Sells Chicago, Evansville, Indiana, & Anne Arundel, Maryland Assets To Radiate
November 1, 2021 – WOW! Internet, Cable & Phone has announced the completion of the sale of its Chicago, Evansville, Indiana, and Anne Arundel, Maryland service areas to Radiate HoldCo, LLC, for $661 million. WOW! describes itself as “one of the nation’s leading broadband providers, with an efficient, high-performing network that passes 1.9 million residential, business and wholesale consumers. Radiate HoldCo is “a telecommunications holding company affiliated with RCN Telecom Services, LLC, Grande Communications Networks, LLC and WaveDivision Holdings, LLC (collectively “Astound Broadband”). Among other things, the press release provides the following information on the deal:
The completion of the Astound Broadband transaction follows WOW!'s completed sale of its Cleveland and Columbus, Ohio service areas to Atlantic Broadband, announced in September 2021. Combined, the two transactions have generated gross proceeds of $1.8 billion, enabling WOW! to significantly lower its debt, strengthen the company's financial position and accelerate its broadband-first strategy.
"The completion of the Astound Broadband transaction is another important step in the execution of our broadband-first strategy," said Teresa Elder, CEO of WOW!. "We remain committed to providing customers with reliable, accessible and fast broadband solutions, and now we have an even greater ability to enhance our network and expand our footprint through greenfield and Edge-out opportunities."
Since announcing the sale in June 2021, WOW! has worked with Astound Broadband to ensure a seamless transition of its employees and customers in the Chicago, Evansville, Indiana, and Anne Arundel, Maryland, service areas to Astound Broadband. WOW! has entered into a Transition Services Agreement with Astound Broadband to support continuity of service during the transition period following the completion of the transaction.
BofA Securities acted as financial advisor to WOW!, and Wachtell, Lipton, Rosen & Katz, as well as Honigman LLP, served as legal counsel. Simpson Thacher & Bartlett LLP and Kelley Drye & Warren LLP served as legal counsel to Astound Broadband.
October 2021
President Biden Appoints Jessica Rosenworcel As FCC Chair; Nominates Gigi Sohn As FCC Commissioner
October 26, 2021 – President Joe Biden has announced his intent to nominate Jessica Rosenworcel and Gigi Sohn for Commissioners of the Federal Communications Commission. President Biden has designated Jessica Rosenworcel as FCC Chair, making her the first woman in history to serve in this capacity. The announcement includes the following information on the two nominees:
Jessica Rosenworcel presently serves as Chair of the Federal Communications Commission, where she previously served as a Commissioner since 2012. During her time at the agency, she has worked to promote greater opportunity, accessibility, and affordability in our communications services in order to ensure that all Americans get a fair shot at 21st century success. From fighting to protect an open internet, to ensuring broadband access for students caught in the Homework Gap through the FCC’s Emergency Connectivity Fund, to making sure that households struggling to afford internet service stay connected through the Emergency Broadband Benefit program, she has been a champion for connectivity for all. She is a leader in spectrum policy, developing new ways to support wireless services from Wi-Fi to video and the Internet of Things. She has fought to combat illegal robocalls and enhance consumer protections in our telecommunications policies.
Prior to joining the agency, she served as Senior Communications Counsel for the United States Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation, under the leadership of Senator John D. Rockefeller IV and Senator Daniel Inouye. Before entering public service, Jessica practiced communications law. She is a native of Hartford, Connecticut and a graduate of Wesleyan University and New York University School of Law. She lives with her family in Washington, DC.
Gigi B. Sohn is a Distinguished Fellow at the Georgetown Law Institute for Technology Law & Policy and a Benton Senior Fellow and Public Advocate. Gigi is one of the nation’s leading public advocates for open, affordable, and democratic communications networks. For over thirty years, Gigi has worked to defend and preserve the fundamental competition and innovation policies that have made broadband Internet access more ubiquitous, competitive, affordable, open, and protective of user privacy. If she is confirmed, Gigi would be the first openly LGBTIQ+ Commissioner in the history of the FCC.
From 2013-2016, Gigi served as Counselor to Former FCC Chairman Tom Wheeler, and from 2001-2013 was Co-Founder and CEO of Public Knowledge, a leading communications and technology policy advocacy organization serving the interests of consumers. She was previously a Project Specialist in the Ford Foundation’s Media, Arts and Culture unit and Executive Director of the Media Access Project, a communications public interest law firm. Gigi holds a B.S. in Broadcasting and Film, Summa Cum Laude, from the Boston University College of Communication and a J.D. from the University of Pennsylvania Law School. She resides with her family in Washington, DC.
Verizon Announces Collaboration With Amazon’s Project Kuiper Satellite Network
October 26, 2021 – Verizon Communications Inc. has announced a “strategic collaboration” with Amazon’s Project Kuiper low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite network “to develop connectivity solutions for unserved and underserved communities.” The new partnership will allow the two companies “to design and deploy new connectivity solutions across a range of domestic and global industries, from agriculture and energy to manufacturing and transportation.” The press release provides the following information:
The partnership seeks to expand coverage and deliver new customer-focused connectivity solutions that combine Amazon’s advanced LEO satellite system and Verizon’s world-class wireless technology and infrastructure. To begin, Amazon and Verizon will focus on expanding Verizon data networks using cellular backhaul solutions from Project Kuiper. The integration will leverage antenna development already in progress from the Project Kuiper team, and both engineering teams are now working together to define technical requirements to help extend fixed wireless coverage to rural and remote communities across the United States.
RUS Releases ReConnect Program Funding Opportunity Announcement – Application Window Opens November 24th & Closes February 22, 2022
October 25, 2021 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Rural Utilities Service (RUS) has released a Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) for the Rural eConnectivity Program (the ReConnect Program). RUS will accept applications for the fiscal year 2022 ReConnect Program beginning on November 24, 2021, until 11:59 a.m. Eastern on February 22, 2022. Applications can be submitted through the RUS ReConnect Program on-line application portal. For FY 22, the ReConnect Program will award loans, grants, and loan/grant combinations for the costs of construction, improvement, or acquisition of facilities and equipment needed to facilitate broadband deployment in rural areas. Details of the FOA include the following:
Eligible Areas: For a proposed funded service area (PFSA) to be eligible for funding, at least 90 percent of the households in the PFSA must lack sufficient access to broadband. Sufficient access to broadband means any rural area in which households have access to fixed, terrestrial broadband service of at least 100 Mbps downstream and 20 Mbps upstream. Applicants must submit evidence that sufficient access to broadband does not exist for 90 percent of the households in the PFSA, identify all existing providers in the PFSA, and indicate what level of service is being provided. If these areas are found to have sufficient service, the application will be rejected.
Funding Obligations: Facilities proposed to be constructed with award funds must be capable of delivering 100 Mbps symmetrical service to every premise in the PFSA. Capable of delivering 100 Mbps symmetrical service to every premise means that all premises in the PFSA must be able to receive this service at the same time.
100 Percent Grant Funding: Applicants for 100 percent grant funding must provide a matching contribution equal to at least 25 percent of the cost of the overall project. This matching contribution requirement applies only to the 100 percent grant funding category.
USDA will prioritize projects that will serve low-density rural areas with locations lacking internet access services at speeds of at least 25/3Mbps. USDA will also consider, among other things, the economic needs of the community to be served; the extent which a provider will offer affordable service options; a project’s commitment to strong labor standards; and whether a project is serving tribal lands or is submitted by a local government, Tribal Government, non-profit or cooperative. The entire FOA is available online.
USDA To Begin Accepting ReConnect Applications On November 24th
October 22, 2021 – U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Secretary Tom Vilsack has announced that USDA will begin accepting applications for up to $1.15 billion in ReConnect Program loans and grants on November 24, 2021. Funding will awarded to expand the availability of broadband internet access service in rural areas. To be eligible for ReConnect Program funding, an applicant must serve an area without broadband service at speeds of 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload, and commit to building facilities capable of providing broadband service at speeds of 100 Mbps, download and upload, to every location in its proposed service area. USDA will prioritize projects that will serve low-density rural areas with locations lacking internet access services at speeds of at least 25/3Mbps. USDA will also consider, among other things, the economic needs of the community to be served; the extent which a provider will offer affordable service options; a project’s commitment to strong labor standards; and whether a project is serving tribal lands or is submitted by a local government, Tribal Government, non-profit or cooperative.
FTC Report Says Largest ISPs Collect Too Much Data About Customers
October 21, 2021 – The Federal Trade Commission has released a report titled “A Look At What ISPs Know About You: Examining the Privacy Practices of Six Major Internet Service Providers” that “highlights the ISP industry’s data surveillance and privacy practices.” In the report, FTC staff finds that the six largest internet service providers (ISPs) “collect and share far more data about their customers than many consumers may expect – including access to all of their Internet traffic and real-time location data – while failing to offer consumers meaningful choices about how this data can be used.” The six ISPs, which make up about 98 percent of the mobile internet access market, identified in the report are:
AT&T Mobility LLC;
Cellco Partnership, which does business as Verizon Wireless;
Charter Communications Operating LLC;
Comcast Cable Communications, which does business as Xfinity;
T-Mobile US Inc.; and
Google Fiber Inc.
FCC Denies LTD Broadband ETC Waiver Request; LTD Stripped Of RDOF Support In Iowa, Nebraska, & North Dakota
October 20, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released an Order partially denying a petition filed by LTD Broadband LLC seeking waiver of a Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction long-form requirement.
LTD Broadband sought waiver of the FCC’s June 7, 2021 deadline requiring each RDOF long form applicant “to demonstrate, with appropriate documentation, that it has been designated as an eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) in each of the geographic areas for which it seeks to be authorized for [RDOF] support.” LTD Broadband requested the waiver for eight states where it won support. The Wireline Competition Bureau, in a decision issued in July 2021, denied the waiver with respect to California, Kansas, and Oklahoma. It will rule on the merits of LTD’s waiver with respect to South Dakota and Texas in a future decision.
In this Order, the Bureau has denied “LTD’s request to waive the deadline to submit documentation of its ETC designations in Iowa, Nebraska, and North Dakota.” As for its reasoning, the Bureau “note[d] that LTD did not file its ETC applications in any of these three states within the 30-day ‘good faith presumption’ window,” and concluded that LTD Broadband failed to demonstrate good cause justifying waiver of the June 7th ETC documentation deadline. As a consequence of the decision, LTD Broadband is in default of its winning bids in Iowa, Nebraska, and North Dakota. Accordingly, LTD will lose the following support amounts it was awarded from the RDOF auction:
Iowa – $23,184,786.30 in ten-year support to serve 12,916 locations
Nebraska – $33,228,644.00 in ten-year support to serve 28,729 locations
North Dakota – $ 8,574,318.00 in ten-year support to serve 831 locations
FCC Denies NW Fiber LLC Waiver Request; Strips Company Of $7 Million In RDOF Support In Washington
October 20, 2021 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released an Order denying a petition filed by NW Fiber, LLC seeking waiver of the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction long-form requirement.
NW Fiber, an ISP headquartered in Colfax, Washington, participated in the RDOF auction as part of a two-entity consortium with St. John Telephone, Inc., a rural local exchange carrier that provides services in and around St. John, Washington. The consortium was the winning bidder in 14 census block groups in Washington, all of which were subsequently assigned to NW Fiber. Specifically, the company was awarded $7,116,876.00 in ten-year support to serve 1,057 locations. However, as explained in its waiver petition, NW Fiber was unaware of the RDOF auction’s long-form requirement because it “had relied upon St. John for the consortium’s FCC filings and compliance.” NW Fiber learned of the January 29, 2021 long-form filing deadline on February 8, 2021, after the FCC contacted St. John to inquire about the missing long-form. NW Fiber then requested a waiver of the deadline with respect to 14 census block groups in Washington where it won support.
The Bureau has denied NW Fiber’s waiver request, concluding NW Fiber “has not established special circumstances to warrant a waiver of the January 29 deadline.” To explain its decision, the Bureau explained that “[i]t is well established that a lack of familiarity with or ignorance of the Commission’s rules and procedures does not constitute special circumstances that justify granting a waiver.” Also, the Bureau noted that even after NW Fiber filed its waiver petition, the company “has continued to miss required deadlines and failed to complete the requirements of the program established by the Commission.” To drive the point home, the Bureau then said it doubted NW Fiber’s ability to follow through on the RDOF program’s obligations:
Given the company’s continued failure to meet the Auction 904 long-form requirements and deadlines, we have significant concerns about its ability to fulfill the ongoing deployment and reporting requirements that all Auction 904 support recipients must satisfy.
The Bureau will release a public notice in the near future finding NW Fiber in default on its bids in Washington.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Ready To Authorize Support For 1774 Winning Bids
October 20, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced they are ready to authorize support for 1774 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bids. A list showing each winning bid ready to be authorized, the corresponding long-form applicant, each winning bid’s total amount of 10-year support, and other details is available as Attachment A to the Public Notice.
The FCC reviewed the long-form applications associated with each winning bid, and determined they met all legal, financial, and technical requirements. To be authorized to receive the listed support amounts, however, each RDOF winning bidder must submit acceptable irrevocable stand-by letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters for each state where they have winning bids that are ready to be authorized prior to 6:00 p.m. ET on November 3, 2021.
FCC staff are reviewing RDOF long-form applications on a rolling basis, and will announce other approvals of long-forms in future public notices.
Final Agenda For FCC’s October 26th Open Meeting
October 19, 2021 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for the FCC’s open meeting scheduled for 10:30 am on Tuesday October 26, 2021:
National Security Matter – The Commission will consider a national security matter.
Updating Digital Television Table of Allotments – The Commission will consider an Order that will update the digital television Table of Allotments, and delete or revise rules rendered obsolete by the broadcast incentive auction and the digital television transition. (GN Docket No. 12-268)
Selecting Third Round of Applicants for Connected Care Pilot Program – The Commission will consider a Public Notice announcing the third round of selections for the Commission’s Connected Care Pilot Program to provide Universal Service Fund support for health care providers making connected care services available directly to patients. (WC Docket No. 18-213)
Disaster Communications Field Hearing – The Commission will conduct a virtual field hearing on communications recovery and resiliency during disasters. The Commission will hear testimony about communications issues during and following Hurricane Ida and other recent disasters.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Ready To Authorize Support For 484 Winning Bids
October 7, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced they are ready to authorize support for 484 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bids. A list showing each winning bid ready to be authorized, the corresponding long-form applicant, each winning bid’s total amount of 10-year support, and other details is available as Attachment A to the Public Notice. However, the support amounts listed in Attachment A are subject to change.
According to the FCC’s News Release, “[i]n this funding wave, 42 broadband providers will bring fiber-to-the-home gigabit broadband to approximately 65,000 locations in 21 states over the next 10 years.”
The FCC reviewed the long-form applications associated with each winning bid, and determined they met all legal, financial, and technical requirements. To be authorized to receive the listed support amounts, however, each RDOF winning bidder must submit acceptable irrevocable stand-by letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters for each state where they have winning bids that are ready to be authorized prior to 6:00 p.m. ET on October 22, 2021. FCC staff are reviewing long-form applications on a rolling basis, and will announce other approvals of long-forms in future public notices.
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: 85 Winning Bidders Reject RDOF Support In 5,089 Census Blocks
October 7, 2021 – The FCC’s Rural Broadband Auctions Task Force, Wireline Competition Bureau, and Office of Economics and Analytics have released a preliminary list of areas where Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction winning bidders have notified the FCC that they do not intend to pursue RDOF support.
In July 2021, the FCC sent letters notifying 197 RDOF winning bidders that some census blocks where they won support are already served or raise concerns about wasteful spending. Specifically, these problematic census blocks are “already served by one or more service providers that offer 25/3 Mbps broadband service or otherwise raise significant concerns about wasteful spending” because they contain parking lots, international airports, or otherwise do not contain residential or business locations. Each letter contained a list of the specific census blocks for each RDOF winner. In the letter, the FCC directed the RDOF winner “to conduct due diligence” by assessing whether existing broadband service in the identified census blocks will affect their ability to meet RDOF requirements and deployment milestones.
According to the FCC, “85 winning bidders have chosen not to pursue buildout in 5,089 census blocks in response to letters the FCC sent asking applicants to review their bids in areas where there was evidence of existing service or questions of potential waste.” The preliminary list of the identified areas where letter recipients indicated they will no longer pursue funding is available on the FCC’s RDOF – Auction 904 website under the “Results” tab.
FCC Releases Tentative Agenda For October 26th Open Meeting
October 5, 2021 – Acting Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel has released the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Tuesday October 26, 2021:
National Security Matter – The Commission will consider a national security matter.
Updating Digital Television Table of Allotments – The Commission will consider an Order that will update the digital television Table of Allotments, and delete or revise rules rendered obsolete by the broadcast incentive auction and the digital television transition. (GN Docket No. 12-268)
Selecting Third Round of Applicants for Connected Care Pilot Program – The Commission will consider a Public Notice announcing the third round of selections for the Commission’s Connected Care Pilot Program to provide Universal Service Fund support for health care providers making connected care services available directly to patients. (WC Docket No. 18-213)
Disaster Communications Field Hearing – The Commission will conduct a virtual field hearing on communications recovery and resiliency during disasters. The Commission will hear testimony about communications issues during and following Hurricane Ida and other recent disasters.
NTIA Releases Proposed Service Areas Of Broadband Infrastructure Program Applications – Providers May Submit Challenges By October 19th
October 4, 2021 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released the proposed service areas of all applications for funding through NTIA’s Broadband Infrastructure Program. Broadband service providers now have 15 days to submit challenge information about existing broadband services offered in any of the proposed service areas.
Challengers can download an excel spreadsheet showing each applicant and their proposed service areas, census blocks, and State or Territory associated with each application. Instructions for submitting challenges is also available online.
NTIA received over 230 applications seeking more than $2.5 billion in funding across 49 states and territories for its Broadband Infrastructure Program. NTIA will award BIP grants to “covered partnerships” for “covered broadband projects.” Covered partnership means a partnership between: (1) a State, or one or more political subdivisions of a State; and (2) a provider of fixed broadband service. Covered broadband project means a competitively and technologically neutral project for the deployment of fixed broadband service that provides qualifying broadband service (25/3 Mbps and low latency) in an eligible service area. The term eligible service area means a census block in which broadband service is not available at one or more households or businesses in the census block.
NTIA expects the award process will be highly competitive. Funding priority will be given to applications with proposed broadband projects that: (1) are designed to provide broadband service to the greatest number of households in an eligible service area; (2) will provide broadband service to rural areas (an eligible service area that is wholly within any area other than: (i) a county, city, or town that has a population of more than 50,000 inhabitants; and (ii) the urbanized area contiguous and adjacent to a city or town of more than 50,000 inhabitants); (3) are the most cost-effective, prioritizing such projects in areas that are the most rural; and (4) are designed to provide broadband service with speeds of at least 100/20 Mbps. NTIA expects to complete its selection of award by November 15, 2021, and begin announcing winners no earlier than November 29, 2021.
Syniverse Was Victim Of Ongoing Breach That Began In May 2016
October 4, 2021 – According to a recent U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission filing, Global telecommunications and technology company Syniverse was the victim of an ongoing breach that began in May 2016. Information about the breach was disclosed on a Schedule 14A, preliminary proxy statement, filed with the SEC by M3-Brigade Acquisition II Corp. According to the SEC filing, Syniverse discovered the breach in May 2021, and after an investigation, determined an “individual or organization gained unauthorized access to databases within its network on several occasions, and that login information allowing access to or from its Electronic Data Transfer...environment was compromised for approximately 235 of its customers.” The SEC filing contains the following additional information about the Syniverse breach:
Syniverse has notified all affected customers of this unauthorized access where contractually required, and Syniverse has concluded that no additional action, including any customer notification, is required at this time.
Syniverse did not observe any evidence of intent to disrupt its operations or those of its customers and there was no attempt to monetize the unauthorized activity. Syniverse did not experience and does not anticipate that these events will have any material impact on its day-to-day operations or services or its ability to access or process data. Syniverse has maintained, and currently maintains, cyber insurance that it anticipates will cover a substantial portion of its expenditures in investigating and responding to this incident.
While Syniverse believes it has identified and adequately remediated the vulnerabilities that led to the incidents described above, there can be no guarantee that Syniverse will not uncover evidence of exfiltration or misuse of its data or IT systems from the May 2021 Incident, or that it will not experience a future cyber-attack leading to such consequences. Any such exfiltration could lead to the public disclosure or misappropriation of customer data, Syniverse’s trade secrets or other intellectual property, personal information of its employees, sensitive information of its customers, suppliers and vendors, or material financial and other information related to its business. The release of any of this information could have a material adverse effect on Syniverse’s business, reputation, financial condition and results of operations.
Court Dismisses Texas City’s Lawsuit Seeking Franchise Fees From Netflix & Hulu
October 1, 2021 – The U.S. District Court for the Eastern District Of Texas, Texarkana Division, has dismissed the City of New Boston’s class action lawsuit filed against Netflix, Inc. and Hulu, LLC. In its complaint, the City of New Boston, Texas, claimed video streaming service providers Netflix and Hulu violated Texas law by failing to pay video service franchise fees to Texas municipalities. Netflix and Hulu sought dismissal of the suit, arguing the law “does not apply to them because they are not holders of a state-issued certificate of franchise authority.” The court agreed, finding the statutory language clearly requires only a holder of a state-issued certificate of franchise authority to pay the franchise fee. While Netflix and Hulu may be video service providers, the court concluded it is undisputed that they do not have state-issued certificates of franchise authority. Further, the court shot down the City’s request for declaratory relief, explaining that it “does not have the authority to issue the certificates of franchise underpinning this case for franchise fees.”
Cyber Incident Reporting Act Would Require Critical Infrastructure To Report Cyber Attacks
October 1, 2021 – The Cyber Incident Reporting Act of 2021 has been introduced in the U.S. Senate. If passed, it would “require critical infrastructure owners and operators to report to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) if they experience a cyber-attack, and most entities to report if they make a ransomware payment.” The full text of the bill is available here.