The Latest News
FCC | Broadband | Wireless | Congress
Fifth Circuit Grants Petition For Rehearing En Banc In Consumers’ Research v. FCC Universal Service Fund Challenge
June 29, 2023 – The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit has granted a Petition For Rehearing En Banc in Consumers’ Research v. FCC. In March 2023, a three-judge panel of the Court issued a unanimous opinion in favor of the FCC. Consumers’ Research thereafter requested the case be reheard en banc. By granting the Petition, the Fifth Circuit has vacated the March 2023 decision. At a later date, the Court will announce the schedule for oral argument and the filing of supplemental briefs.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For July 20th Open Meeting
June 29, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s open meeting scheduled for Thursday, July 20, 2023:
Enhancing Support for Connectivity in Tribal Communities – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would adopt rules to enhance Tribal communities’ access to the E-Rate program by streamlining certain program rules, making Tribal college and university libraries eligible for E-Rate support, and reducing administrative burdens in the program. The Commission will also seek comment on ways to further improve and simplify program rules for all E-Rate applicants. (CC Docket Nos. 02-6, 96-45, 97-21)
Ensuring the Reliability and Resiliency of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to ensure that when there is a communications service outage that potentially affects people’s ability to reach the 988 Lifeline, the Commission and those who provide life-saving 988 crisis intervention services receive timely and actionable information. (PS Docket Nos. 23-5, 15-80; WC Docket No. 18-336)
Preserving Local Radio Programming – The Commission will consider a Report and Order allowing a limited group of existing channel 6 low power television stations to continue to provide analog FM radio service as an ancillary or supplementary service under specified rules. (MB Docket No. 03-185)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
NTIA Releases BEAD Program’s State Funding Allocations
June 26, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released the Broadband, Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program’s funding allocations to all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories. A list of the BEAD funding allocations by state is available on NTIA’s press release. Each state and territory will use funding from the $42.45 billion BEAD Program to administer programs that award grants to deploy affordable, reliable high-speed broadband Internet service to everyone in America. States and territories will receive a formal notice of allocation on June 30, 2023. They will then have 180 days to submit their Initial Proposals describing how they propose to run their grant programs. Initial Proposals may be submitted starting on July 1, 2023. Once NTIA approves an Initial Proposal, which will occur on a rolling basis, states and territories will be permitted to request access to at least 20 percent of their allocated funds. Below are the allocations for every state and territory, ranked by total funding:
FCC Announces July 13th Workshop On Opportunities And Challenges Of Artificial Intelligence For Communications Networks And Consumers
June 20, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has announced it will hold a workshop with the National Science Foundation on Opportunities and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence for Communications Networks and Consumers. The workshop will be held on July 13, 2023, from 9:00 am to 12:30 pm, EDT, in the FCC’s Commission Meeting Room at the FCC Headquarters, 45 L Street, NE, Washington, DC. It also will be streamed live online at the FCC’s web page at www.fcc.gov/live.
FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel will open the workshop with a speech, followed by remarks from NSF Director Dr. Sethuraman Panchanathan and FCC Commissioner Nathan Simington. Dr. Margaret Martonosi, Assistant Director for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE) at NSF, will provide a keynote speech. The workshop will then continue with two panels: (1) AI’s Dramatic Impact on Communications Networks and Technologies; and (2) AI as a Tool and Challenge for Consumer Empowerment. The announcement contains the following description of the workshop:
This half-day workshop will convene a diverse array of stakeholders—network operators and vendors, leading academics, federal agencies, and public-interest representatives—to discuss the promise and challenge of artificial intelligence (AI) in the telecommunications and technology sectors. The workshop will cover a wide range of issues, including AI’s transformative potential to optimize network traffic; improve spectrum policy and facilitate sharing; and enhance resiliency through self-healing networks. The workshop will also explore how AI will affect the fight against illegal robocalls and robotexts; efforts to foster digital equity and combat discrimination; and initiatives to bring greater transparency and affordability to broadband access.
FCC Chairwoman Circulates Order On High-Cost USF Support
June 16, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced that she has circulated an item to the other FCC Commissioners on high-cost universal service fund (USF) support. According to the FCC news release, the item contains an order which would create an Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) program requiring the deployment of 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband service to all locations served by the program. The order also would provide an opportunity for rate-of-return carriers that receive legacy USF high-cost support to deploy 100/20 Mbps broadband service to their locations in return for a term of stable support.
The item also contains a “rulemaking and inquiry” that would seek public comment “on further reforms to the legacy rate-of-return system and methods for modifying the Universal Service Fund’s high-cost program to support ongoing expenses for broadband networks, particularly those built with capital funds from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and other recent federal and state efforts.”
NTIA Awards $930 Million In Middle Mile Grants
June 16, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has announced it has awarded $930,021,354.34 in middle mile grant funds. NTIA’s $1 billion Middle Mile program funds construction, improvement, or acquisition of middle mile infrastructure that does not directly connect end-user locations. The awards will fund middle mile projects covering over 350 counties across 35 states and Puerto Rico. NTIA’s grants range from $2.7 million to $88.8 million, with an average award amount of $26.6 million. In total, the awarded projects will deploy over 12,000 miles of new fiber that will pass within 1,000 feet of 6,961 community anchor institutions. Information on the awardees and their projects is available here.
House Communications & Technology Subcommittee Schedules FCC Oversight Hearing
June 16, 2023 – The House Energy and Commerce Committee’s Communications and Technology Subcommittee has scheduled a Federal Communications Commission (FCC) oversight hearing for June 21, 2023. All FCC Commissioners are set to testify. The hearing is schedule to begin at 10:30 am.
FCC Chairwoman Wants Notice Of Inquiry On Broadband Data Caps
June 15, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced she will ask her fellow FCC Commissioners to support a formal Notice of Inquiry on broadband data caps. The Notice of Inquiry is intended to help the FCC understand how broadband providers use data caps on consumer plans; the current state of data caps, how broadband data caps impact consumers; how consumers are informed about data caps on service offerings; how data caps impact competition; the FCC’s legal authority to take actions regarding data caps; and whether the FCC should consider taking action to ensure that data caps do not cause harm to competition or consumers’ ability to access broadband Internet services. Ahead of the Notice of Inquiry, the FCC has created a portal for consumers to share information on how data caps have affected them and their broadband service. The new portal is available online.
DISH Network 5G Now Available to Over 70 Percent Of U.S. Population
June 15, 2023 – DISH Network Corporation has announced that its 5G wireless service is now available to over 70 percent of the U.S. population, fulfilling its commitment to the FCC. DISH also announced it has satisfied its other June 14, 2023 FCC commitments: at least 15,000 5G Sites deployed, and at least 30 MHz of DISH’s downlink 5G spectrum averaged over all DISH 5G Sites deployed nationwide. DISH became a nationwide mobile wireless provider following the T-Mobile / Sprint merger and the combined entity’s divestiture of spectrum, prepaid wireless businesses, cell sites, and physical assets to Dish. Thereafter, the FCC’s Wireless Telecommunications Bureau modified the license terms and construction deadlines for various spectrum licenses held by DISH, and added certain obligations to provide 5G services using the spectrum.
USF Contribution Factor For Third Quarter Of 2023: 29.2 Percent
June 14, 2023 – The FCC’s Office of Managing Director (OMD) has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the third quarter of 2023 will be 29.2 percent. If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. The 29.2 percent USF contribution factor for 3Q 2023 is minute increase from the 29 percent contribution factor from last quarter.
For the third quarter of 2023, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $8.534206 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected ($8.761743 billion was collected for 2Q 2023). USAC estimates that $1.912440 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms (revenue requirement) in the third quarter of 2023 (the 2Q 2023 demand was $1.951900 billion).
Total third quarter 2023 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, which breaks out among the USF support mechanisms as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $586.77 million (2Q 2023 was $609.15 million)
Rural Health Care: $66.17 million (2Q 2023 was $159.36 million)
High-Cost: $1.04415 billion (2Q 2023 was $972.91 million)
Lifeline: $206.97 million (2Q 2023 was $202.05 million)
Connected Care: $8.38 million (2Q 2023 was $8.43 million)
FCC Creates Privacy & Data Protection Task Force
June 14, 2023 – FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel has announced that the FCC has created a new Privacy and Data Protection Task Force. FCC Enforcement Bureau Chief Loyaan A. Egal will lead the task force, with other members pulled from FCC staff from across the agency. The new task force will coordinate across the agency on the rulemaking, enforcement, and public awareness needs in the privacy and data protection sectors, while focusing on data breaches and supply chain vulnerabilities involving third-party vendors that service regulated communications providers. Additional information on the task force is available at www.fcc.gov/privacy-and-data-protection-task-force.
Music Publishers Sue Twitter For Copyright Infringement
June 14, 2023 – A group of 17 music publishers has filed a copyright infringement suit against Twitter in the U.S. District Court For The Middle District Of Tennessee, Nashville Division (Case 3:23-cv-00606). The complaint alleges three claims: direct copyright infringement, contributory infringement, and vicarious infringement. The plaintiff music publishers allege that prior to and after Twitter was purchased by Elon Musk, “Twitter has engaged in, knowingly facilitated, and profited from copyright infringement, at the expense of music creators, to whom Twitter pays nothing.” The Plaintiffs allege that unlike other popular social media platforms such as TikTok, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and Snapchat, Twitter has failed to enter into “proper licenses and agreements for the use of musical compositions on [its] platforms.” They further allege “Twitter consistently and knowingly hosts and streams infringing copies of musical compositions,” and “also routinely continues to provide specific known repeat infringers with use of the Twitter platform, which they use for more infringement.” The music publishers are seeking statutory damages of up to $150,000 per work infringed (for a total of more than $250 million in damages), and injunctive relief prohibiting Twitter from infringing any of Publishers’ exclusive rights in copyrighted works.
RUS Announces $714 Million In ReConnect Awards In 19 States
June 12, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has announced $714 million in ReConnect Program awards in 19 states for the deployment of reliable, affordable high-speed broadband internet services. RUS’s ReConnect Program provides loans, grants, and loan/grant combinations to facilitate broadband deployment in rural areas. The awards are part of the program’s fourth funding round. The $714 million in awards are going to broadband providers in the following 19 states: Alaska, Arkansas, Arizona, California, Georgia, Idaho, Kansas, Kentucky, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah and Washington. Information on each award is available here.
FCC NPRM Proposes Nationwide Transition To Next Generation 911 Networks
June 9, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking intended to advance the nationwide transition to Next Generation 911 (NG911) networks. According to the FCC, moving from Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)-based 911 networks to Internet Protocol (IP)-based NG911 networks will result in new capabilities, improved interoperability, and system resilience, and reduce costs vulnerabilities because 911 authorities will no longer have to maintain both legacy and IP networks. To facilitate the transition to NG911 networks, the FCC propose three substantive changes:
The FCC proposes to require wireline, interconnected VoIP, and Internet-based TRS providers to complete all translation and routing to deliver 911 calls, including associated location information, in the requested IP-based format to an Emergency Services IP network (ESInet) or other designated point that allows emergency calls to be answered upon request of 911 authorities who have certified the capability to accept IP-based 911 communications. Wireline and interconnected VoIP providers would be subject to this requirement six months from the effective date of the IP service delivery requirement, or six months after a valid request for IP based service by a state or local 911 authority, whichever is later. Internet-based TRS providers would be subject to this requirement twelve months from the effective date of the IP service delivery requirement, or twelve months after a valid request for IP-based service by a state or local 911 authority, whichever is later.
The FCC proposes to require wireline, interconnected VoIP, CMRS, and Internet-based TRS providers to transmit all 911 calls to destination points in those networks designated by a 911 authority, including to a public safety answering point (PSAP), designated statewide default answering point, local emergency authority, ESInet, or other points designated by 911 authorities that allow emergency calls to be answered, upon request of 911 authorities who have certified the capability to accept IP-based 911 communications.
The FCC proposes that in the absence of agreements by states or localities on alternative cost recovery mechanisms, wireline, interconnected VoIP, CMRS, and Internet-based TRS providers must cover the costs of transmitting 911 calls to the point(s) designated by a 911 authority, including any costs associated with completing the translation and routing necessary to deliver such calls and associated location information to the designated destination point(s) in the requested IP-based format. States and localities would remain free to establish alternative cost allocation arrangements with providers, but in the absence of such arrangements, providers would be presumptively responsible for the costs associated with delivering traffic to the destination points identified by the appropriate 911 authority.
FCC Issues Final Agenda For June 8th Open Meeting
June 1, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its open meeting scheduled for Thursday, June 8, 2023. The meeting is set to begin at 10:30 a.m., and will be streamed live online at www.fcc.gov/live and on the FCC’s YouTube channel.
Advancing the Transition to Next Generation 911 – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would expedite the transition to NG911 and help ensure that the nation’s 911 system functions effectively and with the most advanced capabilities available. (PS Docket No. 21-479)
Strengthening Consumer Consent for Robocalls and Robotexts – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking proposing rules to strengthen the ability of consumers to decide which robocalls and robotexts they wish to receive by exercising their right to grant and revoke consent to callers. The item also proposes to codify the Commission’s past guidance on prior express consent to make these requirements more apparent to callers and consumers. (CG Docket No. 02-278)
Access to Video Conferencing – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would find that the accessibility requirements of section 716 of the Act and Part 14 of the Commission’s rules apply to all services and equipment meeting the definition of “interoperable video conferencing service.” An accompanying Notice of Proposed Rulemaking would propose to amend Part 14 of the Commission’s Rules to enhance the accessibility of interoperable video conferencing services and explore whether the Interstate Telecommunications Relay Services Fund can be used to support the integrated provision of relay service in video conferences. (CG Docket Nos. 23-161, 10-213, and 03-123)
Shared Use of the 42-42.5 GHz Band – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would explore how spectrum in the 42 GHz band (42-42.5 GHz) might be made available through one of several innovative, non-exclusive spectrum access models which have the potential to provide solutions in this evolving space. (WT Docket No. 23-158; GN Docket No. 14-177)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
USAC Files Data On Third Quarter 2023 USF Contribution Base: $8,534,205,926
June 1, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed projected universal service fund (USF) contribution base data for the third quarter of calendar year 2023. The data will be used to determine the next USF contribution factor. For the third quarter of 2023, USAC has determined that the total projected collected interstate and international end user revenue base for the USF support mechanisms is $8,534,205,926. The 3Q contribution base data was calculated using projected revenue amounts for July - September 2023 reported by telecommunications service providers on their FCC Forms 499-Q which were due May 1, 2023. To provide a comparison, USAC’s total projected USF contribution base amounts for the first two quarters of 2023 and for 2022 were as follows:
Second Quarter 2023 – $8,761,742,607
First Quarter 2023 – $8,749,749,511
Fourth Quarter 2022 – $8,624,083,282
Third Quarter 2022 – $8,285,056,307
Second Quarter 2022 – $8,751,403,396
First Quarter 2022 – $9,235,845,776
For the third quarter of 2023, USAC received projected revenue data from 3,210 USF contributors who filed the February 2023 Form 499-Q. USAC estimated revenue data for 259 non-de minimis service providers that had previously submitted Form 499-Q information to USAC, but failed to make the latest filing. After the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approves the total USF contribution base, the quarterly funding requirements for USF support mechanisms, and projected USF administrative costs, the FCC will establish a USF contribution factor for the third quarter of 2023. The new contribution factor will be announced by an FCC Public Notice. USAC will then bill USF contributors on a monthly basis for their individual obligations based on the approved contribution factor.
FCC Announces Start Date For Performance Measures Testing For Rural Digital Opportunity Fund Support Recipients
June 1, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced the broadband network speed and latency testing dates for Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) support recipients. Specifically, for the carriers participating in RDOF, pre-testing will begin on January 1, 2025, and testing will begin on January 1, 2026.
In general, under the FCC’s Connect America Fund regime, broadband providers that receive high-cost universal service support must offer broadband service that meets certain basic performance requirements – speed and latency – in the areas where they receive that support. Testing is conducted from the premises of active subscribers to a remote test server located at, or reached by passing through, an FCC-designated Internet exchange point. Broadband providers undergo a pre-testing period prior to the actual testing start date in order to familiarize themselves with the process. During actual testing, providers whose broadband service fails to meet the minimum requirements will have universal service support withheld and be subject to additional reporting requirements.
In the Public Notice announcement, the Bureau has recommended that RDOF recipients review the FCC’s rules, the FCC’s Performance Measures Order, and the FCC’s Performance Measures Reconsideration Order. Additionally, USAC has published available resources online to assist broadband providers in preparing, timely submitting, and properly filing test results and certifications.
T-Mobile Fake Ringtone Class Action Lawsuit: Court Dismisses Civil Conspiracy Claim & Punitive Damages Claim
June 1, 2023 – The U.S. District Court for the Northern District Of Illinois, Eastern Division, has dismissed Craigville Telephone’s and Consolidated Telephone’s civil conspiracy count and claim for punitive damages against T-Mobile USA, Inc. T-Mobile filed a motion requesting the claims be dismissed following the Court’s February 2023 Order granting Inteliquent, Inc.’s motion for judgment on the pleadings and dismissing the civil conspiracy count pending against Inteliquent. The Court granted T-Mobile’s motion and dismissed the civil conspiracy and punitive damages claims for the same reasons outlined in the February 2023 Inteliquent Order.
In November 2019, Craigville Telephone Co. and Consolidated Telephone Co., two rural communications providers, filed a class action lawsuit against T-Mobile USA, Inc., and Inteliquent, Inc., for damages stemming from T-Mobile’s violation of the FCC’s rural call completion rules. They claimed T-Mobile “engaged in a scheme to perpetuate call connection issues for calls originating from cell phones and terminating to landline telephones located in certain rural areas, which they covered up by inserting false ring tones on the caller’s end.” The Court’s February 2023 Order dismissed the last remaining claim against Inteliquent, leaving T-Mobile as the only defendant.
FCC Vacates Treble Damages Forfeiture Methodology For Violations Of Payment Requirements
June 1, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued a Memorandum Opinion and Order that vacates the treble damages methodology used to determine forfeitures for violations of FCC’s rules establishing payment requirements for the Universal Service Fund (USF), Telecommunications Relay Service (TRS) Fund, Local Number Portability (LNP), North American Numbering Plan (NANP), and federal regulatory fees. The FCC’s order officially vacates the 2015 Forfeiture Policy Statement, and will enable the FCC to exercise discretion when issuing forfeiture penalties for USF, TRS, LNP, NANP, and regulatory fee payment violations by addressing the individualized circumstances of each future adjudication. Ultimately, the move will allow the FCC to apply factors in Section 503(b)(2)(E) of the Communications Act, the FCC’s 1997 Forfeiture Guidelines Order, and Section 1.80 of the FCC’s rules, and conclude that individual circumstances warrant forfeitures that are higher than forfeitures calculated using the treble damages methodology.
May 2023
FCC Releases Version 2 Of National Broadband Map
May 30, 2023 – FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has authored a blog post announcing the release of an updated version of the FCC’s national broadband map. Version 2 of the map, which shows where broadband service is available as of the end of 2022, reflects changes that were made after the FCC adjudicated challenges from consumers, states, localities, Tribes and other stakeholders. Chairwoman Rosenworcel’s announcement includes the following key takeaways for Version 2 of the national broadband map:
More than 8.3 million U.S. homes and businesses lack access to high-speed broadband. If we want everyone, everywhere to have access to high-speed internet service, we will need to deploy broadband service to 8.3 million new locations. On net, the improvements to the map since November helped to identify nearly 330,000 more unserved locations.
Our challenge processes are powerful tools to improve accuracy. Stakeholders have stepped up to provide lots of information and challenges to our data. Our mapping team has reviewed challenges to availability data for more than 4 million locations. Over 75% of those challenges have already been resolved and the majority have led to updates in the data on the map showing where broadband is available. At the same time, the new map also reflects a net increase of more than one million new serviceable locations, as compared to the November 2022 pre-production draft.
Collaboration is key. Our mapping team met individually with representatives from every state at least once, and, in total, hosted over 200 individual sessions with state, local, and Tribal governments. These discussions were crucial to helping all stakeholders understand what we were showing on the map, how to submit—and respond to—challenges, and how this first-of-its-kind map could be improved. We also responded to more than 7,600 technical assistance requests from internet providers and challengers.
We’re using all the data quality tools at our disposal. Beyond the challenge process, the FCC has built automated checks into the new system to validate submissions from internet providers. FCC staff have also begun to use the verification and enforcement tools available to ensure accurate availability filings, initiating over 800 verification inquiries thus far. More stringent verification resulted in updates to over 600 submissions from providers and a clearer picture of broadband availability in every state and territory.
Our maps are continuously becoming more accurate, and will only continue to improve. The Commission has a duty under the law to develop these maps in an iterative fashion. We are going to continue to release a major update twice a year, which overlays availability data from providers onto the tens of millions of serviceable locations. In addition to those major bi-annual updates, we have been making minor updates to the availability data in the map regularly for most of 2023. These incremental updates reflect both challenge outcomes and any corrections providers make to their filings. We will continue to accept challenges every day, every week and every month, and those challenges will continue to improve the map.
NTIA Announces Version 2 Of The FCC’s National Broadband Map
May 31, 2023 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has announced that the FCC has released Version 2 of the National Broadband Map. The map shows location-level information about the availability of broadband service across the U.S. It is publicly available online at https://broadbandmap.fcc.gov/home. The FCC’s National Broadband Map will play an important role in NTIA’s Broadband, Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program. NTIA has provided three key takeaways from the latest data in the national broadband map:
Through challenges and additional work that the FCC has been doing to improve the map’s underlying Fabric—a dataset of all locations where Internet service can be installed—the FCC added nearly three million Broadband Serviceable Locations (BSLs) while removing nearly two million for reasons ranging from updated data to the use of sophisticated tools to identify and remove structures like garages and sheds.
The FCC’s challenge process resolved more than 3.7 million challenges to the availability data – a dataset that shows whether Internet service is, in fact, available at each location, resulting in a more accurate picture of the high-speed Internet service currently available across the nation.
The overall national story remains consistent: From version 1 to version 2 of the FCC’s map, the percentage of unserved locations nationwide increased by 0.2 percentage points.
Amazon Settles FTC Charges Alleging Amazon’s Alexa Violated The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act; Will Pay $25 Million Fine
May 31, 2023 – Amazon has agreed to settle charges brought by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) alleging Amazon’s Alexa collects voice data from children under the age of 13 in violation of the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) Rule. Under COPPA, an operator of a commercial website or online service directed to children under 13 years of age is required to notify parents about the information collected from children, obtain parents’ consent for the collection of that data, and allow them to delete that information at any time. The complaint, filed by the U.S. Department of Justice against Amazon on behalf of the FTC, alleged Amazon “deceived parents and users of the Alexa voice assistant service about its data deletion practices.” Pursuant to a Stipulated Order For Permanent Injunction, Civil Penalty Judgment, And Other Relief, Amazon “will be required to delete inactive child accounts and certain voice recordings and geolocation information and will be prohibited from using such data to train its algorithms.” The Stipulated Order also requires Amazon to pay a $25 million civil penalty.
FCC Renews FirstNet’s Spectrum License
May 26, 2023 – The FCC’s Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau has granted the First Responder Network Authority’s (FirstNet) application to renew its spectrum license (call sign WQQE234), “subject to certain reporting conditions.” The Bureau’s decision “renews FirstNet’s license for ten years from the expiration of [its] initial license, or for the remaining period of its authorization from Congress, whichever is sooner.” FirstNet’s nationwide license is in the 700 MHz band – 758-769/788-799 MHz – and is used in the deployment of the nationwide public safety broadband network. FirstNet is an independent authority within the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration.
FCC Waives R-o-R Budget Control Mechanism for July 2023 - June 2024 Tariff Year
May 23, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC or Commission), on its own motion, has waived the application of the budget control mechanism for rate-of-return carriers for the July 2023 to June 2024 tariff year. The waiver is applicable to rate-of-return carriers that receive high-cost universal service fund support from legacy mechanisms – high cost loop support (HCLS) and Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS).
The budget control mechanism was created by the FCC in the Rate-of-Return Reform Order as a method for enforcing the rate-of-return carrier legacy budget in the event total support is forecasted to exceed $2 billion in a given year. When applied, carriers receive pro rata support reductions, but no carrier’s support can be reduced below a certain minimum threshold level.
For July 1, 2023 to June 30, 2024, projected total support for legacy rate-of-return carriers will exceed the budget by approximately 18.35%. This results in a projected budget control of 0.8165. The FCC’s order waives this budget constraint and reduces it to 0% for the 2023-2024 tariff year. The Commission determined “a waiver is in the public interest given the substantial reduction in support that would result from imposition of the budget constraint, as well as the unique and continued cash flow and other economic challenges carriers face as they emerge from the pandemic.”
Etheric Communications Defaults On RDOF Winning Bids In California
May 23, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced that Etheric Communications LLC has defaulted on its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) winning bids in California, and has been referred to the FCC’s Enforcement Bureau. For defaulting, Etheric is subject to a base forfeiture per violation of $3,000, subject to a 15% limitation of its total assigned support for the bid for the support term, and dependent on an upward or downward adjustment based on FCC forfeiture guidelines. In a related Order on Reconsideration, the Bureau denied Etheric Communications petition for reconsideration of a Bureau decision to dismiss Etheric’s request for waiver of the RDOF eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) designation documentation deadline.
FCC Denies Wavelength LLC’s RDOF ETC Waiver Petition, Resulting In Default On California RDOF Bids
May 23, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has dismissed as moot, and in the alternative, denied, Wavelength LLC’s petition for waiver of the June 7, 2021, Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) designation documentation deadline for winning RDOF bids in California. In February 2023, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) issued a decision denying Wavelength’s request for ETC designation, rendering the waiver petition moot. The Bureau denied the waiver petition on the merits after concluding that it does not serve the public interest to delay action “while Wavelength pursues what could be a lengthy process seeking recourse” before the CPUC. Wavelength won RDOF support to deploy gigabit, low latency service to more than 68,000 locations in California and Arizona. The Bureau will release a future public notice announcing Wavelength’s default on its California RDOF bids.
President Biden Nominates Anna Gomez To Federal Communications Commission; Renominates Starks & Carr
May 22, 2023 – President Biden has announced he will nominate Anna M. Gomez to be a Commissioner of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Upon confirmation by the Senate, Ms. Gomez will fill the remaining open seat on the FCC. Additionally, President Biden has renominated current FCC Commissioners Geoffrey Starks and Brendan Carr. In the announcement, the White House provided the following biography for Ms. Gomez:
Anna M. Gomez is a telecommunications attorney with extensive experience in domestic and international communications law and policy. Gomez serves as a Senior Advisor for International Information and Communications Policy in the Bureau of Cyberspace and Digital Policy. Gomez served as the National Telecommunications and Information Administration Deputy Administrator from 2009 to 2013. She also served for 12 years in various positions at the Federal Communications Commission, including as Deputy Chief of the International Bureau and as Senior Legal Advisor to then-Chairman William E. Kennard. Gomez also served briefly as Counsel on the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation Subcommittee on Communication and as Deputy Chief of Staff of the National Economic Council during the Clinton Administration. Prior to joining the State Department in 2023, Gomez was a partner in Wiley LLP’s telecommunications media and technology group. Gomez also was Vice president for Federal and State Government Affairs at Sprint Nextel and an Associate at Arnold and Porter.
FCC Instructs USAC To Fully Fund E-Rate Category One & Two Service Requests For Funding Year 2023
May 19, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released a Public Notice which directs the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) to fully fund E-Rate eligible category one and category two requests submitted for funding year 2023. The Bureau made the announcement after determining there is sufficient funding available to fully meet USAC’s estimated demand for category one and category two E-Rate service requests. USAC estimates the following funding demands for the E-Rate program:
Total estimated E-Rate demand for funding year 2023 will be $2.944 billion
Total estimated E-Rate demand for category one services is $1.658 billion
Total estimated E-Rate demand for category two services is $1.286 billion
In March 2023, the Bureau announced that for funding year 2023, the E-Rate program funding cap is $4.768 billion. Subsequently, USAC projected that $440.22 million in unused funds from prior funding years is available for use in E-Rate funding year 2023. Accordingly, based on the E-Rate funding cap, carry-over funding, and demand projections, the Bureau has determined there is sufficient funding to fully fund all category one and two requests for 2023. The Bureau has directed USAC to use $250 million in E-Rate carry-over funds this year, and reserve the remaining amount for future use.
FCC Considering New Rules To Expand Next Generation 911 Networks
May 18, 2023 – During its June 8, 2023 open meeting, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) will vote to release a Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) concerning new rules designed to advance the nationwide transition to Next Generation 911 communications networks. The transition to Next Generation 911 networks involves the replacement of legacy circuit-switched 911 networks with Internet Protocol (IP)-based networks and applications that will support new 911 capabilities, including text, video, and data, as well as improved interoperability and system resilience. The FCC has released a public draft of the NPRM, which includes the following summary of the significant proposals:
The NPRM proposes to require that, upon valid request of 911 authorities who have established the capability to accept NG911-compatible, IP-based communications:
Wireline, interconnected VoIP, and Internet-based TRS providers must complete all translation and routing to deliver 911 calls, including associated location information, in IP-based format, and
Wireline, CMRS, interconnected VoIP, and Internet-based TRS providers must transmit all 911 calls to destination point(s) designated by a 911 authority.
The NPRM proposes to require that, in the absence of agreement by states or localities on alternative cost recovery mechanisms, wireline, CMRS, interconnected VoIP, and Internet-based TRS providers must cover the costs of transmitting 911 calls in IP-based format to the point(s) designated by a 911 authority.
FCC Tentative Agenda For June 8th Open Meeting
May 18, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s open meeting scheduled for Thursday, June 8, 2023:
Advancing the Transition to Next Generation 911 – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would expedite the transition to NG911 and help ensure that the nation’s 911 system functions effectively and with the most advanced capabilities available. (PS Docket No. 21-479)
Strengthening Consumer Consent for Robocalls and Robotexts – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking proposing rules to strengthen the ability of consumers to decide which robocalls and robotexts they wish to receive by exercising their right to grant and revoke consent to callers. The item also proposes to codify the Commission’s past guidance on prior express consent to make these requirements more apparent to callers and consumers. (CG Docket No. 02-278)
Shared Use of the 42-42.5 GHz Band – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would explore how spectrum in the 42 GHz band (42-42.5 GHz) might be made available through one of several innovative, non-exclusive spectrum access models which have the potential to provide solutions in this evolving space. (WT Docket No. 23-158; GN Docket No. 14-177)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
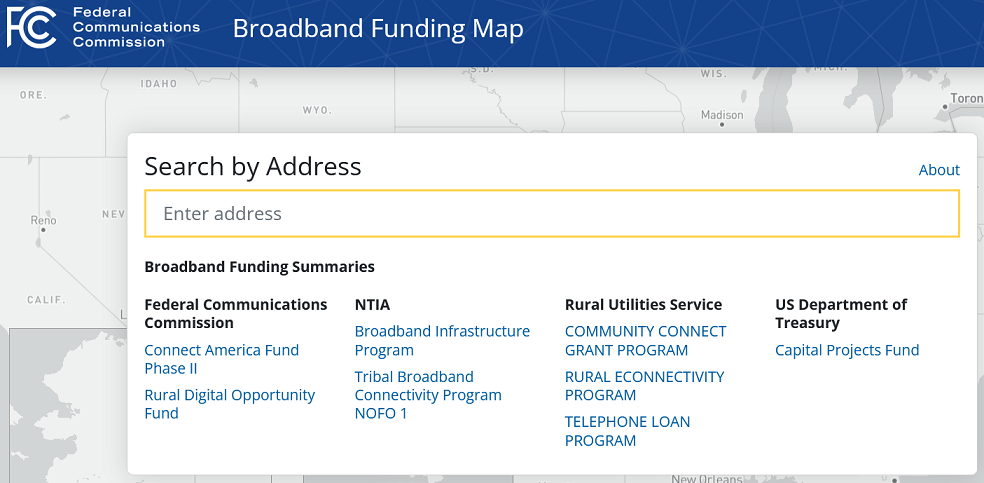
New FCC Broadband Funding Map Shows Broadband Infrastructure Deployment Projects Funded By Federal Government
May 15, 2023 – The FCC’s Office of Economics and Analytics and Wireline Competition Bureau have released a new Broadband Funding Map which details broadband infrastructure deployment projects funded by the Federal Government. The map and its underlying data are available online at https://fundingmap.fcc.gov/. It contains data from the FCC, the Department of Agriculture (USDA), the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), and the Department of Treasury.
New FCC Rule Requires Electronic Filing For CALEA Plans
May 15, 2023 – The FCC’s Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau has issued an order which revises the FCC’s rules to require electronic filing of new and updated System Security and Integrity Policies and Procedures (SSI Plans) by covered entities under the Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act (CALEA). The new rule is effective on June 29, 2023. New and updated SSI Plans must be filed using the CALEA Electronic Filing System (CEFS). A CEFS Manual containing guidance on electronic filing is available online. Additional information about the CEFS and electronic filing are available on the FCC’s CALEA website.
FCC Issues Final Agenda For May 18, 2023 Open Meeting
May 11, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued the final agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, May 18, 2023. The meeting will begin at 10:30 am, and will be streamed live online at: www.fcc.gov/live.
Amendment of Section 15.255 of the Commission’s Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would provide new opportunities for unlicensed field disturbance sensor devices, such as radars, to operate in the 57-71 GHz band (60 GHz band) and foster innovative products and services while ensuring coexistence with other unlicensed technologies and Federal incumbents in the band. (ET Docket No. 21-264)
Expanding Flexible Use of the 12.2-12.7 GHz Band; Expanding Use of the 12.7-13.25 GHz Band for Mobile Broadband or Other Expanded Use – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would ensure that current and future satellite services are preserved and protected in the 12.2-12.7 GHz (12.2 GHz) band by declining to authorize mobile operations in the band, while further investigating the potential to expand fixed use or permit unlicensed use. The Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Order would continue development of a pipeline of mid-band spectrum by proposing to authorize the 12.7-13.25 GHz (12.7 GHz band) for mobile broadband and other expanded uses. (WT Docket No. 20-443, GN Docket No. 22-352)
Expanding Call Blocking Requirements – The Commission will consider an Order, Further Notice, and Notice of Inquiry that would expand our call blocking requirements to ensure even greater protections for consumers. The item would enlist service providers in the fight against unwanted robocalls by extending our 24-hour traceback requirement to cover all voice service providers in the call path, enhancing existing requirements to effectively mitigate illegal traffic upon Commission notification and expanding our know-your-upstream-provider requirements to all voice service providers. The item would also seek comment on several other options to further enhance consumer protections, including a proposal to require terminating providers to offer analytics-based call blocking. (CG Docket No. 17-59, WC Docket No. 17-97)
Media: Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
FCC Considers Modifying Calculation Of Broadband Reasonable Comparability Benchmarks & Urban Rate Survey
May 8, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on modifying the calculation of the FCC’s broadband reasonable comparability benchmarks for the Urban Rate Survey to account for a wider spectrum of service speeds and make other improvements. Comments are due on or before June 8, 2023. Reply comments are due June 23, 2023.
Eligible telecommunications carriers (ETCs) that receive high-cost federal universal service fund are required to offer broadband services (in addition to voice telephony service) throughout their designated service areas at rates that are reasonably comparable to rates charged for similar services in urban areas. The ETCs that are subject to the reasonable comparability benchmarks are rate-of-return ILECs, incumbent price-cap carriers receiving Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II support, Rural Broadband Experiment providers, CAF Phase II Auction winners, and Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Auction winners. To set the benchmarks, Wireline Competition Bureau staff annually collects data on fixed voice and broadband service rates offered to consumers in urban areas by a random sample of service providers. Using this data, the Bureau calculates a national range of rates for broadband service that is then used to ensure that USF recipients offer voice and broadband services at reasonably comparable rates to those in urban areas. Specifically, the Bureau uses a weighted linear regression analysis to estimate the mean rate for a specific set of service characteristics and then adds two standard deviations to the mean to determine the benchmark.
In the Public Notice, the Bureau requests comment on whether it should change how it calculates the broadband benchmarks using data collected through the Urban Rate Survey. Comment is invited on whether limiting itself to the use of weighted least squares regression may be hindering the Bureau’s ability to optimally set benchmarks. The Bureau also seeks comment on the use of additional non-linear statistical techniques for this analysis, and whether other methodologies could provide more useful benchmarks.
The Bureau originally adopted the weighted linear regression methodology for speeds ranging from 4 Mbps to 40 Mbps. Currently, it must create benchmarks for service speeds ranging from 4 Mbps to gigabit speeds. Comment is requested on the range of speeds for which the Bureau should set broadband benchmarks. Relatedly, the Bureau seeks comment on whether it should have the flexibility to exclude variables such as upload speed and capacity allowances when their inclusion has only a small or insignificant effect on the benchmarks. Finally, the Bureau requests public comment on issues related to requiring survey respondents to report only non-discounted rates and a new definition of an urban tract for the purpose of the Urban Rate Survey.
NTIA Issues Reports On Federal Investments In High-Speed Broadband
May 8, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released two reports highlighting federal investments in high-speed Internet programs: The 2022 Office of Internet Connectivity and Growth Annual Report and The 2022 Federal Broadband Funding Report. The two reports highlight how federal government agencies are coordinating on implementation of various high-speed Internet programs, and include the following: a description of the activities of NTIA’s Office of Internet Connectivity and Growth; a description of how many households were provided broadband by universal service program or federal broadband support; and, a framework to guide future estimates of the economic impact of broadband deployment efforts. Additionally, NTIA has created a dashboard to accompany the Federal Broadband Funding Report, which includes spending data from 13 agencies across 98 federal high-speed Internet programs; reports Tribal broadband funding for the first time; includes data by federal program at the state level; and breaks out funding by appropriated (budgeted by Congress), obligated (awarded for spending by the program) and outlayed (spent by the program).
Senate Broadband Subcommittee Announces May 11 Hearing On The State of Universal Service
May 5, 2023 – The Senate Commerce Committee’s Subcommittee on Communications, Media and Broadband has announced it will convene a hearing titled “The State of Universal Service” on Thursday, May 11, 2023, at 10:00 a.m. ET. The announcement explains that the hearing “will examine the need for connectivity in rural and insular areas, for health professionals in providing telemedicine and telehealth, for low-income households that otherwise could not afford internet access and for access to broadband in our nation’s schools and libraries.” Additionally, the hearing will “explore potential reforms” to the USF. Witnesses have not been announced. The Subcommittee’s USF hearing will be streamed live online at the Commerce Committee’s website.
Another Loss For Consumers’ Research – Sixth Circuit Says Universal Service Fund Is Constitutional
May 4, 2023 – The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit has denied Consumers’ Research’s Petition For Review challenging the constitutionality of the Universal Service Fund (USF). Consumers’ Research is now 0 for 2 on its USF legal challenges. In March 2023, a three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit rejected a nearly identical Petition For Review. There are Petitions awaiting a decision at the Eleventh Circuit and the D.C. Circuit Courts of Appeal.
Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, and a handful of individuals filed the Petition in September 2021, challenging the fourth quarter 2021 USF contribution factor by claiming that the USF “exceeds the FCC’s statutory authority and violates the Constitution and other federal laws.” Specifically, the group argued that Section 254 of the Communications Act, which created the USF and empowers the FCC to administer it, violates the nondelegation doctrine. They also argued that the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) role in the USF system violates the private-nondelegation doctrine.
Under the nondelegation doctrine, when Congress delegates power to executive agencies to implement laws, it must provide an intelligible principle which adequately guides, limits, and restrains the agency. The private nondelegation doctrine prohibits agencies from delegating unrestrained power to private entities.
The three-judge panel of the Sixth Circuit disagreed with Consumers’ Research on all fronts, and denied the Petition. Among other things, the Court determined that the USF principles in Section 254(b) “provide comprehensive and substantial guidance and limitations on how to implement Congress’s universal-service policy, and in turn, how the FCC funds the USF.” It said the “[Consumers’ Research] argument that these principles are too abstract, ‘lofty,’ and ‘aspirational only’ is unpersuasive.”
With respect to the private nondelegation argument, the Sixth Circuit found “that there is no private-nondelegation doctrine violation because USAC is subordinate to the FCC and performs ministerial and fact-gathering functions.” With respect to USAC’s role, the Court said “[a] private entity may assist an agency with this sort of ministerial support.” The Court concluded that “[b]ecause USAC is appropriately subordinated to the FCC and serves a fact-gathering and ministerial function without exercising decision-making power, there is no private-nondelegation doctrine violation.”
House Energy and Commerce Committee Announces Hearing On Use Of Federal Funds For Broadband Deployment
May 3, 2023 – The U.S. House Of Representative’s Energy and Commerce Committee’s Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations has announced it will hold a hearing titled “Closing the Digital Divide: Overseeing Federal Funds for Broadband Deployment” on Wednesday, May 10 at 10:30 am. Witnesses have not been announced. The open hearing will be live streamed online at https://energycommerce.house.gov/.
Consumers’ Research Objects To USAC’s Third Quarter 2023 USF Funding Requirements
May 2, 2023 – Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, and 12 individuals have submitted comments and objections to the FCC in response to the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections for Third Quarter 2023.
USAC’s filing details the universal service fund’s (USF) total projected funding requirements for 3Q 2023, such as costs attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each support mechanism. USAC’s fund size projections will be used by the FCC to calculate the 3Q 2023 USF contribution factor.
The Consumers’ Research has previously challenged many of the FCC’s past actions setting the quarterly USF contribution factors, and its recent objection to the USAC filing mirrors those filings. In general, Consumers’ Research argues the USF “is an unconstitutional tax raised and spent by an unaccountable federal agency—which in turn has delegated almost all authority over this revenue-raising scheme to a private company registered in Delaware.” It wants the FCC to set the proposed 3Q USF contribution factor at zero.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Abu Dhabi sovereign Wealth Fund Invests $500 Million In Brightspeed
May 2, 2023 – The Abu Dhabi sovereign investor, Mubadala Investment Company, has announced it is investing US $500 million in Brightspeed. Mubadala Investment Company is now a minority owner. Brightspeed is majority owned by Apollo Global Management. Brightspeed is the fifth-largest incumbent local exchange carrier in the U.S., serving rural and suburban communities in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and the U.S. Midwest and Southeast. In 2022, Brightspeed acquired Lumen Technologies’ ILEC businesses in 20 states.
USAC Submits Estimated Third Quarter 2023 Universal Service Funding Requirements
May 2, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed the Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections for the third quarter of 2023. The filing details the universal service fund’s (USF) total projected funding requirements for 3Q 2023, which includes costs that can be directly attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each mechanism. All of USAC’s filings to the FCC are available here. USAC’s data shows the following total projected 3Q 2023 funding requirements for each USF support mechanism:
High Cost Support Mechanism – $1.044 billion (the 2Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $972.91 million; the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $1.152 billion). USAC initially calculated the high cost funding requirement as $1.049 billion, but the amount was decreased by prior period adjustments of $23.40 million, and increased by administrative costs of $17.95 million.
Low Income Support Mechanism – $206.97 million (the 2Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $202.05 million; the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $201.21 million). USAC initially estimated funding requirements of $261.56 million for Lifeline and $0.06 million for Link-Up, resulting in a total of $261.62 million. This amount was decreased by prior period adjustment of $78.30 million, and increased by $23.65 million for administrative costs.
Rural Health Care Support Mechanism – $170.57 million (the 2Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $159.36 million; the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $70.79 million).
Connected Care Pilot Program – $8.38 million (the 2Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $8.43 million; the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $8.5 million).
E-Rate Schools and Libraries Support Mechanism – $586.77 million (the 2Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $609.15 million; the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $697.13 million).
USAC projects a consolidated budget of $68.04 million for 3Q 2023. This breaks out to $35.13 million in direct costs for all four support mechanisms, and $32.91 million in joint and common costs which include costs associated with billing, collection, and disbursement of universal service funds. (USAC projected a consolidated budget of $71.91 million for 2Q 2023, and $67.28 million for 1Q 2023.) The FCC will use the of the quarterly funding requirements for the four USF Support Mechanisms, the projected administrative expenses, and the USF contribution base amount to calculate the quarterly USF contribution factor. Copies of USAC’s historical USF filings are available on its website.
Kansas Announces $30 Million Lasting Infrastructure And Network Connectivity (LINC) Grant Program
May 2, 2023 – Kansas Governor Laura Kelly has announced the creation of the Lasting Infrastructure and Network Connectivity (LINC) program which will provide $30 million in grants to improve broadband infrastructure, middle mile connectivity, and Internet Exchange Point capabilities within Kansas. The LINC program application window opens on May 5, 2023, and closes on June 19, 2023. Award announcements are initially targeted for September 2023.
The Kansas Office of Broadband Development will implement the LINC program by providing grants in two categories: (1) broadband infrastructure, and (2) internet exchange point and middle mile. The broadband infrastructure category will provide funding for deploying broadband to end user locations with a minimum of 100/20 Mbps speeds. The maximum grant will be $5 million. The second category will fund middle mile infrastructure projects that reduce the overall costs of delivering broadband to end users, and internet exchange point facility projects that improve the overall internet access service quality for all Kansans. The maximum grant will be $5 - $10 million. Internet service providers, political subdivisions, tribal governments, cooperatives, and non-profit organizations are eligible to apply for LINC program grants. Applications previously submitted to Kansas’ Capital Projects Fund broadband grant program can be considered for LINC awards. Additional information is available on the LINC program website.
FCC Issues $8.7 Million In Fines To Rural Digital Opportunity Fund Applicants That Defaulted On Their Bids
May 1, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice of Apparent Liability (NAL) covering 22 Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I Auction applicants that apparently defaulted on their bids for support between May 3, 2022, and December 16, 2022. Each of the 22 RDOF applicants identified in the NAL apparently willfully violated Section 1.21004(a) of the FCC’s rules by defaulting on its respective bid for support by withdrawing its application with respect to certain areas, or by its failure to meet deadlines and requirements to which it agreed when it participated in the RDOF auction. The 22 applicants’ defaults span 2,994 Census Block Groups. The NAL proposes forfeitures totaling $8,778,527.39.
Appendix A to the NAL explains the relevant, unique facts pertaining to each of the 22 RDOF applicants, and describes with each entity’s conduct in relation to the RDOF auction. Appendix B identifies the specific Census Block Groups in default that were subject to forfeiture and the attendant assigned USF support. Appendix C lists the mailing address for each of the 22 RDOF applicants.
NTIA Releases Guidance On BEAD Program Challenge Process
May 1, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released proposed guidance for the Broadband, Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program’s state challenge process. The BEAD Program will provide $42.45 billion in grants to expand high-speed internet access by funding planning, infrastructure deployment, and adoption programs in all 50 states, Washington D.C., and U.S. territories. States will use BEAD Program grant funding to prioritize the expansion of broadband internet access to unserved locations (no access to 25/3 Mbps broadband service) and underserved locations (no access to 100/20 Mbps broadband service). Pursuant to the challenge process, an entity may challenge a determination made by a State as to whether a particular location or community anchor institution is eligible for BEAD funding, including whether a particular location is unserved or underserved. The BEAD challenge process Policy Notice, containing additional guidance and the model challenge process are available online from NTIA. NTIA has requested public comments on the proposed challenge process guidance. Comments can be submitted via to BEAD@NTIA.gov no later than midnight EDT on May 5, 2023.
April 2023
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For May 18 Open Meeting
April 27, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, May 18, 2023:
Amendment of Section 15.255 of the Commission’s Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would provide new opportunities for unlicensed field disturbance sensor devices, such as radars, to operate in the 57-71 GHz band (60 GHz band) and foster innovative products and services while ensuring coexistence with other unlicensed technologies and Federal incumbents in the band. (ET Docket No. 21-264)
Expanding Flexible Use of the 12.2-12.7 GHz Band; Expanding Use of the 12.7-13.25 GHz Band for Mobile Broadband or Other Expanded Use – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would ensure that current and future satellite services are preserved and protected in the 12.2-12.7 GHz (12.2 GHz) band by declining to authorize mobile operations in the band, while further investigating the potential to expand fixed use or permit unlicensed use. The Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Order would continue development of a pipeline of mid-band spectrum by proposing to authorize the 12.7-13.25 GHz (12.7 GHz band) for mobile broadband and other expanded uses. (WT Docket No. 20-443, GN Docket No. 22-352)
Expanding Call Blocking Requirements – The Commission will consider an Order, Further Notice, and Notice of Inquiry that would expand our call blocking requirements to ensure even greater protections for consumers. The item would enlist service providers in the fight against unwanted robocalls by extending our 24-hour traceback requirement to cover all voice service providers in the call path, enhancing existing requirements to effectively mitigate illegal traffic upon Commission notification and expanding our know-your-upstream-provider requirements to all voice service providers. The item would also seek comment on several other options to further enhance consumer protections, including a proposal to require terminating providers to offer analytics-based call blocking. (CG Docket No. 17-59, WC Docket No. 17-97)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
FCC Announces Access To Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric For Conducting Non-Commercial Research On Broadband Availability
April 19, 2023 – The FCC’s Broadband Data Task Force and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced that parties may now obtain a license to use the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric for purposes of conducting non-commercial academic or public-policy research directly related to broadband availability. Serving as the underlying foundation of the FCC’s new broadband availability map, the Fabric is a common dataset of all locations in the U.S. where the FCC has determined fixed broadband internet access service can be installed. To access the Fabric, non-commercial academic or public-policy research entities must first obtain a username, password, and FRN (FCC Registration Number) via the Commission Registration System (CORES), then log into the BDC system using that username and password, and fill in the Entity Information page for the FRN. Non-commercial academic or public-policy research entities will then receive an email from CostQuest about how to execute a limited end-user license agreement for the Fabric. Depending on its organization type, an entity may need to provide a brief description of how the intended use of the Fabric data supports non-commercial academic or public-policy research and how the organization is involved in issues related to broadband availability. Additional information is available in the Public Notice.
FCC Seeks Comment On T-Mobile & SpaceX Joint Request To Establish Supplemental Coverage From Space For T-Mobile’s Terrestrial Network Using SpaceX Satellites
April 18, 2023 – The FCC’s Space Bureau and Wireless Telecommunications Bureau are seeking comment on filings by Space Explorations Holdings, LLC (SpaceX) and T-Mobile USA Inc. that jointly seek relief to establish supplemental coverage from space for T-Mobile’s terrestrial network using SpaceX satellites. Comments and petitions are due on or before May 18, 2023. Responses to comments and oppositions to petitions are due May 29, 2023. Replies to responses and oppositions are due June 2, 2023. SpaceX has requested modification of its license for its second generation (Gen2) Starlink constellation of low-Earth orbit, non-geostationary orbit satellites to add a direct-to-cellular communications capability on up to 7,500 Gen2 Starlink satellites. T-Mobile has filed a long-term spectrum manager lease notification informing the FCC of an arrangement whereby SpaceX satellites would provide supplemental coverage to T-Mobile’s terrestrial network on Personal Communications Service (PCS) G-block (1910-1915 MHz and 1990-1995 MHz) spectrum licensed to T-Mobile, if the FCC also takes favorable action regarding part 25 licensing.
USDA Announces Broadband Technical Assistance Program Funding To Promote High-Speed Internet In Rural Areas
April 17, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has announced the availability of $20 million in funding under the new Broadband Technical Assistance Program. Funding will support “technical assistance projects such as conducting feasibility studies, completing network designs and developing broadband financial assistance applications.” Program funding “is also available to help organizations access federal resources, and to conduct data collection and reporting.” USDA is encouraging Broadband Technical Assistance Program funding applicants to consider projects that will advance the following key priorities:
Assisting rural communities recover economically through more and better market opportunities and through improved infrastructure;
Ensuring all rural residents have equitable access to USDA Rural Development (RD) programs and benefits from RD funded projects; and
Reducing climate pollution and increasing resilience to the impacts of climate change through economic support to rural communities.
The Broadband Technical Assistance Program consists of the following funding categories:
Technical Assistance Providers: Applicants must propose to deliver broadband technical assistance that will benefit rural communities. Up to $7.5 million is available. The minimum award is $50,000. The maximum is $1 million.
Technical Assistance Recipients: Applicants must be the recipients of the broadband technical assistance. Up to $7.5 million is available. The minimum award is $50,000. The maximum is $250,000.
Projects Supporting Cooperatives: Applicants must propose projects that support the establishment or growth of broadband cooperatives that will benefit rural communities. Up to $5 million is available. The minimum award is $50,000. The maximum is $1 million.
Final Agenda For FCC’s April 20th Open Meeting
April 13, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its April 20, 2023 open meeting:
Promoting Efficient Use of Spectrum and Opportunities for New Services – The Commission will consider a Policy Statement intended to help guide Commission decision-making and stakeholder action to promote efficient co-existence between incumbent and new services. The Policy Statement promotes a balanced and comprehensive approach to spectrum management that holistically considers both transmitter and receiver components of wireless systems. (ET Docket No. 23-122)
Review of International Section 214 Authorizations to Assess Evolving Risks – The Commission will consider an Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would take another important step to protect the nation’s telecommunications infrastructure from threats in an evolving national security and law enforcement landscape by proposing comprehensive changes to the Commission’s rules that allow carriers to provide international telecommunications service pursuant to section 214 of the Communications Act of 1934, as amended (Act). (IB Docket No. 23-119)
Facilitating Satellite Broadband Competition – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would revise rules for spectrum sharing among new satellite broadband constellations. The rule revisions would clarify protection obligations between non-geostationary satellite orbit, fixed-satellite service systems to facilitate the deployment of these next generation systems, including new competitors. (IB Docket No. 21-456)
Updating the Frequency Allocation Table – The Commission will consider an Order to make updates to the International Allocation Table to reflect the International Telecommunication Union Radio Regulations (Edition of 2020) and make other non-substantive, editorial revisions. The Commission will also consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would seek comment on implementing certain of the remaining radiofrequency allocation decisions from the 2015 World Radiocommunication Conference. The NPRM would propose allocation changes and related updates to service rules. (OET Docket Nos. 23-121 and 23-120)
Improving Wireless Emergency Alerts – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would increase the accessibility, performance, and functionality of Wireless Emergency Alerts, including greater accessibility for people with disabilities and through multilingual alerting. (PS Docket Nos. 15-91, 15-94)
Updating the Intercarrier Compensation Regime to Eliminate Access Arbitrage – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order, which would modify its Access Stimulation Rules to close a perceived loophole exploited by opportunistic access-stimulating entities to continue to inflate access charges paid by interexchange carriers. The Order would make this inefficient practice less attractive to arbitrageurs and help prevent interexchange carriers’ end-user customers from bearing costs for services they may not even use. (WC Docket No. 18-155)
Removing Obsolete Analog-Era Provisions from Part 74 Rules – The Commission will consider an Order that would amend its Part 74 rules for low-power television and television translators to remove obsolete rules for analog TV operations. (MB Docket No. 03-185)
House Communications And Technology Subcommittee Announces April 19 Hearing On Broadband Issues
April 12, 2023 – The House Energy and Commerce Committee’s subcommittee on Communications and Technology has announced it will hold a hearing on Wednesday, April 19, 2023 titled “Breaking Barriers: Streamlining Permitting to Expedite Broadband Deployment.” The hearing will focus on bringing broadband to Americans across the U.S. The hearing will be open to the public and streamed live online. The subcommittee will also consider proposed legislation covering broadband issues.
Consumers’ Research Files Another Petition For Review Of The USF Contribution Factor
April 7, 2023 – Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 12 individuals have filed a petition for review with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit challenging the FCC’s proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the second quarter of 2023. The Consumers’ Research group filed comments and objections to the 2Q 2023 contribution factor prior to filing the legal challenge.
The petition for review filed at the D.C. Circuit is similar to others currently being considered by the Sixth Circuit (challenging the USF contribution factor for the 4Q 2021; Case Number 21-3886 (filed September 30, 2021)) and the Eleventh Circuit (challenging the USF contribution factor for the 4Q 2022; Case Number 22-13315 (filed October 3, 2022)). A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit recently issued a unanimous opinion denying Consumers’ Research’s non-delegation doctrine challenge to the USF and the way it is funded and administered by the FCC. The D.C. Circuit petition for review is captioned Consumers’ Research v. FCC., case number 23-1091 (filed Apr. 3, 2023).
FCC To Officially Establish New Space Bureau & Office Of International Affairs On April 11th
April 7, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced that the FCC will officially establish its new Space Bureau and Office of International Affairs on April 11th with an event at 3:00 pm ET at the FCC headquarters in Washington D.C. The new Space Bureau and Office of International Affairs are being created through a reorganization of the FCC’s International Bureau. The FCC has provided the following details on the mission and duties of the new Bureau and Office:
The Space Bureau (SB) will promote a competitive and innovative global communications marketplace by leading policy and licensing matters related to satellite and space-based communications and activities. Among its responsibilities, the Bureau will lead complex policy analysis and rulemakings; authorize satellite and earth station systems used for space-based services; streamline regulatory processes to provide maximum flexibility for operators to meet customer needs; and foster the efficient use of scarce spectrum and orbital resources. The Bureau will also serve as the FCC’s focal point for coordination with other U.S. government agencies on matters of space policy and governance, and collaborate with the Office of International Affairs for consultations with other countries, international and multilateral organizations, and foreign government officials that involve satellite and space policy matters.
The Office of International Affairs (OIA) will be responsible for the Commission’s engagement of foreign and international regulatory authorities, including multilateral and regional organizations. OIA will also facilitate through rulemaking and licensing the Commission’s development of policies regarding international telecommunications facilities and services as well as submarine cables, and advise the Commission on foreign ownership issues. In undertaking these functions, OIA will implement Commission policies to facilitate competition and foreign investment in U.S. international telecommunications markets while ensuring, in consultation with relevant federal partners, that national security, law enforcement, foreign policy, and trade policy concerns are addressed. OIA also will be responsible for intergovernmental leadership, negotiation, and international and inter-agency representational functions. OIA will oversee and coordinate the FCC’s global participation in international and multilateral conferences, regional organizations, cross-border negotiations and international standard setting efforts. OIA will also oversee bilateral meetings with other countries and foreign government officials.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Yellowhammer Networks Acquiring BroadLife Communications’ Alabama RDOF Support & Obligations
April 7, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking public comment on s Section 214 application filed by BroadLife Communications, Inc. and Yellowhammer Networks, LLC requesting consent for the transfer of certain assets from BroadLife to Yellowhammer. The transaction involves the assignment and Yellowhammer’s assumption of BroadLife’s Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) support obligations in certain Alabama census blocks and right to receive corresponding RDOF support. Additionally, the Bureau is seeking comment on Yellowhammer’s petition for designation as an eligible telecommunications carrier in census blocks in Alabama where BroadLife is authorized to receive RDOF support. Comments are due on or before April 21, 2023, and reply comments are due April 28, 2023. Comments on the transfer of control application must reference WC Docket No. 23-23. Pleadings for the ETC Petition must reference WC Docket Nos. 09-197 and 23-23.
BroadLife, a Delaware corporation, describes itself as a “developer and potential provider of broadband Internet access service over fiber-based networks.” BroadLife is an ETC that is authorized to receive $26,461,542 in RDOF support over ten years to provide service to 7,483 locations in Alabama. However, BroadLife does not currently offer any telecommunications services in the RDOF census blocks.
Yellowhammer is a Delaware limited liability company. Yellowhammer and its affiliates are infrastructure development companies that do not currently offer domestic telecommunications services. Yellowhammer is held by private equity funds Meridiam Infrastructure North America Fund III, LP and its parallel funds (collectively, Meridiam Fund III), and thus held indirectly through limited partnership and limited liability company interests by numerous investors. Meridiam Fund III and all its subsidiaries, including Yellowhammer, are managed by Meridiam Infrastructure North America Corporation, a Delaware corporation. Yellowhammer is ultimately controlled Thierry Déau, the President of Meridiam, a citizen of France.
Pursuant to an Assignment and Assumption Agreement, and subject to FCC consent of the Section 214 application and the Yellowhammer ETC Petition, BroadLife has agreed to assign to Yellowhammer:
RDOF support that BroadLife has received and will have received prior to the consummation of the transaction, net of state and federal income taxes owed on RDOF support BroadLife received in 2022;
BroadLife’s entitlement to receipts of all future RDOF support; and
All of BroadLife’s obligations associated with the receipt of RDOF support for the Alabama RDOF locations.
The proposed transaction would involve the exchange and assumption of Universal Service Fund high-cost mechanism obligations. As a result, the parties’ Section 214 application has been accepted for non-streamlined processing in order for the Wireline Bureau to sufficiently analyze whether the parties’ proposed transaction would serve the public interest. Additional information is available from the Bureau’s Public Notice and the parties’ Section 214 application and supplement.
FCC Announces Final List Of Entities Selected For The Affordable Connectivity Pilot Programs
April 6, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced the 34 entities selected for the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) Pilot Programs. There are two ACP Pilot Programs which are intended to provide outreach and application assistance to eligible households: (1) the Your Home, Your Internet Pilot Program, which is focused on ACP outreach and application support to recipients of federal housing assistance; and (2) the ACP Navigator Pilot Program, which provides selected entities access to the National Verifier to help low-income households complete and submit their ACP application. Appendix A to the Bureau’s Public Notice lists the entities selected for the Your Home, Your Internet Pilot Program. Appendix B to lists the entities selected for the ACP Navigator Pilot Program.
Alluvion Communications & Fond du Lac Withdraw From CAF II; FCC To Begin Clawing Back CAF II Support From The Two Defaulted Carriers
April 4, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released a Public Notice announcing that Gila Local Exchange Carrier, Inc. d/b/a Alluvion Communications, Inc. and Fond du Lac Communications, Inc. have notified the FCC of their decisions to withdraw from the Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II auction support program.
In 2020, Alluvion Communications was authorized to receive a total of $104,499.00 in CAF II support over a 10-year term to offer voice and broadband service to 29 locations in Arizona, while Fond du Lac was authorized to receive a total of $55,010.80 in CAF II support over a 10-year term to offer voice and broadband service to 13 locations in Minnesota.
Gila Local and Fond du Lac, in December 2022 and March 2023, respectively, notified the FCC that they are defaulting on their CAF II service obligation milestone, which resulted in the Bureau directing the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) to suspend the two providers’ future CAF II support payments. In the Public Notice, the Wireline Bureau has officially designated Alluvion Communications and Fond du Lac as having defaulted on their CAF Phase II auction service milestones. Accordingly, the Bureau also has directed USAC to recover CAF Phase II support from the two carriers pursuant to the FCC’s rules.
USDA Announces $40 Million In ReConnect Funding In New Mexico
April 3, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has announced $40 million in ReConnect Program funding has been awarded in rural areas of New Mexico. The $40 million in grants are being provided to three broadband projects under the fourth funding round of the ReConnect Program. USDA has provided the following details on the awards:
The Western New Mexico Telephone Company Inc. is receiving a $23.8 million grant to deploy a fiber-to-the-premises network to provide high-speed internet access to people in Catron County. The company will make high-speed internet affordable by participating in the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) Lifeline and Affordable Connectivity Programs (ACP). It also will provide a $34.99 monthly plan with 75 megabits per second upload and download speeds for subscribers within the project area who are enrolled in the ACP.
The E.N.M.R. Telephone Cooperative is receiving a $2.6 million grant to deploy a fiber-to-the-premises network to provide high-speed internet access to people in De Baca, Guadalupe, Harding, Quay, San Miguel, Socorro and Union counties. E.N.M.R. will make high-speed internet affordable by participating in the FCC’s Lifeline and Affordable Connectivity Programs. This project will serve socially vulnerable communities in De Baca, Guadalupe, San Miguel and Socorro counties.
The Peñasco Valley Telephone (PVT) Cooperative is receiving a $13.9 million grant to deploy a fiber-to-the-premises network to provide high-speed internet access to 550 people, 48 farms and 11 businesses in Chaves, Eddy, Otero and Lincoln counties. PVT will make high-speed internet affordable by participating in the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP). PVT also offers a program that can provide free internet for households participating in the ACP. This project will serve socially vulnerable communities in Chaves, Eddy and Otero counties.
FCC Announces Procedures For ILECs’ 2023 Annual Access Charge Tariff Filings
April 3, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has issued an Order establishing procedures for the 2023 filing of annual access charge tariffs and tariff review plans (TRPs) for incumbent local exchange carriers (LECs) subject to price cap regulation, as well as rate-of-return incumbent LECs subject to sections 61.38, 61.39, and 61.50 of the FCC’s rules. Specifically, the Bureau’s Order sets the following procedures and deadlines:
(1) Sets an effective date of July 1, 2023 for 2023 annual access charge tariff filings submitted on 15-days’ notice;
(2) Sets a modified effective date of July 3, 2023 for 2023 annual access charge tariff filings submitted on 7-days’ notice pursuant to a limited waiver;
(3) Establishes the dates for filing petitions to suspend or reject an incumbent LEC’s tariff filing and replies to such petitions;
(4) Addresses service of the petitions and replies; and
(5) Reminds carriers that the FCC adopted new tariff filing fees which took effect on March 2, 2023.
University of Kansas Institute for Policy & Social Research Releases Broadband In Kansas Report
April 1, 2023 – The University of Kansas Institute for Policy & Social Research (IPSR) has released a report titled “Broadband in Kansas: The Challenges of Digital Access and Affordability.” IPSR received funding under the CARES Act to study broadband access in the state of Kansas. To compile the report, IPSR “examined existing data, fielded [its] own survey of broadband speeds and access, conducted focus groups, and commissioned a chapter on the digital divide within the state of Kansas.” A few of the key findings in the report include the following:
The report indicates a rural-urban digital divide in terms of access, affordability, and satisfaction with broadband services. Kansans living outside of cities pay more for slower service than Kansans living in cities.
The data in the report indicate that up to 1,000,000 Kansans live in regions that lack access to high-speed broadband services, now considered to be 100 megabits per second (Mbps) download and 20 Mbps upload (100/20).
Close to half of survey respondents (46%) report dissatisfaction with broadband services.
March 2023
FCC Tentative Agenda For April 20 Open Meeting
March 30, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting, scheduled for Thursday, April 20, 2023:
Promoting Efficient Use of Spectrum and Opportunities for New Services – The Commission will consider a Policy Statement intended to help guide Commission decision-making and stakeholder action to promote efficient co-existence between incumbent and new services. The Policy Statement promotes a balanced and comprehensive approach to spectrum management that holistically considers both transmitter and receiver components of wireless systems. (ET Docket No. 23-122)
Review of International Section 214 Authorizations to Assess Evolving Risks – The Commission will consider an Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would take another important step to protect the nation’s telecommunications infrastructure from threats in an evolving national security and law enforcement landscape by proposing comprehensive changes to the Commission’s rules that allow carriers to provide international telecommunications service pursuant to section 214 of the Communications Act of 1934, as amended (Act). (IB Docket No. 23-119)
Facilitating Satellite Broadband Competition – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would revise rules for spectrum sharing among new satellite broadband constellations. The rule revisions would clarify protection obligations between non-geostationary satellite orbit, fixed-satellite service systems to facilitate the deployment of these next generation systems, including new competitors. (IB Docket No. 21-456)
Updating the Frequency Allocation Table – The Commission will consider an Order to make updates to the International Allocation Table to reflect the International Telecommunication Union Radio Regulations (Edition of 2020) and make other non-substantive, editorial revisions. The Commission will also consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would seek comment on implementing certain of the remaining radiofrequency allocation decisions from the 2015 World Radiocommunication Conference. The NPRM would propose allocation changes and related updates to service rules. (OET Docket Nos. 23-121 and 23-120)
Improving Wireless Emergency Alerts – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would increase the accessibility, performance, and functionality of Wireless Emergency Alerts, including greater accessibility for people with disabilities and through multilingual alerting. (PS Docket Nos. 15-91, 15-94)
Updating the Intercarrier Compensation Regime to Eliminate Access Arbitrage – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order, which would modify its Access Stimulation Rules to close a perceived loophole exploited by opportunistic access-stimulating entities to continue to inflate access charges paid by interexchange carriers. The Order would make this inefficient practice less attractive to arbitrageurs and help prevent interexchange carriers’ end-user customers from bearing costs for services they may not even use. (WC Docket No. 18-155)
Removing Obsolete Analog-Era Provisions from Part 74 Rules – The Commission will consider an Order that would amend its Part 74 rules for low-power television and television translators to remove obsolete rules for analog TV operations. (MB Docket No. 03-185)
Fifth Circuit Completely Rejects Consumers’ Research Non-Delegation Challenge To Universal Service Fund
March 24, 2023 – A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit has issued an unanimous opinion in Consumers’ Research v. FCC, denying a non-delegation doctrine challenge to the universal service fund (USF) and the way it is funded and administered.
In its petition for review, Consumers’ Research challenged: (1) the constitutionality of Congress’s delegation of administration of the USF to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC); and (2) the FCC’s subsequent reliance on the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC), a private entity, for ministerial support. Ultimately, the Fifth Circuit found “there are no nondelegation doctrine violations,” and denied the petition.
Consumers’ Research primarily argued that Section 254 of the Communications Act, the statute creating the US, violates the nondelegation doctrine because: (1) Congress failed to provide the FCC with an intelligible principle; and (2) to the extent Congress provided intelligible principles, they are merely aspirational and place no objective limits on the FCC in its administration of the USF. The Court found that Section 254(b) requires the FCC to base USF policies on various enumerated principles, which means the FCC does not operate the USF without guidance from Congress. After finding that Congress supplied the FCC with intelligible principles, the Court concluded these principles properly limit the FCC and are not merely aspirational.
Last, the Court addressed Consumers’ Research’s argument “that the FCC violated the private nondelegation doctrine when it redelegated its authority over the USF to USAC, a private entity.” The Court concluded “the FCC has not violated the private nondelegation doctrine because it wholly subordinates USAC” for the following reasons: First, federal statutory law expressly subordinates USAC to the FCC; Second, USAC does not enjoy sweeping rulemaking power – instead it makes a series of proposals to the FCC based off expert analysis, which are not binding on carriers until the FCC approves them; Third, the FCC permits telecommunications carriers to challenge USAC proposals directly to the agency and often grants relief to those challenges; and Fourth, the FCC dictates how USAC calculates the USF contribution factor and subsequently reviews the calculation method after USAC makes a proposal.
FCC Chairwoman Issues Update On FCC Broadband Map
March 23, 2023 – FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has authored a blog post which provides an update on the FCC’s broadband availability map. An initial version of the map was released online in November 2022. It shows where fixed and mobile internet services are available throughout the U.S., as of June 30, 2022. The FCC broadband availability map contains two datasets: locations and availability. The locations dataset consists of the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric, which is a common dataset of all locations in the U.S. where fixed broadband internet access service could be installed. The availability dataset is derived from information submitted by broadband service providers through the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection (BDC), and shows what broadband services, if any, are actually available at the Fabric locations.
According to Chairwoman Rosenworcel’s blog post, the version of the Fabric identified over 113 million locations where fixed broadband could be installed. The Fabric now shows “over 114 million broadband-serviceable locations, a net increase of 1.04 million.” This number was derived by adding 2.96 million new broadband-serviceable locations, and removing 1.92 million locations from the first version. Finally, Chairwoman Rosenworcel affirmed that the FCC will release a new broadband availability map that reflects the updated data in the Spring of 2023, as required by the Broadband DATA Act.
FAIR Contributions Act Reintroduced In Senate; Would Require FCC To Examine Collecting USF Contributions From Internet Edge Providers
March 16, 2023 – U.S. Senators Roger Wicker (R-MS), Ben Ray Luján (D-NM), Todd Young (R-IN) and Mark Kelly (D-AZ) have reintroduced the Funding Affordable Internet with Reliable (FAIR) Contributions Act. If passed, the FAIR Contributions Act would require “the FCC to issue a Notice of Inquiry seeking public comment on the feasibility of collecting USF contributions from internet edge providers, and issue a final report on the matter within 180 days.” Also, the proposed legislation would require the FCC to consider the following:
Possible sources of Big Tech revenue, such as digital advertising and user fees;
The fairness of the current system and a system under which contributions could be assessed on Big Tech firms;
The feasibility of assessing contributions on such a broad category of firms that do not currently register with the FCC;
The effects such a change would have on Tribal, low-income, and elderly consumers; and
The changes to current law necessary to implement this system.
USF Contribution Factor For Second Quarter Of 2023: 29 Percent
March 14, 2023 – The FCC’s Office of Managing Director (OMD) has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the second quarter of 2023 will be 29.0 percent. If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. For what it’s worth, the 29 percent 2Q 2023 USF contribution factor is a slight decrease from the 32.6 percent contribution factor used for the first quarter of 2023.
For the second quarter of 2023, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $8.761743 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected ($8.749750 billion was collected for 1Q 2023). USAC estimates that $1.951900 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms (revenue requirement) in the second quarter of 2023 (the 1Q 2023 demand was $2.130060 billion).
Total second quarter 2023 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, which breaks out among the USF support mechanisms as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $609.15 million (1Q 2023 was $697.13 million)
Rural Health Care: $159.36 million (1Q 2023 was $70.79 million)
High-Cost: $972.91 million (1Q 2023 was $1.15243 billion)
Lifeline: $202.05 million (1Q 2023 was $201.21 million)
Connected Care: $8.43 million (1Q 2023 was $8.50 million)
Final Agenda For FCC Open Meeting On March 16, 2023
March 9, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released a final agenda for its open meeting on Thursday, March 16, 2023:
Single Network Future: Supplemental Coverage from Space – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose a new regulatory framework for supplemental coverage from space. Through this proposed framework, satellite operators collaborating with terrestrial providers would be able to operate space stations on currently licensed, flexible-use spectrum to expand coverage to the terrestrial provider’s subscribers. (GN Docket No. 23-65, IB Docket 22-271)
Ensuring Just and Reasonable Rates for Incarcerated People – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Order, which would begin the Commission’s implementation of the Martha Wright-Reed Just and Reasonable Communications Act of 2022. The Notice of Proposed Rulemaking seeks comment on how the Commission should interpret that Act’s language to ensure just and reasonable rates and charges for incarcerated people’s audio and video communications services. The Order will delegate authority to the Wireline Competition Bureau and the Office of Economics and Analytics to update and restructure their most recent data collection as appropriate to fulfill the requirements of the new statute. (WC Docket Nos. 23-62, 12-375)
Enhancing Protections Against Illegal Robocalls – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would close a critical gap in the STIR/SHAKEN caller ID authentication regime, expand robocall mitigation requirements for all providers, adopt more robust enforcement tools, and seek comment on additional steps to further enhance the effectiveness of the STIR/SHAKEN framework. (WC Docket No. 17-97)
Protecting Consumers with Robotext Blocking – The Commission will consider a Report and Order which would require that providers block texts purporting to be from numbers on a reasonable Do-Not-Originate list; and make available a single point of contact for text message blocking complaints. The Commission will also consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would propose to require further blocking of illegal robotexts; expand Do-Not-Call protections to robotexts; and protect consumers from getting robotexts and robocalls from multiple, unexpected callers when they provide their consent on websites for comparison shopping. (CG Docket Nos. 21-402, 02-278)
Updating Equipment Testing Standards – The Commission will consider a Report and Order which would incorporate standards that are to be used in the testing of equipment to ensure compliance with FCC rules. Two are updates to existing standards and two are new standards that would allow in addition to standards referenced in our existing rules. (ET Docket No. 21-363)
Audio Description DMA Expansion – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would propose to expand support for individuals who are blind or visually impaired by expanding audio description requirements to additional market areas. The proposal would help ensure that a greater number of individuals who are blind or visually impaired can be connected, informed, and entertained by television programming. (MB Docket No. 11-43)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Biden Administration Releases Details On National Cybersecurity Strategy
March 2, 2023 – The White House has released its National Cybersecurity Strategy which is intended “to secure the full benefits of a safe and secure digital ecosystem for all Americans.” In the document, the Biden Administration calls for “fundamental shifts in how the United States allocates roles, responsibilities, and resources in cyberspace.” Among other things, the National Cybersecurity Strategy favors regulation over industry-adopted voluntary measures to combat cyber threats:
Regulation Instead Of Voluntary Measures: While voluntary approaches to critical infrastructure cybersecurity have produced meaningful improvements, the lack of mandatory requirements has resulted in inadequate and inconsistent outcomes. Today’s marketplace insufficiently rewards—and often disadvantages the owners and operators of critical infrastructure who invest in proactive measures to prevent or mitigate the effects of cyber incidents. Regulation can level the playing field, enabling healthy competition without sacrificing cybersecurity or operational resilience.
Forward-Looking Regulations: Regulations should be performance-based, leverage existing cybersecurity frameworks, voluntary consensus standards, and guidance—including the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)’s Cybersecurity Performance Goals and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity— and be agile enough to adapt as adversaries increase their capabilities and change their tactics. In setting cybersecurity regulations for critical infrastructure, regulators are encouraged to drive the adoption of secure-by-design principles, prioritize the availability of essential services, and ensure that systems are designed to fail safely and recover quickly. Regulations will define minimum expected cybersecurity practices or outcomes, but the Administration encourages and will support further efforts by entities to exceed these requirements.
Closing Cybersecurity Gaps In Cloud-Based Services: Cloud-based services enable better and more economical cybersecurity practices at scale, but they are also essential to operational resilience across many critical infrastructure sectors. The Administration will identify gaps in authorities to drive better cybersecurity practices in the cloud computing industry and for other essential third-party services, and work with industry, Congress, and regulators to close them.
USAC Files Data On 2nd Quarter 2023 USF Contribution Base: $8,761,742,607
March 2, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed projected universal service fund (USF) contribution base data which will be used to determine the USF contribution factor for the second quarter of calendar year 2023. USAC has determined that the total projected collected interstate and international end user revenue base to be used in determining the contribution factor for the Universal Service support mechanisms for the first quarter of 2023 is $8,761,742,607. This is an increase in the USF base from the first quarter of 2023 ($8,749,749,511). The contribution base data was calculated using projected revenue amounts for April through June 2023 reported by telecommunications service providers on their FCC Forms 499-Q which were due February 1, 2023. To provide a historical comparison, USAC’s total projected USF contribution base amounts for the past 13 quarters were as follows:
First Quarter 2023 – $8,749,749,511
Fourth Quarter 2022 – $8,624,083,282
Third Quarter 2022 – $8,285,056,307
Second Quarter 2022 – $8,751,403,396
First Quarter 2022 – $9,235,845,776
Fourth Quarter 2021 – $9,517,295,012
Third Quarter 2021 – $9,665,944,070
Second Quarter 2021 – $9,905,669,690
First Quarter 2021 – $10,068,712,553
Fourth Quarter 2020 – $10,428,377,862
Third Quarter 2020 – $10,219,123,520
Second Quarter 2020 – $10,865,131,593
First Quarter 2020 – $11,129,976,956
For the second quarter of 2023, USAC received projected revenue data from 3,276 USF contributors who filed the February 2023 Form 499-Q. USAC estimated revenue data for 181 non-de minimis service providers that had previously submitted Form 499-Q information to USAC, but failed to make the latest filing. After the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approves the total USF contribution base, the quarterly funding requirements for USF support mechanisms, and projected USF administrative costs, the FCC will establish a USF contribution factor for the second quarter of 2023. The new contribution factor will be announced by an FCC Public Notice. USAC will then bill USF contributors on a monthly basis for their individual obligations based on the approved contribution factor.
February 2023
Mergers & Acquisitions: Australian Infrastructure Fund Purchasing Rainier Connect
February 24, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking public comment on a Section 214 application filed by Mashell, Inc., Mashell Telecom, Inc. d/b/a Rainier Connect, and Alphaboost Purchaser, LLC, requesting consent to transfer control of Mashell Telecom to Alphaboost. Comments are due on or before March 10, 2023. Reply comments are due March 17, 2023.
Mashell, Inc. is a Washington corporation that acts as a holding company for Mashell Telecom and its affiliates, which collectively provide telecommunications services to approximately 25,000 residential customers and approximately 2,200 commercial customers in the state of Washington. Mashell Telecom is an eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) and incumbent local exchange carrier (LEC) that provides telecommunications services in Washington.
Alphaboost is a Delaware limited liability company that was recently created to carry out the transaction. Alphaboost is indirectly owned by Palisade Diversified Infrastructure Fund No. 3, an Australian infrastructure fund. When the deal closes, Mashell Telecom will be an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of Alphaboost. Ultimately, though, Mashell Telecom will be owned directly or indirectly by funds managed by Palisade Americas Management, LLC (PAM) and Palisade Investment Partners Limited (PIPL), an Australia specialist infrastructure investment manager.
The Section 214 application is not subject streamlined treatment, and has been referred to relevant Executive Branch agencies for their views on any national security, law enforcement, foreign policy, or trade policy concerns related to the foreign ownership of the applicants.
FCC Releases Tentative Agenda For March 2023 Open Meeting
February 23, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, March 16, 2023:
Single Network Future: Supplemental Coverage from Space – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose a new regulatory framework for supplemental coverage from space. Through this proposed framework, satellite operators collaborating with terrestrial providers would be able to operate space stations on currently licensed, flexible-use spectrum to expand coverage to the terrestrial provider’s subscribers. (GN Docket No. 23-65, IB Docket 22-271)
Ensuring Just and Reasonable Rates for Incarcerated People – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Order, which would begin the Commission’s implementation of the Martha Wright-Reed Just and Reasonable Communications Act of 2022. The Notice of Proposed Rulemaking seeks comment on how the Commission should interpret that Act’s language to ensure just and reasonable rates and charges for incarcerated people’s audio and video communications services. The Order will delegate authority to the Wireline Competition Bureau and the Office of Economics and Analytics to update and restructure their most recent data collection as appropriate to fulfill the requirements of the new statute. (WC Docket Nos. 23-62, 12-375)
Enhancing Protections Against Illegal Robocalls – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would close a critical gap in the STIR/SHAKEN caller ID authentication regime, expand robocall mitigation requirements for all providers, adopt more robust enforcement tools, and seek comment on additional steps to further enhance the effectiveness of the STIR/SHAKEN framework. (WC Docket No. 17-97)
Protecting Consumers with Robotext Blocking – The Commission will consider a Report and Order which would require that providers block texts purporting to be from numbers on a reasonable Do-Not-Originate list; and make available a single point of contact for text message blocking complaints. The Commission will also consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would propose to require further blocking of illegal robotexts; expand Do-Not-Call protections to robotexts; and protect consumers from getting robotexts and robocalls from multiple, unexpected callers when they provide their consent on websites for comparison shopping. (CG Docket Nos. 21-402, 02-278)
Updating Equipment Testing Standards – The Commission will consider a Report and Order which would incorporate standards that are to be used in the testing of equipment to ensure compliance with FCC rules. Two are updates to existing standards and two are new standards that would allow in addition to standards referenced in our existing rules. (ET Docket No. 21-363)
Audio Description DMA Expansion – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would propose to expand support for individuals who are blind or visually impaired by expanding audio description requirements to additional market areas. The proposal would help ensure that a greater number of individuals who are blind or visually impaired can be connected, informed, and entertained by television programming. (MB Docket No. 11-43)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Treasury Department Announces $355 Million In Capital Projects Fund Awards For Arizona, Tennessee, & Wyoming
February 21, 2023 – The U.S. Department of the Treasury has announced the award of approximately $355 million in Coronavirus Capital Projects Fund support to Arizona, Tennessee, and Wyoming to increase access to high-speed broadband internet service for over 189,000 homes and businesses. Below is a description of each award:
Arizona is approved to receive $99.4 million for high-speed internet infrastructure, which the state estimates will connect an estimated 127,807 households and businesses to high-speed internet access. Arizona’s award will fund the two high-speed internet infrastructure programs that aim to provide reliable internet access to areas of the state lacking adequate service. The Arizona Broadband Development Rural Infrastructure Grant program (ABDG-Rural) is a competitive grant program designed to expand high-speed broadband in the state’s thirteen rural counties. The Arizona Broadband Development Urban Infrastructure Grant program (ABDG-Urban) is a competitive grant program designed to improve and expand broadband infrastructure in the state’s two urban counties. Each of the internet service providers funded by the program will participate in the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program. The plan submitted to Treasury and being approved today represents 52% of the state’s total allocation under the Capital Project Funds program. Arizona submitted plans for the remainder of their Capital Project Funds and these applications are currently under review by Treasury.
Tennessee is approved to receive $185 million for high-speed internet infrastructure, which the state estimates will connect an estimated 50,000 households and businesses to high-speed internet access. Tennessee’s award will fund two high-speed internet infrastructure programs that aim to provide reliable internet access in areas of the state lacking adequate service. Tennessee’s Last Mile Connection program is a competitive grant program designed to provide service to remote areas of the state where internet infrastructure projects would not be feasible without assistance. Tennessee’s Middle Mile Buildout Program is a competitive grant program designed to deploy middle mile infrastructure in rural areas of the state to improve and expand last mile connections. Each of the internet service providers funded by the program will participate in the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program. The plan submitted to Treasury and being approved today represents 86% of the state’s total allocation under the Capital Project Fund program. Tennessee submitted plans for the remainder of their Capital Project Funds and these applications are currently under review by Treasury.
Wyoming is approved to receive $70.5 million for high-speed internet infrastructure, which the state estimates will connect an estimated 11,700 households and businesses to high-speed internet access. Wyoming’s award will fund the Connect Wyoming grant program, a competitive grant program designed to fund last mile broadband infrastructure projects in areas throughout the state that currently lack access to internet at speeds of 100/20 Mbps to facilitate access to work, education, and health monitoring. Each of the internet service providers funded by the program will participate in the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program. The plan submitted to Treasury and being approved today represents 64% of the state’s total allocation under the CPF program. Wyoming submitted plans for the remainder of their CPF funds and these applications are currently under review by Treasury.
FCC Reports To Congress On Impact Of Broadband Interagency Coordination Act
February 17, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has delivered a report on the impact of the Broadband Interagency Coordination Act to the Senate Commerce Committee and House Energy and Commerce Committee. The Broadband Interagency Coordination Act directed the FCC, National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to take a whole-of-government approach to U.S. broadband deployment. In the report, the Bureau explains that “the Interagency Agreement has significantly facilitated efficient use of federal funds for broadband deployment, and strengthened and improved coordination workstreams.” Among other things, the Bureau also recommended that the three agencies continue to coordinate and identify and implement standardization in broadband data.
FCC NPRM Proposes Ways To Increase Tribal E-Rate Participation
February 16, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has adopted a Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) which seeks comment on proposals to improve E-Rate program rules and encourage greater Tribal participation in the E-Rate program. The NPRM is the next step in the FCC’s efforts to address the underrepresentation of Tribal libraries in the E-Rate program. It follows the FCC’s January 2022 clarification that Tribal libraries are eligible to participate in E-Rate and the launch of the Tribal Library Pilot Program. In general, the NPRM seeks public comment on the following proposals to encourage greater E-Rate participation by eligible Tribal applicants:
Simplifying E-Rate forms and cost-allocation requirements;
Providing an additional competitive bidding exemption for low-cost services and equipment for Tribal applicants;
Increasing the maximum discount rate for Category Two services from 85% to 90% for Tribal applicants;
Allowing Tribal college libraries that serve a dual role by also serving as the Tribal community’s public library to be eligible for E-Rate support;
Providing an extended or separate application filing window for Tribal libraries to align with their Tribal procurement requirements and approval processes;
Increasing the Category Two $25,000 funding floor for Tribal applicants;
Adding a Tribal representative to the Universal Service Administrative Company’s Board of Directors, which administers the program for the FCC; and
Considering other potential reforms to encourage greater participation by Tribal or similarly situated small or rural applicants, particularly if they face barriers that impede equitable access to the E-Rate program.
Final Agenda For FCC February 16 Open Meeting
February 9, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued the final agenda for its open meeting scheduled for 10:30 am on Thursday, February 16, 2023:
Helping Domestic Violence Survivors Access Safe and Affordable Connectivity – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would begin the Commission’s required implementation of the Safe Connections Act of 2022. The proposal seeks to help survivors of domestic violence and similar crimes separate lines from shared mobile accounts that include their abusers, protect the privacy of calls made by survivors to domestic abuse hotlines, and support survivors who face financial hardship through the Commission’s affordability programs. (WC Docket Nos. 22-238, 11-42, 21-450)
E-Rate: Connecting Tribal Communities To Broadband – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would seek comments on improvements to the E-Rate program that would increase access for Tribal applicants generally as well as within the Tribal Libraries E-Rate Pilot Program. (CC Docket Nos. 02-6, 96-45, 97-21)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
Mergers & Acquisitions: GI Partners Acquires Rise Broadband
February 2, 2023 – Private equity firm GI Partners has acquired Rise Broadband, a fixed wireless broadband provider. The deal’s financial terms were not disclosed. Rise Broadband provides fixed wireless and fiber-based broadband services in 16 states. GI Partners is a private equity firm with $35 billion in assets under management
Annual Customer Proprietary Network Information (CPNI) Certifications Due March 1, 2023
February 1, 2023 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has issued an Enforcement Advisory to remind telecommunications carriers and interconnected VoIP providers that they must file an annual certification documenting compliance with the FCC’s Customer Proprietary Network Information (CPNI) rules by March 1, 2023. Pursuant to Section 64.2009(e) of the FCC’s rules, telecommunications carriers and interconnected VoIP providers must certify annually that they have established operating procedures that are adequate to ensure compliance with the FCC’s CPNI rules. Additionally, those carriers must provide a statement accompanying the certificate explaining how their operating procedures ensure that they are in compliance with the rules; include an explanation of any actions taken against data brokers; and provide a summary of all customer complaints received in the past year concerning the unauthorized release of CPNI. Annual CPNI certifications for 2023 must be filed on or before March 1, 2023 in EB Docket No. 06-36, for data pertaining to the previous calendar year, 2022.
RUS Requests Comment On ReConnect Program Rule Changes – March 31, 2023
February 1, 2023 – The Rural Utilities Service (RUS) has requested comment on a final rule which proposes changes to the Rural eConnectivity Program (ReConnect Program). RUS has proposed changes to the ReConnect Program’s rules “to remove outdated requirements, ensure that the requirements in the regulation are clear, accurate as presented and in compliance with federal reporting requirements.” RUS’s ReConnect Program provides loans, grants, and loan/grant combinations to facilitate broadband deployment in rural areas. Comments may be submitted on or before March 31, 2023, in docket number RUS-22-Telecom-0056 and Regulatory Information Number 0572-AC62 using the online portal at https://www.regulations.gov.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Stonepeak Completes Purchase Of Intrado’s Safety Business
February 1, 2023 – Stonepeak has announced that it has completed its acquisition of Intrado Corporation’s Life & Safety business. The $2.4 billion deal was announced in September 2022. Stonepeak is a leading alternative investment firm specializing in infrastructure and real assets with approximately $53.4 billion of assets under management. Intrado is a leading provider of 911 technology solutions for traditional phone companies, wireless carriers, satellite and cable operators, VoIP providers, and public safety and government agencies across North America.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Nextlink Internet Acquires Bluestem Network Assets
February 1, 2023 – Nextlink Internet has announced it has acquired most of the assets of Bluestem Network, based in Lancaster and Seward Counties in Nebraska. Nextlink Internet is a rural-focused provider of high-speed internet and phone services, investing over $1 billion in unserved and underserved communities with its fiber and wireless infrastructure. Bluestem Network is a local fiber-to-the-home internet and phone service provider, with service in small communities across southeast Nebraska.
January 2023
USAC Files Estimated Second Quarter 2023 Universal Service Funding Requirements
January 31, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed the Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections for the second quarter of 2023. The filing details the universal service fund’s (USF) total projected funding requirements for 2Q 2023, which includes costs that can be directly attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each mechanism. USAC’s data shows the following total projected 2Q 2023 funding requirements for each USF support mechanism:
High Cost Support Mechanism – $972.91 million (the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $1.152 billion). USAC initially calculated the funding requirement as $1.024 billion, but the amount was decreased by prior period adjustments of $68.97 million and increased by administrative costs of $18.26 million.
Low Income Support Mechanism – $202.05 million (the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $201.21 million). USAC initially estimated funding requirements of $295.31 million for Lifeline and $0.06 million for Link-Up, resulting in a total of $295.37 million. This amount was decreased by prior period adjustment of $116.97 million and increased by $23.65 million in administrative costs.
Rural Health Care Support Mechanism – $159.36 million (the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $70.79 million).
Connected Care Pilot Program – $8.43 million (the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $8.5 million).
E-Rate Schools and Libraries Support Mechanism – $609.15 million (the 1Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $697.13 million).
USAC projects a consolidated budget of $71.91 million for 2Q 2023. This breaks out to $38.01 million in direct costs for all four support mechanisms, and $33.90 million in joint and common costs which include costs associated with billing, collection, and disbursement of universal service funds. The 2Q 2023 consolidated budget of $71.91 is $4.62 million more than USAC’s projected budget last quarter ($67.28 million for 1Q 2023).
The FCC will use the of the quarterly funding requirements for the four USF Support Mechanisms, the projected administrative expenses, and the USF contribution base amount to calculate the quarterly USF contribution factor. Copies of USAC’s historical USF filings are available on its website.
FCC Releases Tentative Agenda For February 16 Open Meeting
January 26, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, February 16, 2023:
Helping Domestic Violence Survivors Access Safe and Affordable Connectivity – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would begin the Commission’s required implementation of the Safe Connections Act of 2022. The proposal seeks to help survivors of domestic violence and similar crimes separate lines from shared mobile accounts that include their abusers, protect the privacy of calls made by survivors to domestic abuse hotlines, and support survivors who face financial hardship through the Commission’s affordability programs. (WC Docket Nos. 22-238, 11-42, 21-450)
Connecting Tribal Communities to Broadband – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would seek comments on improvements to the E-Rate program that would increase access for Tribal applicants generally as well as within the Tribal Libraries E-Rate Pilot Program. (CC Docket Nos. 02-6, 96-45, 97-21)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
FCC Releases Best Practice Information For Submitting Challenges To Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric
January 25, 2023 – The FCC’s Broadband Data Task Force has released information on recommended best practices for submitting bulk challenges to the most recent version of the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric data. Serving as the underlying foundation of the FCC’s new broadband availability map, the Fabric is a common dataset of all locations in the U.S. where the FCC has determined fixed broadband internet access service can be installed. In December 2022, the FCC announced that Version 2 of the Fabric will be used for the next Broadband Data Collection (BDC) filing – broadband availability as of December 31, 2022. The Fabric Version 2 contains data from additional data sources, other improvements by the FCC and CostQuest, and the results of bulk Fabric challenges submitted by state and local governments and broadband providers on or before November 10, 2022. Among other things, the Task Force’s Public Notice provides the following guidance:
As of January 3, 2023, the BDC system only accepts bulk Fabric challenges based upon the data in version two of the Fabric.
Any bulk challenges to version one of the Fabric that were filed between November 11, 2022, and January 2, 2023, are being “carried over” and reviewed and adjudicated against version two, and therefore do not need to be refiled; bulk challenges submitted on or after January 3, 2023 however, must be submitted against version two of the Fabric.
Bulk Fabric challengers should submit their challenges to version two of the Fabric as soon as possible and, in any case, no later than March 15, 2023, to have the best opportunity to be considered in time for preparation of the next version of the Fabric (version three).
Bulk Fabric challenges submitted after March 15, 2023, are unlikely to be considered for version three of the Fabric and will instead be reviewed and adjudicated as part of a future iteration of the Fabric.
Comment Deadlines Set For FCC Data Breach Notification NPRM: February 22, 2023 & March 24, 2023
January 23, 2023 – The FCC has announced comment deadlines for its Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) which recommends revising the existing customer proprietary network information (CPNI) data breach notification rules. Comments are due on or before February 22, 2023. Reply comments are due on or before March 24, 2023.
In the NPRM, the FCC requests comment on the following revisions to its CPNI data breach notification rules:
Expansion the FCC’s definition of “breach” to include inadvertent disclosures of customer information and adoption of a harm-based trigger for breach notifications;
Requiring carriers to notify the FCC, in addition to the Secret Service and FBI, as soon as practicable after discovery of a breach;
Elimination of the mandatory waiting period before notifying customers and instead requiring carriers to notify customers of CPNI breaches without unreasonable delay after discovery of a breach unless requested differently by law enforcement;
Whether the FCC should adopt minimum requirements for the content of customer breach notices;
The impact of the Congressional disapproval of the 2016 Privacy Order on the FCC’s legal authority to issue the rules proposed in the NPRM for telecommunications carriers; and
Revisions to the FCC TRS data breach reporting rule consistent with those proposed for the CPNI breach reporting rule.
NIST Begins Considering Updates To Cybersecurity Framework
January 19, 2023 – The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released a concept paper outlining potential changes to its Cybersecurity Framework. Published in 2014 and updated in 2018, NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework helps organizations to better understand and improve their management of cybersecurity risk. The concept paper, NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 Concept Paper: Potential Significant Updates to the Cybersecurity Framework, outlines significant potential changes that NIST is considering in developing the Cybersecurity Framework version 2.0. NIST has invited public comment on the proposals in the paper. Comments must be submitted by March 3, 2023 to cyberframework@nist.gov. NIST will make all relevant comments and material publicly available on the NIST CSF 2.0 website.
Final Agenda For FCC January 2023 Open Meeting
January 19, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its open meeting on Thursday, January 26, 2023, at 10:30 a.m. The meeting will be webcast at www.fcc.gov/live. The final agenda contains the following items:
Ensuring 988 Reliability and Resiliency – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would consider establishing reporting and notice requirements for service outages potentially affecting the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline. (PS Docket Nos. 23-5, 15-80; WC Docket No. 18-336)
Rural Health Care Program – The Commission will consider an Order on Reconsideration, Second Report and Order, Order, and Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would rescind rules requiring support for the Rural Health Care Telecommunications Program to be calculated using a database, improve processes for invoicing and program caps, and propose additional enhancements to calculations of support and a mechanism to allow the participation of newly-eligible health care providers. (WC Docket 17-310)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC Announces Conclusion Of CAF Phase II Auction Long-Form Application Review
January 19, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced that it has concluded the Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II auction long-form application review process. All CAF II auction (Auction 903) winning bids have been authorized or defaulted. The long-form applications submitted by CAF II auction winners are now publicly available from the Auction 903 website. However, certain information in the long-form applications for which confidential treatment was granted, such as detailed technology and system design descriptions, project funding descriptions, and other financial information will remain confidential. Bidding in the CAF II auction concluded on August 21, 2018, and winners were required to submit a long-form application no later than October 15, 2018. In total, there were 195 authorized applicant state combinations, totaling $1.48 billion authorized in 10-year support, covering 708,494 locations in 45 states.
T-Mobile Discloses Massive Data Breach Impacting 37 Million Customers
January 19, 2023 – T-Mobile USA, Inc. has publicly disclosed that it has experienced a massive data breach exposing data for approximately 37 million current postpaid and prepaid customer accounts. In its Form 8-K filing with the Securities And Exchange Commission, T-Mobile provided the following explanation of what happened:
On January 5, 2023, T-Mobile US, Inc. (the “Company,” “we,” or “our”) identified that a bad actor was obtaining data through a single Application Programming Interface (“API”) without authorization. We promptly commenced an investigation with external cybersecurity experts and within a day of learning of the malicious activity, we were able to trace the source of the malicious activity and stop it. Our investigation is still ongoing, but the malicious activity appears to be fully contained at this time, and there is currently no evidence that the bad actor was able to breach or compromise our systems or our network.
Our systems and policies prevented the most sensitive types of customer information from being accessed, and as a result, based on our investigation to date, customer accounts and finances were not put at risk directly by this event. The API abused by the bad actor does not provide access to any customer payment card information (PCI), social security numbers/tax IDs, driver’s license or other government ID numbers, passwords/PINs or other financial account information, so none of this information was exposed. Rather, the impacted API is only able to provide a limited set of customer account data, including name, billing address, email, phone number, date of birth, T-Mobile account number and information such as the number of lines on the account and plan features. The preliminary result from our investigation indicates that the bad actor(s) obtained data from this API for approximately 37 million current postpaid and prepaid customer accounts, though many of these accounts did not include the full data set.
We currently believe that the bad actor first retrieved data through the impacted API starting on or around November 25, 2022. We are continuing to diligently investigate the unauthorized activity. In addition, we have notified certain federal agencies about the incident, and we are concurrently working with law enforcement. Additionally, we have begun notifying customers whose information may have been obtained by the bad actor in accordance with applicable state and federal requirements.
Kansas Awards Nearly $45 Million In Broadband Grants
January 18, 2023 – Kansas Governor Laura Kelly has announced that $44.5 million will be awarded to nine service providers to extend high-speed broadband internet service to 18,468 locations in 15 underserved counties across Kansas. The awards are being made under the third and final round of the $83.5 million Kansas Capital Project Funds (CPF) Broadband Infrastructure Program.
In total, the $83.5 million CPF awards, combined with roughly $42 million in matching funds, will result in more than 24,500 homes, businesses, schools, health care facilities, and other public institutions being connected to fast, reliable broadband internet access services for the first time. The third-round CPF awards are being made to the following:
AT&T (Sedgwick County) – $2,206,491 – The proposed service area is 99% unserved on the fringes of the Wichita metro area, targeting multi-dwelling unit properties. The project will offer a subsidy to assist with discounted broadband services.
Butler Rural Electric Cooperative Association (Butler, Cowley, Sedgwick, and Sumner counties) – $9,815,894 – The multi-county region targeted is 83% unserved, and 50% of the area is located in an economically disadvantaged county. This significant investment will bring connectivity to south-central Kansas.
Cox Communications (Jackson, Shawnee, and Wabaunsee counties) – $6,373,948 – This multi-county project is 100% unserved. To connect these rural areas northwest of Topeka, Cox will use an affordable, scalable solution already deployed in the KC metro region.
Cunningham Communications (Mitchell County) – $1,192,735 – Hundreds of residences and businesses in this 98% unserved area will be positively impacted by the Fiber To The Home network that will be provided by Cunningham Communications.
GBT Rural (Pawnee and Stafford counties) – $6,782,694 – More than 365 square miles of an economically distressed area with a 92% unserved population will be covered by GBT Rural.
Iowa Tribe (Doniphan County) – $1,424,945 – This very rural, remote, and economically disadvantaged area in the northeast corner of Kansas is 91% unserved. The project will be based on a partnership between the Iowa Tribe, Doniphan County, Rainbow Telecommunications, and the City of White Cloud.
Mokan Dial (Miami County) – $5,590,145 – The 65-square-mile project area is 97% unserved. Mokan Dial will ensure symmetrical speeds up to 1G will be available and affordable to everyone in the targeted region.
Nex-Tech (Decatur and Saline counties) – $10,764,700 – Two separate project areas servicing a 99% unserved area of Saline County and a 93% unserved area of Decatur County. These awards will allow Nex-Tech to build the necessary infrastructure required to reach these rural areas.
WANRack (Johnson County) – $400,000 – This award will target a 100% unserved area of Johnson County. WANRack’s project will enable Kansans to participate in telehealth, remote work, educational opportunities, and the digital economy.
ISP Trade Associations Ask FCC To Clarify Two Aspects Of New Broadband Label Rules
January 17, 2023 – Internet service provider trade associations ACA Connects, CTIA, NCTA, NTCA, and USTelecom have filed a petition asking the Federal Communications Commission to clarify or reconsider to elements of its new broadband label rules. In November 2022, the FCC approved a Report And Order that requires “ISPs to display, at the point of sale, labels that disclose certain information about broadband prices, introductory rates, data allowances, and broadband speeds, and to include links to information about their network management practices, privacy policies, and the Commission’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP).”
The trade associations’ Joint Petition For Clarification Or, In The Alternative, Reconsideration focuses on the requirements to: (1) display certain fees imposed by state and local governments; and (2) document consumer interactions regarding labels that occur through alternative sales channels.
With respect to displaying certain state and local fees, “the Associations propose that providers be deemed in compliance with the requirement if they include a statement similar to what they provide regarding tax disclosures: that these fees may change from time-to-time in response to state and local government actions. In the alternative, the Associations ask for clarification that that they be deemed in compliance if they identify generally the maximum dollar figure that will be passed through per month.”
With respect to alternative sales channel documentation, “the Associations urge the Commission to clarify that the requirement is satisfied if providers establish the business practices and processes they will follow in distributing the label through alternative sales channels, retain training materials and related business practice documentation for two years, and provide such information to the Commission upon request.”
NTIA Will Not Delay BEAD Program Timeline
January 13, 2023 – In a blog post, the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has announced it will not delay the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program timeline. This means it will not extend the time period for challenging the FCC’s National Broadband Map. NTIA is still targeting June 30, 2023 as the deadline for allocating each U.S. state and territory’s BEAD Program broadband funding. It explained that it has heard concerns about the broadband map challenge process, and received numerous requests for delaying the timeline, but declined the requests because “a delay in the timeline would mean a delay in providing funding to communities who desperately need it, and it will not address many of the process concerns we have heard.” NTIA also noted that “[t]he FCC already has received over 1 million challenges to provider reported availability data and has updated the map’s underlying Fabric to add more than one million additional locations.”
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund: FCC Authorizes RDOF Support For 1,764 Winning Bids (17th RDOF Authorization) (Hughes Network Systems, LLC & Resound Networks, LLC)
January 13, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has authorized Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I auction support for 1,764 winning bids. This is the seventeenth Public Notice authorizing RDOF support. Attachment A to the Bureau’s Public Notice contains a list of the authorized winning bids, which belong to Hughes Network Systems, LLC (Rhode Island) and Resound Networks, LLC (Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas).
The 1,764 winning bid authorizations were granted after the Bureau reviewed long-form application information for each authorized winning bidder, including letters of credit and Bankruptcy Code opinion letters, and concluded the submissions were acceptable. Consequently, the Bureau has directed and authorized the Universal Service Administrative Company to obligate and disburse Universal Service Fund support to each winning bidder. Support will be disbursed in 120 monthly payments, beginning at the end of January 2023. The first service obligation that must be met by the RDOF support recipients authorized by the Public Notice is the deployment of broadband service to 40% of locations in a state by December 31, 2025. The broadband service must meet the standards for which support was received (i.e., speed levels and latency). After that, these RDOF support recipients must achieve the following broadband service deployment obligations: 60% of locations in a state by December 31, 2026; 80% of locations in a state by December 31, 2027; and 100% of locations in a state by December 31, 2028.
SEC Files Subpoena Enforcement Action Against Covington & Burling LLP To Obtain List Of Clients Impacted By Firm’s Cyberattack
January12, 2023 – The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission has filed an application seeking an order directing the law firm Covington & Burling LLP to comply with an investigative subpoena for documents. Specifically, the SEC is attempting to force Covington & Burling to disclose a list of its clients who were impacted by a cyberattack experienced by the law firm. The action was filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia.
In November 2020, “threat actors associated with the Microsoft Hafnium cyberattack maliciously and unlawfully obtained access to Covington’s computer network and certain individual devices, including access to non-public files of nearly 300 Covington clients that are regulated by the SEC.”
After learning of the incident in early 2022, the SEC subpoenaed Covington for the names of clients whose files were viewed, copied, modified or exfiltrated by the threat actors. The SEC wants the information in order to identify any suspicious trading by the threat actors or others in the Covington clients’ securities, and determine whether such trading was illegal based on material non-public information that the threat actors viewed or exfiltrated as part of the cyberattack. Also, the SEC will use the information to determine “whether the impacted clients made all required disclosures to the investing public about any material cybersecurity events in connection with the cyberattack.” Covington has refused to provide the SEC with the names of all but two of its clients. Covington has objected to the SEC’s request by asserting privilege and client confidentiality.
The SEC’s Application For An Order To Show Cause And For An Order Requiring Compliance With Subpoena seeks a District Court order directing Covington to show cause as to why the court should not compel it to produce the documents as required by the subpoena.
Sixth Circuit Court Of Appeals Sets Oral Argument For Consumers’ Research Challenge To USF Contribution Factor
January 10, 2023 – The U.S. Court Of Appeals For The Sixth Circuit has set the date for oral arguments in Consumers' Research v. FCC (Case No. 21-3886). It will be held on March 17, 2023 at 9:00 am Eastern before a three-judge panel in Cincinnati, Ohio.
In September 2021, nonprofit organization Consumers’ Research, communications provider Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and five individual consumers filed a petition for review with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit challenging the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) approval of the proposed fourth quarter 2021 universal service contribution factor. The Petitioners claim the FCC’s approval of the 4Q 2021 contribution factor (and the proposed contribution factor itself) “exceeds the FCC’s statutory authority and violates the Constitution and other federal laws.”
The group has filed two other petitions in different U.S. Courts of Appeals challenging other FCC approvals of the USF contribution factor: in the 5th Circuit challenging the USF contribution factor for the 1Q 2022, Case Number 22-60008 (filed January 5, 2022); and in the 11th Circuit challenging the USF contribution factor for the 4Q 2022, Case Number 22-13315 (filed October 3, 2022).
FCC Releases NPRM Proposing Changes To CPNI Data Breach Rules
January 6, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released a Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) proposing revisions to its customer proprietary network information (CPNI) breach notification rules. Comments are due on or before 30 days after the NPRM is published in the Federal Register. Reply comments are due 60 days after publication. Under existing FCC CPNI rules, adopted in 2007, telecommunications carriers and interconnected VoIP providers are required to notify customers and federal law enforcement of breaches of CPNI in their possession. In the NPRM, the FCC proposes the following revisions to its rules and requests comment on the following issues:
Expansion the FCC’s definition of “breach” to include inadvertent disclosures of customer information and adoption of a harm-based trigger for breach notifications.
Requiring carriers to notify the FCC, in addition to the Secret Service and FBI, as soon as practicable after discovery of a breach.
Elimination of the mandatory waiting period before notifying customers and instead requiring carriers to notify customers of CPNI breaches without unreasonable delay after discovery of a breach unless requested differently by law enforcement.
Whether the FCC should adopt minimum requirements for the content of customer breach notices.
The impact of the Congressional disapproval of the 2016 Privacy Order on the FCC’s legal authority to issue the rules proposed in the NPRM for telecommunications carriers.
Revisions to the FCC TRS data breach reporting rule consistent with those proposed for the CPNI breach reporting rule.
Comment On Use Of E-Rate Funding For Next-Generation Firewalls & Services Due February 13, 2023
January 6, 2023 – Deadlines have been announced for the Federal Communications Commission’s request for comment on “the use of E-Rate program funds to support advanced or next-generation firewalls and services, as well as other network security services.” Comments are due on or before February 13, 2023, and reply comments are due March 30, 2023.
In a December 2022 Public Notice, the FCC requested comment on using E-Rate funds to support next-generation firewalls and services, as well as the following related issues:
Definition of Advanced or Next-Generation Firewalls and Services. The E-Rate program currently defines firewall as “a hardware and software combination that sits at the boundary between an organization’s network and the outside world, and protects the network against unauthorized access or intrusions.” Comment is requested on this definition and whether any modifications may be appropriate.
Eligible Equipment and Services and their Costs. Comment is requested on the specific equipment and services that E-Rate should support to fund as advanced or next-generation firewalls and services, as well as the costs associated with funding these services.
Categorization of Firewall Services and Components. Under current E-Rate rules, basic firewall service provided as part of a vendor’s Internet access service is eligible as a Category One service. Separately priced basic firewall services and components are eligible as a Category Two service. Comment is sought on whether advanced or next-generation firewall services and components should be eligible as a Category One and/or Category Two service.
Cost-Effective Purchases. If the FCC makes advanced or next-generation firewall services eligible as only Category Two service, comment is sought on whether this would be an effective way to ensure applicants are making cost-effective choices when requesting these services and equipment.
Legal Authority Issues. Comment is sought on the FCC’s legal authority to add advanced or next-generation firewalls and services as an eligible service for the E-Rate program.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For January 2023 Open Meeting
January 5, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting on January 26, 2023:
Ensuring 988 Reliability and Resiliency – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would consider establishing reporting and notice requirements for service outages potentially affecting the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline. (PS Docket Nos. 23-5, 15-80; WC Docket No. 18-336)
Rural Health Care Program – The Commission will consider an Order on Reconsideration, Second Report and Order, Order, and Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would rescind rules requiring support for the Rural Health Care Telecommunications Program to be calculated using a database, improve processes for invoicing and program caps, and propose additional enhancements to calculations of support and a mechanism to allow the participation of newly-eligible health care providers. (WC Docket 17-310)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Comment Deadlines For Broadband Label Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking Extended By 30 Days
January 4, 2023 – The FCC’s Consumer and Governmental Affairs Bureau has extended the comment deadlines for the Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on the FCC’s broadband label requirements. Comments are now due on or before February 16, 2023. Reply comments are now due March 16, 2023.
In November 2022 the FCC approved a Report And Order requiring ISPs to display labels that disclose terms and conditions of their broadband services. In the accompanying Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, the FCC is seeking comment on further steps to ensure that consumers have the information they need to make informed broadband service purchasing decisions. More specifically, further comment is requested on general issues related to the following: accessibility and languages; performance characteristics; service reliability; cybersecurity; network management and privacy; formatting; and whether ISPs should submit label information to the FCC.
Biden Renominates Gigi Sohn To The Federal Communications Commission
January 3, 2023 – President Joe Biden has once again nominated Gigi B. Sohn to be a member of the Federal Communications Commission for a term of five years. Ms. Sohn, if confirmed by the Senate, would serve a term of five years from July 1, 2021. President Biden previously nominated Ms. Sohn to the FCC in January 2022. The Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation held a hearing on her nomination in February 2022, but thereafter, the full Senate failed to hold a vote on her nomination. As a result, the FCC has continued to operate with four Commissioners, rather than the full five throughout Biden’s presidency.