The Latest News
FCC | Broadband | Wireless | Congress
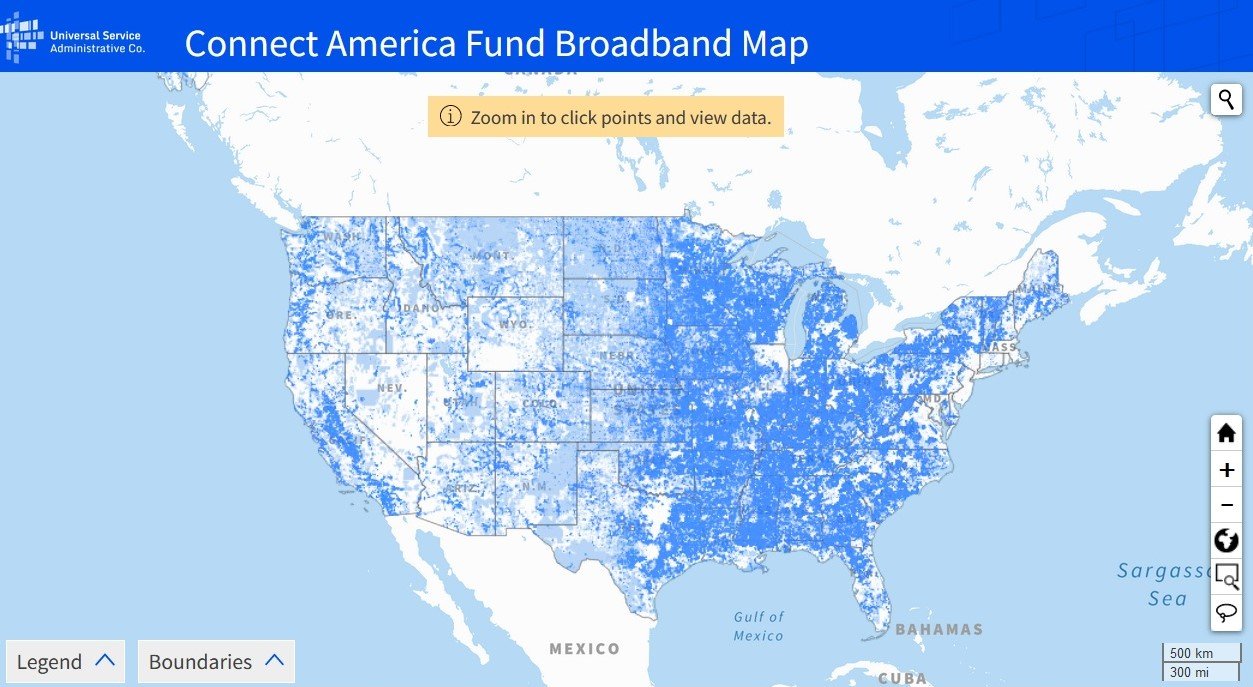
USAC Updates Connect America Fund Broadband Map
January 26, 2024 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has released an updated version of the Connect America Fund (CAF) Broadband Map. The updated version of the CAF map depicts where CAF programs have supported fixed broadband deployments throughout the U.S., as of Sept. 30, 2023, that were reported to USAC. More specifically, it displays the geographic locations, using latitude and longitude, where broadband providers that receive CAF support from the following programs have built out high-speed fixed Internet service:
Connect America Fund Phase II Model (CAF II Model)
Connect America Fund Phase II Auction (CAF II Auction)
Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM)
Alternative Connect America Cost Model II (A-CAM II)
Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS)
Rural Broadband Experiments (RBE)
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF)
Bringing Puerto Rico Together (Uniendo a Puerto Rico) Fund and the Connect the USVI Fund (PR Fixed)
FCC Requests Public Comment On Broadband Data Collection Challenge Process
January 19, 2024 – The FCC’s Broadband Data Task Force has requested public comment on the Broadband Data Collection (BDC) challenge processes. Comments are due on or before February 19, 2024. Reply comments are due March 5, 2024. Under the 2020 Broadband Deployment Accuracy and Technological Availability Act, the FCC is required to submit a report to Congress that evaluates the BDC challenge processes and considers whether additional tools are needed to improve the accuracy of BDC data. In the Public Notice, Broadband Data Task Force has requested comment on a wide range of issues, such as participation in the fixed broadband availability challenge process; the National Broadband Map challenge interface; evidentiary standards; the time period for challenges and responses; participation in the mobile broadband availability challenge process; challenges to the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric, and the need for other tools to help identify potential inaccuracies in the data that providers report.
U.S. Department Of Health And Human Services Issues 2024 Federal Poverty Guidelines
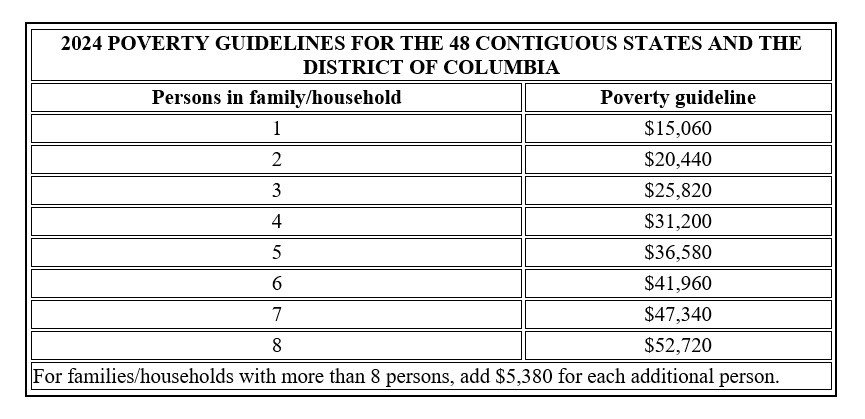
January 17, 2024 – The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has issued the 2024 Federal poverty guidelines used to determine financial eligibility for certain governmental assistance programs. Under the FCC’s rules, a consumer can qualify for participation in the universal service Lifeline program if the consumer’s household income is at or below 135% of the Federal poverty guidelines for a household of that size. There are separate guidelines for the 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia, Alaska, and Hawaii.
John Deere Announces Agreement With SpaceX To Enable Starlink Connectivity In Farm Equipment
January 16, 2024 – Deere & Company has entered into an agreement with SpaceX that will enable John Deere farm equipment to connect to Starlink’s satellite communications (SATCOM) service. Starlink, a wholly-owned subsidiary of SpaceX, operates a constellation of low earth orbit satellites that deliver internet access service. In the press release announcing the agreement, Deere & Company provided the following additional information:
The SATCOM solution will connect both new and existing machines through satellite internet service and ruggedized satellite terminals. This will fully enable technologies such as autonomy, real-time data sharing, remote diagnostics, enhanced self-repair solutions, and machine-to-machine communication, all of which help farmers work more efficiently while minimizing downtime.
“John Deere has led the agriculture equipment industry for more than two decades with satellite-based precision guidance technology,” said Jahmy Hindman, Senior Vice President & Chief Technology Officer at John Deere. “Now, we are bringing satellite communications service to the farm at scale so farmers with cellular coverage challenges can maximize the value of connectivity to their operations. The SATCOM solution unlocks the John Deere tech stack so every farmer can fully utilize their current precision agriculture technology in addition to the new innovative solutions they will deploy in the future. We initiated this process with a fierce focus on delivering value to our customers, and this partnership ensures we have a solution that meets their needs today and in the future.”
John Deere’s SATCOM solution will leverage SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet constellation. To activate this solution, John Deere dealers will install a ruggedized Starlink terminal on compatible machines, along with a 4G LTE JDLink modem to connect the machine to the John Deere Operations Center. The SATCOM solution will initially be available through a limited release in the United States and Brazil starting in the second half of 2024.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For January 25th Open Meeting
January 4, 2024 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s open meeting scheduled for Thursday, January 25, 2024:
Improving Network Reliability, Resiliency, and Transparency During Disasters – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to ensure participation in, and enhance the use of, its Disaster Information Reporting System, where service providers report on their operational status during emergencies. (PS Docket Nos. 21-346, 15-80; ET Docket No. 04-35)
Improving Wireless 911 Call Routing – The Commission will consider a Report and Order requiring wireless providers to implement location-based routing for wireless calls and real-time texts (RTT) to 911 in order to reduce misrouting and improve emergency response times. (PS Docket No. 18-64)
Mitigating Orbital Debris to Support Space Innovation – The Commission will consider an Order on Reconsideration addressing the issues raised in three petitions for reconsideration filed in response to the Orbital Debris Mitigation Report and Order released in 2020 which comprehensively updated the Commission’s existing rules regarding orbital debris mitigation. (IB Docket No. 18-313)
Modernizing and Expanding Access to the 70/80/90 GHz Bands – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would adopt new rules and update preexisting rules for the 70/80/90 GHz bands. The item would authorize certain point-to-point links to endpoints in motion in the 70 GHz and 80 GHz bands for aeronautical and maritime use; provide for smaller, lower-cost antennas to facilitate backhaul service in those bands; and adopt changes to the link registration process. The item would also seek comment on the potential inclusion of Fixed Satellite Service earth stations in the light-licensing regime for the 70 GHz and 80 GHz bands. (WT Docket No. 20-133)
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter from the Media Bureau.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
December 2023
Filing Reminder: FCC Form 555 – Annual Lifeline Recertification – Due January 31, 2024
December 29, 2023 – All eligible telecommunications carriers (ETCs) must submit the results of their Lifeline recertification efforts using FCC Form 555 on or before January 31, 2024. The FCC Form 555, “Annual Lifeline Eligible Telecommunications Carrier Certification Form,” is used by all Lifeline service providers to report the results of their annual recertification process and includes required data accuracy certifications. The Form 555 must be submitted to the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) using USAC’s online One Portal, the FCC in Docket 14-171 using the FCC’s EFCS, relevant state regulatory authorities, and Tribal governments if Lifeline service is provided to subscribers that reside on Tribal lands.
FCC Defers Next CAF-BLS Five-Year Deployment Obligation Until January 1, 2025
December 27, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released a Second Report And Order which defers the commencement of the next five-year deployment obligation term for legacy rate-of-return carriers receiving Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS) in 2024 until January 1, 2025. The deferment will allow the FCC to consider whether to modify future deployment obligations for CAF BLS recipients and explore general reforms to the high-cost universal service program that were raised in a July 2023 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking. Rate-of-return carriers on legacy CAF-BLS support will remain subject to the FCC’s rules requiring the offering of broadband service at actual speeds of at least 25/3 Mbps to the previously determined number of unserved locations under the current five-year term that ends on December 31, 2023.
FCC Announces Revised 2024 Urban Rate Survey Broadband Services Benchmarks & Waiver Of Implementation Date To February 1, 2024
December 26, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has issued a Public Notice revising the 2024 reasonable comparability benchmarks for fixed broadband services for eligible telecommunications carriers (ETCs) that are subject to broadband public interest obligations. The revised benchmarks have been issued after the Bureau determined there was an error in calculation of the broadband rates it previously released on December 15, 2023. The revised broadband rates and explanatory notes are available on the FCC’s urban rate survey data and resources website. Because of the revision, the Bureau has extended the requirement that ETCs meet the revised benchmarks by one month, to February 1, 2024. The reasonable comparability benchmark for voice services ($55.13) and the required minimum usage allowance for fixed broadband (660 GB) remain unchanged.
The Bureau has provided the following table showing the revised 2024 benchmark for several different broadband service offerings. For broadband service with characteristics not shown in the table, the Bureau has provided an excel file which broadband providers can use to calculate the benchmark for services in the U.S. and Alaska.
FCC Announces Conclusion Of RDOF Long-Form Application Review
December 20, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced the conclusion of the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) auction (Auction 904) long-form application review. RDOF long-form applications (FCC Form 683) are available through the “Application Search” tab on the Auction 904 web page. However, certain information provided by long-form applicants that is subject to a request for confidential treatment that has been granted or remains pending is not publicly available.
The RDOF auction began on October 29, 2020, and ended on November 25, 2020. The FCC has authorized 379 entities to receive over $6 billion in RDOF support over a ten-year term to provide broadband service to just under 3.5 million locations in 48 states and one U.S. territory. For over 97% of these locations, the RDOF support recipient is required to provide Gigabit speed broadband service.
FCC Denies Waiver Of Enhanced A-CAM Cybersecurity Plan Rules; Issues Clarification For Enhanced A-CAM Carriers Using NIST CSF Draft Version 2.0
December 20, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has denied a request for waiver of Section 54.308(e) of the FCC’s rules which requires carriers that have elected to receive Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) support to certify and submit their initial cybersecurity and supply chain risk management plans by January 2, 2024 or within 30 days of approval under the Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA), whichever is later. The waiver, submitted by NTCA, requested that Enhanced A-CAM carriers be permitted to certify and submit their initial cybersecurity and risk management plans by the later of the deadline for 2024 FCC Form 481 submissions (July 1, 2024), or within 30 days of approval under the PRA.
Under the FCC’s Enhanced A-CAM rules, carriers must implement operational cybersecurity and supply chain risk management plans by January 1, 2024 – the start of the Enhanced A-CAM support term – and certify they have done so to the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) by January 2, 2024 or within 30 days of approval under the PRA, whichever is later. While Enhanced A-CAM carriers must still implement their cyber operational plans by January 1, 2024, the certification rules are still awaiting Office of Management and Budget approval, and are not yet effective. The Bureau expects the earliest possible approval to be in early February 2024. Enhanced A-CAM carriers’ cybersecurity and supply chain risk management plans must reflect the latest version of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity (CSF), which is version 1.1, although version 2.0 is expected in early 2024. If an Enhanced A-CAM carrier makes a substantive modification to its cyber plans, it must submit its updated plan to USAC within 30 days of making the modification. In the Order denying the NTCA waiver, the Bureau has provided the following clarification related to Enhanced A-CAM carriers use of the draft NIST CSF 2.0 Framework in cyber plans:
“[I]f an Enhanced A-CAM carrier submits a cybersecurity risk management plan that complies with the Draft 2.0 Framework, the Enhanced A-CAM carrier will have met the requirement to implement a plan that reflects the latest version of the NIST framework. The Draft 2.0 Framework has been available since early August 2023 – weeks before the Bureau announced the offers of Enhanced A-CAM support, and NIST is not planning to release another draft prior to releasing the finalized framework. The Draft 2.0 Framework encompasses the current NIST CSF 1.1 so that if an Enhanced A-CAM carrier submits a plan that reflects the Draft 2.0 Framework, the plan will also reflect NIST CSF 1.1. Nevertheless, if the finalized NIST CSF 2.0 makes changes to the Draft 2.0 framework that require an Enhanced A-CAM carrier to make a substantive modification to its cybersecurity risk management plan, the Enhanced A-CAM carrier must submit an updated plan within 30 days of making the substantive modification as required by the Commission’s rules.”
FCC Broadband Data Collection Filing Window Opens January 2, 2024 & Closes March 1, 2024 – Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric Version 4 Announced
December 20, 2023 – The FCC’s Broadband Data Task Force has announced that the Broadband Data Collection (BDC) filing window for submitting broadband availability and other data as of December 31, 2023, will open on January 2, 2024. Service providers must submit all availability and subscription data no later than March 1, 2024. Facilities-based broadband service providers must use the BDC system to submit data that shows where they made mass-market broadband internet access service available as of December 31, 2023. Facilities-based broadband service providers and providers of fixed voice services must also submit their December 31, 2023, subscription data (required under FCC Form 477) into the BDC system. The BDC system is available online at https://bdc.fcc.gov/bdc. Information on filing BDC data is available at https://www.fcc.gov/BroadbandData/filers.
Additionally, the Broadband Data Task Force has announced that the December 2023 update (Version 4) of the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric (Fabric) will be available to existing Fabric licensees starting on December 27, 2023. This updated version – Version 4 – must be used by filers of fixed broadband availability for their availability data as of December 31, 2023. It “incorporates data from updated data sources and other improvement efforts conducted by the FCC and CostQuest, and the results of Fabric challenges submitted by state, Tribal, and local governments, broadband service providers, and the public through the National Broadband Map.”
FCC Declares Wavelength LLC Has Defaulted On RDOF Winning Bids In Arizona
December 20, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced that Wavelength LLC has defaulted on its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) winning bids in Arizona. Wavelength participated in the RDOF auction as a member of Consortium 2020, which won $19,787,039.50 in 10-year support to provide service to 15,636 locations in Arizona, and $29,131,921.40 in 10-year support to provide service to 52,456 locations in California. All Consortium 2020 winning bids were assigned to Wavelength through the RDOF long-form “Divide Winning Bids” process. Upon concluding its review of Wavelength’s RDOF long-form application, the Bureau determined Wavelength failed to demonstrate that it is financially qualified to receive RDOF support and meet its RDOF program obligations in the areas where it was a winning bidder in Arizona which were not already announced as being in default. The Bureau provided the following explanation of its decision:
Wavelength - Arizona. The Bureau has concluded its review of Wavelength’s long-form application in Arizona. Wavelength proposes to deploy service to 12,418 estimated RDOF locations in Arizona. The Bureau has determined that, based on the totality of the long-form application and its inadequate responses to the Bureau’s follow-up questions, Wavelength has failed to demonstrate that it is financially qualified to receive support to meet its RDOF program obligations in the areas where it has winning bids in Arizona. The Commission has an obligation to protect limited Universal Service Funds and to avoid extensive delays in providing needed service to rural areas, including by not subsidizing risky proposals that propose deployment plans that are unrealistic or that are predicated on aggressive assumptions and predictions. Accordingly, we deny Wavelength’s long-form application in Arizona, and Wavelength is in default on all winning bids not already announced as defaulted, as listed in Attachment A. We will refer these defaults to the Enforcement Bureau for further consideration.
Consumers’ Research Loses Again – Eleventh Circuit Says Universal Service Fund Is Constitutional
December 14, 2023 – The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Eleventh Circuit has issued an opinion denying Consumers’ Research’s Petition For Review challenging the constitutionality of the Universal Service Fund (USF).
Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, and a handful of individuals filed the Petition, which directly challenged the fourth quarter 2022 USF contribution factor. The group argued that Section 254 of the Communications Act, which created the USF and empowers the FCC to implement it, violates the nondelegation doctrine. Additionally, they argued that the FCC’s use of the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) to help administer the USF system violates the private-nondelegation doctrine.
In a unanimous opinion, the Eleventh Circuit ultimately found that “[b]ecause § 254 provides an intelligible principle and the FCC maintains control and oversight of all actions by the private entity, we hold that there are no unconstitutional delegations and therefore DENY the petition.”
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit issued a similar order upholding the constitutionality of the USF in May 2023. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit rejected a nearly identical Petition For Review in March 2023, but thereafter vacated the decision and granted a rehearing en banc. A decision in that case is expected soon.
USF Contribution Factor For First Quarter Of 2024: 34.6 Percent – New Record High
December 14, 2023 – The FCC’s Office of Managing Director (OMD) has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the first quarter of 2024 will be 34.6 percent. The 34.6 percent USF contribution factor for 1Q 2024 is a new record high, barely beating out the previous high of 34.5 percent from 4Q 2023. If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. Historical information on quarterly universal service fund contribution factors is available online from the FCC.
For the first quarter of 2024, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $8.313338 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected ($8.172483 billion was projected for 4Q 2023). USAC estimates that $2.118730 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms (revenue requirement) in the first quarter of 2024 (the 4Q 2023 demand was estimated at $2.078830 billion).
Total first quarter 2024 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, which breaks out among the USF support mechanisms as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $634.96 million (4Q 2023 was $652.04 million)
Rural Health Care: $168.60 million (4Q 2023 was $97.22 million)
High-Cost: $1.09021 billion (4Q 2023 was $1.06688 billion)
Lifeline: $225.47 million (4Q 2023 was $262.71 million)
Connected Care: ($0.51) million (4Q 2023 was ($0.02) million)
FCC Issues $21.7 Million Forfeiture Against LTD Broadband (And GigFire LLC) For Defaulting On RDOF Winning Bids
December 5, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture against LTD Broadband LLC for defaulting on Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I Auction winning bids, in apparent violation of the FCC’s rules. Specifically, the FCC found “that LTD apparently committed 7,238 violations by defaulting on 7,238 [Census Block Groups] subject to forfeiture.” As a consequence, LTD Broadband must pay a forfeiture penalty in the amount of $21,714,000. Additionally, the FCC has proposed to hold GigFire LLC jointly and severally liable for the total amount of LTD Broadband’s forfeiture. GigFire is an entity created by the owner of LTD apparently to replace LTD, and to which most or all of LTD’s assets have been transferred. The FCC concluded that this “raises the possibility that GigFire may have been founded for the purpose of evading liability for LTD’s actions.” Appendix A to the Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture describes LTD Broadband’s apparent violation of the FCC’s rules and RDOF requirements. Appendix B lists the LTD’s defaulted census block groups subject to forfeiture, which are in California, Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, Texas, and Wisconsin. Appendix A contains the following explanation of the deficiencies in LTD Broadband’s post-auction long-form application and its inability to fulfill the requirements of the RDOF auction:
LTD’s application was lacking in a number of ways. First, LTD failed to provide proof of Eligible Telecommunications Carrier (ETC) designation, a requirement to receive universal service funds, in three of the states in which it had winning bids. Second, LTD did not show that it had available funds for all project costs that exceed the amount of support to be received for the first two years of its support term. In particular, WCB determined that LTD would not be able to meet the initial prerequisites of a new term sheet for a loan and equity fundraising round submitted with its final financial plan. Third, LTD did not, as required, differentiate between anticipated project costs and related funding for each of the areas for which LTD was seeking support, nor did LTD explain why its apparent assumption that all deployment costs are equal across all of its winning bids states and rural regions within each state might be reasonable. Fourth, a number of the cost assumptions on which LTD based its deployment costs were unrealistic, raising concerns that the overall determination of deployment costs was too low. Fifth, LTD did not provide evidence that it could cover the necessary debt service payments over the life of its loans. Sixth, LTD failed to provide specific and localized project designs; instead, LTD applied an unrealistic one-size-fits-all approach for the vast areas where it would be required to deploy last-mile fiber to every serviceable location and the supporting middle-mile and core infrastructures. LTD’s technical submissions reflect a lack of understanding of how significantly their business needs to scale up to achieve equipment purchases, hiring, construction, deployment, maintenance, operations, and customer service for the sizeable network of LTD’s remaining winning bids. For these reasons and “based on the totality of the long-form [application], the expansive service areas reflected in [its] winning bids, and [its] inadequate responses to the Bureau’s follow-up questions,” WCB concluded that LTD was “not reasonably capable of complying with the Commission’s requirements.”
FCC Denies LTD Broadband Application For Review Of Decision Denying RDOF Support
December 5, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC or Commission) has denied an Application For Review from LTD Broadband, LLC, which sought review of a decision by the FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau that denied LTD’s long-form application to receive Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) auction support. Following a “careful review” of the Bureau’s decision, the Commission concluded that “the Bureau followed Commission guidance as adopted for the RDOF program and correctly concluded that LTD is not reasonably capable of offering the required gigabit-speed, low-latency service throughout the broad areas where it won auction support.”
Upon conclusion of the RDOF auction, “LTD was the largest winning bidder in the auction, with winning bids to deploy gigabit speed low-latency service to 528,088 locations in 15 states with $1,320,920,719 in 10-year support.” To put the size of LTD’s RDOF win and the accompanying obligations in perspective, when the RDOF auction started, LTD had a relatively “small deployment footprint and subscriber base of approximately 15,000 customers.” Immediately after becoming the largest winning bidder, LTD had trouble complying with the FCC’s post-auction RDOF requirements. LTD received eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) designation in eight states where it won RDOF support prior to the June 7, 2021 deadline, but in the other seven states in which it won support (California, Iowa, Kansas, Oklahoma, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota), LTD filed a request for waiver of the ETC deadline. The Bureau denied LTD’s request for waiver of the ETC certification deadline for California, Kansas, Oklahoma, Iowa, Nebraska, and North Dakota. LTD eventually defaulted on its winning bids in California, Iowa, Kansas, and Oklahoma, but pursued reconsideration of the waiver denial for Nebraska and North Dakota.
During the review of LTD Broadband’s long-form application, the Wireline Bureau identified numerous legal, technical, operational, and financial deficiencies. The Bureau ultimately denied LTD’s application, concluding “LTD was not reasonably capable of complying with the Commission’s public interest requirements established for the RDOF program for a number of both financial and technical reasons.” LTD was declared to be in default of its remaining RDOF winning bids. The Bureau also dismissed LTD’s reconsideration of the ETC waiver denial for Nebraska and North Dakota. LTD then filed an Application for Review of the Bureau’s decision.
The Commission reviewed LTD’s application, and identified four primary arguments as to why the decision should be reversed. However, every argument put forth by LTD was soundly rejected, causing the Commission to deny the application. Concurrent with the denial order, the Commission issued a Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture against LTD Broadband for defaulting on its RDOF winning bids. As a consequence, LTD Broadband must pay a forfeiture penalty in the amount of $21,714,000.
FCC Issues $732,000 Forfeiture Against Etheric Communications LLC For Defaulting On RDOF Winning Bids
December 5, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture against Etheric Communications LCC for defaulting on Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) Phase I Auction (Auction 904) winning bids, in apparent violation of the FCC’s rules. Specifically, the FCC found “that Etheric apparently committed 244 violations by defaulting on 244 [Census Block Groups] subject to forfeiture.” Consequently, Etheric Communications must pay a forfeiture penalty in the amount of $732,000. Appendix A to the Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture describes Etheric Communications’ apparent violation of the FCC’s rules and RDOF requirements. Appendix B lists the Etheric’s defaulted census block groups subject to forfeiture, all of which are in California. Appendix A contains the following explanation of why Etheric was found to have defaulted on its winning RDOF bids in California:
Etheric is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Etheric Networks Incorporated, which provides custom broadband services through a combination of fixed wireless and fiber technologies to residential and business customers across 10 counties in the San Francisco Bay Area. Etheric timely submitted its Short-Form Application to participate in Auction 904 and was a successful bidder. WCB declared Etheric to be in default on May 23, 2023, and referred the company to the Bureau for enforcement action, after WCB denied Etheric’s petition for reconsideration of the Bureau’s decision to dismiss as moot and alternatively, denied Etheric’s petition seeking waiver of the deadline for demonstrating, with appropriate documentation, that it had been designated as an eligible telecommunications carrier in each of the geographic areas for which it sought to be authorized for Auction 904 support. The Commission finds that Etheric apparently committed 244 violations by defaulting on 244 CBGs subject to forfeiture, which places the company’s base forfeiture at $732,000. Etheric’s total assigned support for the CBGs in default subject to forfeiture amounted to $218,641,793.80, thereby capping the maximum possible forfeiture at $32,796,269.07, which is 15 percent of Etheric’s defaulted support subject to forfeiture in Auction 904. Because the base forfeiture is less than the 15 percent cap established in the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund Order, the Commission finds that the forfeiture amount of $732,000 against Etheric is appropriate here.
FCC Provides Guidance On Performance Measures Requirements For Carriers Transitioning To Enhanced A-CAM And Carriers Remaining On CAF BLS Support
December 4, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has issued guidance regarding performance measures requirements for Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) I, A-CAM II, and Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS) carriers authorized to begin receiving Enhanced A-CAM support on January 1, 2024. Additionally, the Bureau’s Public Notice announces that the mixed support (Hargray) condition applicable to some carriers taking Enhanced A-CAM support has been sunset. The full guidance from the Bureau’s Public Notice is below:
A-CAM I and A-CAM II Carriers Moving to Enhanced A-CAM. A-CAM I and A-CAM II carriers authorized for Enhanced A-CAM are still required to comply with performance testing requirements for 2023, and by July 1, 2024 must certify the testing results. After July 1, 2024, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) and the Bureau will process the certified testing data and implement any support withholding, as required, against monthly Enhanced A-CAM disbursements. Once a carrier shows that it has come back into compliance with its A-CAM I or A-CAM II performance requirements, it will receive its full monthly Enhanced A-CAM disbursement and have its withheld support restored. Continuing to conduct performance testing in 2024 may, therefore, be in a carrier’s interest because compliance with A-CAM I or A-CAM II performance requirements certified for any quarter of 2024 and even prior to processing 2023 testing data means such carrier will not have Enhanced A-CAM support withheld.
CAF BLS Carriers. Carriers that are currently on CAF BLS regardless of whether they have elected Enhanced A-CAM must show that they were in compliance with their CAF BLS performance requirements in 2023, the final year of their five-year deployment term. For carriers that transition from CAF BLS to Enhanced A-CAM, if they are in compliance with performance measures standards for the year 2023, then no further testing is needed until 2026. However, any CAF BLS carrier that is not in compliance with performance measures for 2023 will be subject to support recovery under section 54.320(d) of the Commission’s rules or may attempt to return to compliance within a one-year cure period by conducting another year of performance testing using a statistically valid sample of locations. A carrier must request such a sample from USAC no later than August 1, 2024 and begin the one year of testing in the fourth quarter of 2024. For those carriers choosing to do an additional year of testing with a statistically valid sample, any support recovery for failing to meet end of term performance obligations will be calculated after the one-year cure period. Moreover, carriers that did not elect Enhanced A-CAM and thus remain on CAF BLS support must continue performance testing even after they have shown they are in compliance for the five-year obligation.
Mixed Support Condition. We also announce the sunsetting of the mixed support (i.e., Hargray) condition on the mixed support transactions of 22 CAF BLS/High Cost Loop Support (HCLS) companies that will be receiving Enhanced A-CAM support as of January 1, 2024, as detailed in the Appendix. In the Hargray/ComSouth Order, the Commission approved a mixed support transaction, i.e., a transaction involving the combination of one or more entities receiving fixed high-cost support and one or more entities receiving cost-based support, subject to a condition to prevent cost shifting and to protect the finite resources of the high-cost universal service fund. This condition (the Hargray condition) capped the high-cost cost-based universal service support received based on the operating expenses of the rate-of-return carriers receiving cost-based support for a term of seven years (and any other rate-of-return affiliates acquired during the time in which the condition is in effect (together, covered entities)) or until all covered entities were converted to fixed support. The Commission directed the Bureau to apply this condition to future mixed-support transactions. The 22 companies listed in the Appendix were part of such transactions and were made subject to the Hargray condition as per Commission and Bureau releases, as indicated therein. The conversion of the support received by each of these 22 companies from cost-based support to fixed Enhanced A-CAM (including fixed transitional support) will render the Hargray condition on the company’s associated transaction obsolete. The Hargray condition and related obligations will continue to apply to all cost and revenue data that is applicable to the 2023 calendar year, and these companies must file their compliance certification and financial report for 2023 by January 1, 2024.
Mergers & Acquisitions: LightStream Acquiring Monon Telephone Company In Indiana
December 1, 2023 – LightStream has announced that it has entered into an agreement to purchase Monon Telephone Company, Inc. LightStream, formerly known as Pulaski White Rural Telephone Cooperative, is a cooperative-based communications services provider headquartered in Buffalo, Indiana. The company “provides fiber-based gigabit internet and telecommunications services in the greater Buffalo, Monticello, Pulaski, Royal Center, Star City, and Winamac areas.” Monon Telephone Company was founded in the town of Monon, Indiana in August of 1900, and has been family owned since 1921. The transaction is subject to regulatory approvals, but is expected to close in the first half of 2024. The purchase price and other terms of the deal were not disclosed.
USCellular Announces 3G CDMA Network Shutdown
December 1, 2023 – Mobile wireless carrier USCellular has announced it will shutter its 3G CDMA network on January 14, 2024. Doing so, says USCellular, will allow it to focus on upgrading its network to 4G and 5G. USCellular provided the following information to subscribers on its website:
Major wireless carriers have already shut down their 3G CDMA networks and you’re likely starting to notice the effects on your older devices. When we shut down our network, 3G devices will lose service completely. We are committed to supporting our customers and are ready and available to assist you through this transition. To keep you connected, we’re offering big discounts on 4G/5G devices.
Kansas Governor Announces Advancing Digital Opportunities To Promote Technology (ADOPT) Program
December 1, 2023 – Kansas Governor Laura Kelly has announced the opening of the application window for Kansas’ Advancing Digital Opportunities to Promote Technology (ADOPT) program. The 7-week application window opens on December 7, 2023, and closes at 5:00 pm CST on January 30, 2024. The 2-week public comment window opens on February 7, 2024. A total of $14.7 million will be available from the ADOPT program in the form of grant awards to organizations addressing the challenges of broadband accessibility, affordability, and device availability. ADOPT program grants will be awarded through two sub-programs: (1) Equipment Distribution Program, and (2) Public Wi-Fi Enablement Program.
The Equipment Distribution Program will award grants to eligible entities to make devices available to individuals who do not subscribe to broadband connectivity due to a lack of devices and equipment. Eligible entities will provide devices such as computers, laptops, and tablets to qualifying individuals through no-cost, short or long-term loan programs. The maximum individual award is $500,000, and applicants are not required to provide matching funds. The Public Wi-Fi Enablement Program will award grants for projects that provide access to high-quality, reliable public Wi-Fi based broadband in Kansas. The maximum individual award is $1 million, and applicants are required to provide 10% matching funds.
U.S. Court Of Appeals For The D.C. Circuit Sets Oral Argument In Consumers’ Research V. FCC – January 26, 2024
December 1, 2023 – The U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit has announced it will hold an oral argument in Consumers’ Research v. FCC (case number 23-1091) on January 26, 2024, at 9:30 am. Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 12 individuals filed a petition for review with the Court challenging the FCC’s proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the second quarter of 2023. The Consumers’ Research group claims the USF is unconstitutional, violates statutory authority, and is otherwise illegal for numerous reasons. The group also filed comments and objections to the 2Q 2023 contribution factor with the FCC prior to filing its legal challenge.
November 2023
FCC Consent Decree Requires TracFone To Pay $23.5 Million Penalty For Violations Of FCC Lifeline & Emergency Broadband Benefit Program Rules
November 29, 2023 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has entered into a Consent Decree with TracFone Wireless, Inc., which resolves the Bureau’s investigation into whether TracFone violated the FCC’s rules governing Lifeline service and the provision of broadband service under the Emergency Broadband Benefit (EBB) Program. To resolve the investigation, the Consent Decree requires TracFone to (1) implement a compliance plan, (2) pay a $17,487,000 civil penalty, and (3) pay the FCC’s $6,013,000 Notice of Apparent Liability (NAL) issued to TracFone in 2020 for apparent Lifeline rule violations. The Enforcement Bureau’s investigation of TracFone considered whether TracFone: (1) sought and obtained Lifeline or EBB support for, or failed to de-enroll, ineligible subscribers without eligibility documentation or whose applications were supported by falsified tax forms; (2) sought and obtained Lifeline support for subscribers who should have been de-enrolled or not claimed for reimbursement because they lacked qualifying usage of their Lifeline-supported service; (3) sought and obtained EBB support for subscribers who should not have been claimed for reimbursement because they lacked qualifying usage of their EBB-supported service; and (4) directly or indirectly compensated field enrollment representatives based on commission, rather than on an hourly basis. TracFone is a wholly owned subsidiary of Verizon Communications Inc. Shortly after TracFone was acquired by Verizon, TracFone self-identified and reported to the FCC and the Universal Service Administrative Company certain instances in which it may have violated the FCC’s Lifeline and EBB rules.
FCC Issues Tentative Agenda For December 2023 Open Meeting
November 22, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting, scheduled for Wednesday, December 13, 2023:
Protecting Consumers from Early Termination and Billing Cycle Fees – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would adopt rules to protect consumers from video service junk fees, including early termination fees and billing cycle fees. (MB Docket No. 23-405)
Targeting and Eliminating Unlawful Text Messages – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order, Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Waiver Order to combat illegal robotexts by facilitating blocking of illegal robotexts, codifying do-not-call rules for texting, and closing a loophole that allows certain callers to inundate consumers with unwanted robocalls and robotexts. The item also seeks comment on further efforts to combat illegal robocalls and robotexts. (CG Docket Nos. 21-402, 02-278, 17-59)
Achieving 100% Wireless Handset Model Hearing Aid Compatibility – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that tentatively concludes that hearing aid compatibility for 100% of wireless handset models is an achievable objective and seeks comment on proposals to implement this requirement. (WT Docket No. 23-388)
Faster Pole Attachment Processes for Broadband Deployment – The Commission will consider a Fourth Report and Order, Declaratory Ruling, and Third Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to promote the deployment of broadband infrastructure by making the pole attachment process faster, more transparent, and more cost-effective by adopting rules allowing for faster resolution of pole attachment disputes and providing pole attachers with more detailed information about the poles they plan to use as part of their broadband buildouts. The Commission will also seek comment on ways to further facilitate the approval process for pole attachment applications and make ready to enable quicker broadband deployment. (WC Docket No. 17-84)
Improving the Rural Health Care Program – The Commission will consider a Third Report and Order to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the Rural Health Care Program. The improvements under consideration would reduce burdens on, and enhance flexibility for, program participants, simplify existing program rules, and free up for other uses unclaimed program support. (WC Docket No. 17-310)
Data Breach Notification Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to update the Commission’s data breach notification rules in order to ensure that providers are held accountable in their obligations to safeguard sensitive customer information, and provide customers with the tools needed to protect themselves in the event that their data is compromised. (WC Docket No. 22-21)
Implementing the Low Power Protection Act – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to implement the Low Power Protection Act by providing eligible low-power television stations with an opportunity to apply for primary status and protect their ability to deliver local programming. (MB Docket No. 23-126)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC To Consider Elimination Of Video Service Early Termination Fees
November 21, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced that the FCC will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) concerning video service billing practices during its December 13, 2023 open meeting. Specifically, if approved, the NPRM will seek comment on the following proposals:
Adoption of customer service protections that prohibit cable operators and direct broadcast satellite (DBS) service providers from imposing a fee for the early termination of a cable or DBS video service contract; and
Adoption of customer service protections to require cable and DBS service providers to grant subscribers a prorated credit or rebate for the remaining whole days in a monthly or periodic billing cycle after the cancellation of service.
FCC Approves Broadband Service Digital Discrimination Rules
November 20, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has adopted a Report And Order And Further Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking containing “final rules to prevent digital discrimination of access to broadband services based on income level, race, ethnicity, color, religion, or national origin.” In general, the new rules in the Report And Order prohibit broadband providers’ policies or practices that (1) differentially impact consumers’ access to broadband internet access service based on their income level, race, ethnicity, color, religion or national origin, or (2) are intended to have such differential impact. In the accompanying Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, the FCC seeks comment on efforts to facilitate equal access, including reporting obligations for broadband providers and the establishment of an FCC Office of Civil Rights. The FCC summarizes its new digital discrimination rules as follows:
Digital Discrimination of Access Defined – The FCC has adopted the following definition of “digital discrimination of access”: “policies or practices, not justified by genuine issues of technical or economic feasibility, that differentially impact consumers’ access to broadband internet access service based on their income level, race, ethnicity, color, religion or national origin, or are intended to have such differential impact.”
Technical and Economic Feasibility – The definition of digital discrimination of access fully takes into account “issues of technical and economic feasibility.” The FCC defines “technically feasible” to mean “reasonably achievable as evidenced by prior success by covered entities under similar circumstances or demonstrated technological advances clearly indicating that the policy or practice in question may reasonably be adopted, implemented, and utilized.” The FCC defines “economically feasible” to mean “reasonably achievable as evidenced by prior success by covered entities under similar circumstances or demonstrated new economic conditions clearly indicating that the policy or practice in question may reasonably be adopted, implemented, and utilized.”
Consumers Afforded Protection from Digital Discrimination, and Entities and Services that Are Subject to the Prohibition Against Digital Discrimination of Access – The FCC has adopted rules focusing on whether policies and practices differentially impact consumers’ access to broadband internet access service or are intended to do so. “Consumer” means current and prospective subscribers to broadband internet access service, including individuals, groups of individuals, organizations, and groups of organizations. Moreover, the scope of the rules extends not only to providers of broadband internet access service, but also to entities that facilitate and otherwise affect consumer access to broadband internet access service. The rules apply to all policies and practices that affect a consumer’s ability to have equal access to broadband internet access service, including but not limited to deployment, network upgrades, and maintenance. Covered elements of service include both technical and non-technical elements of service that may affect a consumer’s ability to receive and effectively utilize the service.
Enforcement Of Digital Discrimination Rules – The new rules prohibiting digital discrimination of access will be enforced through FCC self-initiated investigations, as well as complaints alleging digital discrimination of access.
Consumer Complaints – The FCC has revised its informal consumer complaint process to accept complaints from consumers or other members of the public that relate to digital discrimination of access by establishing a dedicated pathway for digital discrimination of access complaints including from organizations, and collecting voluntary demographic information from complainants.
State and Local Model Policies and Best Practices – The FCC has adopted the Communications Equity and Diversity Council’s recommendations that propose model policies and practices for states and localities to address digital discrimination of access. However, states and localities may adopt additional measures to ensure equal access to broadband service in their communities.
FCC Announces Version 3 Of National Broadband Map – Data As Of June 30, 2023
November 17, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the release of an updated version of the National Broadband Map. It is the third iteration of the map using the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric to display specific location-level information about broadband services available throughout the country. This Version 3 shows location data and broadband availability data as of June 30, 2023. Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel’s announcement includes the following notable highlights:
The number of unserved homes and businesses is going down. The new Map shows that just over 7.2 million locations lack access to high-speed internet service. That’s down from 8.3 million when the second map was released in May. The digital divide is still significant, but it’s narrowing.
Broadband buildouts are happening. Providers are connecting more locations to high-speed internet services thanks to the Commission’s Rural Digital Opportunity Fund and Connect America Fund, in addition to other federal, state and privately funded programs and projects. And that’s before the deployments funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law kick-in.
Challenges, verifications and audits are all making the Map better. Robust participation in the challenge processes continues to play a valuable role in correcting data shown on the Map. To be specific, the results of 4.8 million challenges to provider reported availability information and over 1.5 million accepted location challenges. Since our last release, we’ve initiated mobile coverage audits in a number of states. We’ve also seen hundreds of corrections to provider reported data based on FCC-initiated verification efforts.
The fluctuations in our location data are getting smaller. This is what you want and expect to see with each new Fabric release. The number of broadband serviceable locations on the current Map is up to 115 million, an increase of 800,000 since May 2023. Looking ahead, we expect that any changes in the number of locations will overwhelmingly reflect on-the-ground changes such as the construction of new housing.
Stakeholder engagement continues to yield results. Providers are continuing to refine their data matching and reporting, challengers are sharpening their evidence, and stakeholders are sharing crowdsource submissions that help us to identify service provider data that may warrant heightened review.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Mutual Telephone Company of Sioux Center, Iowa d/b/a Premier Communications Acquiring Royal Telephone Company of Iowa
November 17, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 application filed by Royal Telephone Company and Mutual Telephone Company of Sioux Center, Iowa d/b/a Premier Communications, requesting approval for the transfer of control of Royal to Premier through a merger transaction by which Noble Acquisition, Inc. will be merged with and into Royal, with Royal surviving that merger. Both companies hold blanket domestic Section 214 authorizations under section 63.01 of the FCC’s rules. Comments are due on or before December 1, 2023. Reply comments are due December 8, 2023.
Royal Telephone Company is an Iowa rural incumbent local exchange carrier (LEC) that provides local and long-distance telecommunications, high-speed Internet access, and access services to roughly 300 residential and business customers in the Royal, Iowa exchange. Royal currently receives Connect America Fund (CAF) Broadband Loop support and high-cost loop support, but has elected to receive Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) support beginning January 1, 2024. No person owns a 10% or greater interest in Royal.
Premier Communications is an Iowa rural incumbent LEC that currently provides local exchange telecommunications service, access service, Internet, and advanced communications services to approximately 3,500 customers in the Sioux Center, Iowa exchange. Premier wholly owns several incumbent LEC and competitive LEC affiliate providers of local exchange service in the state of Iowa. No person owns a 10% or greater interest in Premier.
Pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Merger, Premier Communications will acquire all or substantially all telecommunications operations and assets, property, rights, and interest from Royal to provide broadband and other communications services in and around Royal, Iowa. Upon completion of the transaction, services will be provided by Royal as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Premier Communications. The Section 214 application has been accepted for non-streamlined processing because of the complexity of the proposed transaction.
Lowering Broadband Costs for Consumers Act Introduced In Senate; Would Require Edge Providers & Broadband Providers To Make USF Contributions
November 16, 2023 – Senators Markwayne Mullin (R-OK), Mark Kelly (D-AZ), and Mike Crapo (R-ID) have introduced the Lowering Broadband Costs for Consumers Act of 2023. The primary purpose of the legislation is to require internet edge service providers and broadband service providers to contribute to the universal service fund (USF). If enacted, the bill would require the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to complete a rulemaking to expand the USF contribution base so that broadband providers and edge providers, except those edge providers that earn less than $5 billion in annual revenue, contribute to the USF on an equitable and non-discriminatory basis. The bill defines an “edge provider” as a provider of online content or services, including a digital advertising service, a search engine, a social media platform, a streaming service, an app store, a cloud computing service, an over-the-top messaging service, or any other service that enables texting, a videoconferencing service, a video gaming service, and an e-commerce platform.
Senator Mullin’s press release announcing the Lowering Broadband Costs for Consumers Act explains that the bill would do the following:
Direct the FCC to reform the USF by expanding the base so that edge providers and broadband providers contribute on an equitable and nondiscriminatory basis to preserve and advance universal service.
Limit assessments of edge providers to only those with more than 3% of the estimated quantity of broadband data transmitted in the United States and more than $5 billion in annual revenue.
Direct the FCC to adopt a new mechanism under the current USF high-cost program to provide specific, predictable, and sufficient support for expenses incurred by broadband providers that are not otherwise recovered.
Limit the FCC’s authority over edge providers and broadband providers only to requiring contributions to the USF.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Macquarie Infrastructure Acquiring Control Of CableSouth Media III, LLC d/b/a Swyft Fiber
November 16, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 transfer of control application filed by Hunt Group Holdings, LLC, ITC Holdings, LLC, CableSouth Media III, LLC d/b/a Swyft Fiber (CableSouth), and MIP VI Outlier, LLC, requesting consent to transfer control of CableSouth to MIP VI Outlier. Comments are due on or before November 30, 2023. Reply comments are due December 7, 2023.
CableSouth, a Tennessee LLC, primarily provides broadband, video, and interconnected VoIP services to residential customers throughout the Southeastern U.S., using the brand names “SwyftConnect” and “Swyft Fiber.” It was awarded $152.9 million in Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) support to deploy fiber-to-the-home broadband service to 57,387 locations across Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi.
CableSouth is ultimately wholly owned by CSM Holding Company, LLC (CSM Holding). Hunt Group Holdings, a Louisiana LLC, currently owns 65% of the equity in CSM Holding, while ITC Holdings, a Delaware LLC, owns the remaining 35 percent. Hunt Group has the right to appoint four of the six managers on the board of CSM Holding, with ITC Holdings appointing two. ITC Holdings has veto rights over certain business decisions and activities of CableSouth that, coupled with its ownership stake, provides ITC Holdings with a de facto controlling interest in CableSouth.
MIP VI Outlier, LLC is indirectly owned by investment vehicles managed by or affiliated with Macquarie Infrastructure Partners Inc. (MIP Inc.), which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Macquarie Infrastructure and Real Assets Inc. (MIRA Inc.). MIRA Inc. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Macquarie Holdings (U.S.A.) Inc., which is held by various intermediate Australian entities ultimately held by Macquarie Group Limited (MGL), a publicly traded company incorporated in Australia.
Pursuant to a membership interest purchase agreement, MIP VI Outlier will acquire at least 50% of the equity value of CSM Holding, which MIP VI Outlier will purchase directly from CSM Holding. Also, MIP VI Outlier will acquire 50 percent of the voting and certain approval rights. More specifically, when the deal closes, MIP VI Outlier will have the right to appoint four of the eight managers to the board of managers of CSM Holding, with the other four appointed by Hunt Group. Thus, at closing, MIP VI Outlier and Hunt Group will each have a 50% voting interest in CSM Holding, and ITC Holdings will no longer have any interest in either CSM Holding or CableSouth.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Premier Communications Acquiring Infrastructure & Customers In Iowa Great Lakes Area From IGL Teleconnect
November 14, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 application filed by Great Lakes Communication Corp. d/b/a IGL Teleconnect (GLCC) and Mutual Telephone Company of Sioux Center, Iowa d/b/a Premier Communications (Premier Communications), requesting consent for the acquisition of certain assets of GLCC by Mutual. Comments are due on or before November 28, 2023. Reply comments are due December 5, 2023.
GLCC is an Iowa corporation that provides service as a competitive local exchange carrier (LEC) to approximately 2,700 residential and business customers in the rural exchanges of Milford, Lake Park, and Spencer, Iowa. It also provides Internet services in the counties of Buena Vista, Clay, Dickinson, Emmet, and Osceola, Iowa.
Premier Communications is an Iowa corporation that provides service as a rural incumbent LEC to approximately 3,500 customers in the Sioux Center, Iowa exchange. Premier Communications wholly owns the following incumbent LEC and competitive LEC providers of local exchange service: Northern Iowa Telephone Company, an incumbent LEC providing service in the exchanges of Hinton, Matlock, Maurice, Sanborn, Little Rock, and Granville, Iowa; Webb Dickens Telephone Corporation, an incumbent LEC providing service in the exchanges of Dickens and Webb, Iowa; Heartland Telecommunications Company of Iowa, an incumbent LEC providing service in the exchanges of Akron, Boyden, Doon, Hawarden Hull, Ireton, Rock Rapids, Rock Valley, and Sibley, Iowa, the exchange of North Rock Rapids, Minnesota, and the exchanges of West Akron and West Hawarden, South Dakota; and Premier Communications, Inc., a competitive LEC providing service in the exchanges of Akron, Ashton, Boyden, Doon, Hull, Ireton, Rock Valley, Rock Rapids, LeMars, Ocheyedan, Orange City, George, Merrill, Arnolds Park, Lake Park, Milford, Sheldon, and Spirit Lake, Iowa.
Pursuant to an asset purchase agreement, Premier Communications will acquire from GLCC fixed wireless and fiber-based broadband and telecommunications retail assets, property, rights, and interests (including all customer contracts and customer relationships) used to provide Internet, telephone, video, and other communications services in and around the Iowa Great Lakes area. Upon completion of the transaction, these communications services will be provided by Premier. The application has been accepted for streamlined treatment by the Bureau.
FCC Proposes Creation Of Schools And Libraries Cybersecurity Pilot Program - $200 Million In Funding Over Three Years
November 13, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that proposes the creation of a Schools and Libraries Cybersecurity Pilot Program. Comments on the NPRM are due on or before 30 days after the NPRM is published in the Federal Register. Reply comments are due 60 days after publication. If ultimately approved, the Pilot Program will provide universal service funding “to eligible K-12 schools and libraries to defray the qualifying costs of receiving the cybersecurity and advanced firewall services needed to protect their E-Rate-funded broadband networks and data from the growing number of K-12 school- and library-focused cyber events.” The purpose of the Pilot Program is two-fold: it will allow FCC to “obtain valuable data concerning the cybersecurity and advanced firewall services that would best help K-12 schools and libraries address the growing cyber threats and attacks against their broadband networks and data”; and it will help the FCC “better understand the most effective way USF support could be used to help schools and libraries address these significant [cybersecurity] concerns while promoting the E-Rate program’s longstanding goal of promoting basic connectivity.” The following is a high-level summary of key details of the proposed Schools and Libraries Cybersecurity Pilot Program:
Pilot Program Budget: The FCC proposes a budget of $200 million over the three-year duration of the proposed program.
Pilot Program Duration: The FCC propose that the Pilot Program will make funding available to participants for a three-year term.
Pilot Program Structure: The proposed program will be structured similar to the Connected Care Pilot Program. After submitting an application, selected schools and libraries will be provided an opportunity to apply for funding for eligible services and equipment. Participants will then receive a funding commitment to acquire equipment or services, and submit invoices for reimbursement. The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) will be appointed as the permanent administrator of the program.
Pilot Program Goals: (1) improving the security and protection of E-Rate-funded broadband networks and data; (2) measuring the costs associated with cybersecurity and advanced firewall services, and the amount of funding needed to adequately meet the demand for these services if extended to all E-Rate participants; and (3) evaluating how to leverage other federal K-12 cybersecurity tools and resources to help schools and libraries effectively address their cybersecurity needs.
NTIA Releases National Spectrum Strategy – NTIA To Study Repurposing 2,786 Megahertz Of Spectrum Across Five Bands
November 13, 2023 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has released the Biden Administration’s long-awaited National Spectrum Strategy, which “identifies 2,786 megahertz of spectrum across five spectrum bands for in-depth study to determine suitability for potential new uses.” Specifically, the strategy calls for NTIA to complete a study within two years of the following spectrum bands for potential repurposing: 3.1-3.45 GHz; 5.03-5.091 GHz; 7.125-8.4 GHz; 18.1-18.6 GHz; and 37.0-37.6 GHz. The National Spectrum Strategy is divided into four “pillars,” each of which contain an essential actions for ensuring that spectrum policy advances U.S. innovation, economic vitality, and security:
Pillar 1: A Spectrum Pipeline to Ensure U.S. Leadership in Advanced and Emerging Technologies. Spectrum availability is not just a long-term challenge. Technological advances require more efficient spectrum use today.
Pillar 2: Collaborative Long-Term Planning to Support the Nation’s Evolving Spectrum Needs. A vast range of private stakeholders and government agencies need spectrum to deliver essential products and services. Long-term decisions about spectrum allocation, therefore, must involve broad-based input and transparent processes, which will help spectrum users make prudent long-term investments.
Pillar 3: Unprecedented Spectrum Access and Management Through Technology Development. Cutting-edge spectrum technologies and techniques like spectrum sharing hold great promise for promoting efficient use and ensuring that—even though spectrum is finite—the U.S. is able achieve spectrum abundance for all users. To accelerate spectrum innovation and ensure that the U.S. remains at the leading edge in this critical technology, the Strategy announces an ambitious effort under which the U.S. government will, within 12-18 months, advance research, create investment incentives, and set forth measurable goals to advance spectrum access technology.
Pillar 4: Expanded Spectrum Expertise and Elevated National Awareness. America’s long-term spectrum innovation depends on its leading-edge spectrum workforce, as well as broader public appreciation for spectrum’s vital role in our society.
FCC Sets Final Agenda For November 15 Open Meeting
November 8, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its open meeting on Wednesday, November 15, 2023. The meeting will be streamed live online at www.fcc.gov/live.
1. Preventing Digital Discrimination – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to establish a framework to facilitate equal access to broadband internet access service by preventing digital discrimination of access and seek additional comment on matters pertaining to the Commission’s administration of Section 60506 of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and our efforts to facilitate equal access. (GN Docket No. 22-69)
2. Empowering Survivors of Domestic Violence – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would adopt rules to implement the Safe Connections Act of 2022 to help survivors of domestic violence and similar crimes separate lines from shared mobile accounts that include their abusers, protect the privacy of calls made by survivors to domestic abuse hotlines, and support survivors who face financial hardship through the Commission’s affordability programs. (WC Docket Nos. 22-238, 11-42, 21-450)
3. Understanding Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Robocalls and Robotexts – The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry seeking to better understand the implications of Artificial Intelligence technologies as part of the Commission’s ongoing efforts to protect consumers from unwanted and illegal telephone calls and text messages under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA). (CG Docket No. 23-362)
4. Protecting Consumers from SIM Swapping and Port-Out Fraud – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would adopt rules to protect consumers from SIM swap and port-out fraud, two fraudulent practices that bad actors use to take control of consumers’ cell phones, and would also seek comment on whether to harmonize the Commission’s existing requirements governing customer access to customer proprietary network information with the new SIM change authentication and protection measures in the Report and Order. (WC Docket No. 21-341)
5. Amending Amateur Radio Rules for Greater Flexibility in Data Communications – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would eliminate the symbol rate (also known as baud rate) limitation and establish a bandwidth limitation that would provide flexibility to use modern digital emissions, thereby promoting innovation and experimentation in the amateur service. The item would also propose the removal the baud rate limitation in several additional bands. (WT Docket No. 16-239)
6. Reducing Regulatory Requirements for Rural Provider of Long-Distance Access Service – The Commission will consider a Declaratory Ruling and Memorandum Opinion and Order that would grant the Minnesota Independent Equal Access Corporation (MIEAC) relief from dominant carrier regulation with respect to its provision of centralized equal access (CEA) service, and regulate MIEAC as a non-dominant competitive LEC for this service going forward. In light of declining demand, intervening exchange access service regulatory reforms, and technological changes in the voice services marketplace generally, dominant carrier regulation of MIEAC’s CEA service is no longer necessary to serve the public interest. (WC Docket No. 22-407)
7. Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
8. Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
9. Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Mergers & Acquisitions: H.N.G. Holdings Acquiring Campti-Pleasant Hill Telephone Co. & CP-TEL Network Services From Epic Touch
November 8, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 application filed by Epic Touch Co., Inc. and H.N.G. Holdings, L.L.C., requesting consent to transfer control of CP-TEL Holdings, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiaries Campti-Pleasant Hill Telephone Co., Inc. and CP-TEL Network Services, Inc., from Epic Touch to H.N.G. Holdings. Comments are due on or before November 22, 2023. Reply comments are due November 29, 2023.
Epic Touch, a holding company incorporated in Kansas, owns and operates the following entities: (1) the Elkhart Telephone Company, a Kansas rural ILEC; and (2) CP TEL Holdings, Inc., a Louisiana holding company. CP Tel Holdings wholly owns the following entities: (a) Campi-Pleasant Hill, a Louisiana corporation and rural LEC that provides local exchange and exchange access services in portions of the Natchitoches, Sabine, DeSoto, and Red River Parishes in northwestern Louisiana; and (b) CP-TEL Network Services, Inc, a Louisiana competitive LEC serving portions of Natchitoches, Sabine, DeSoto, and Red River Parishes in northwestern Louisiana.
H.N.G. Holdings, L.L.C., is a Louisiana holding company that wholly owns: (1) Northeast Louisiana Telephone Company, Inc., a Louisiana rural LEC; and (2) Northeast Long Distance, LLC, a Louisiana limited liability company that provides long distance toll services in Morehouse and Ouachita Parishes. Northeast Louisiana Telephone wholly owns Northeast Telephone Services, Inc., a Louisiana corporation that provides competitive LEC and other services in portions of Morehouse and Ouachita Parishes in northeastern Louisiana.
Pursuant to the terms of the proposed transaction, H.N.G. Holdings will purchase from Epic Touch all of the issued and outstanding stock of CP TEL Holdings. As a result, H.N.G. Holdings will indirectly wholly own Campti-Pleasant Hill and CPTN. Due to the complexity of the transaction, the Wireline Bureau has accepted the Section 214 application for non-streamlined processing.
Consumers’ Research Group Files Objection To USAC’s Projected USF Funding Requirements For 1Q 2024
November 7, 2023 – Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 12 individual consumers have filed comments and objections in response to the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) federal universal service support mechanisms fund size projections for the first quarter 2024. USAC’s filing details the universal service fund’s (USF) total projected funding requirements for 1Q 2024, which includes costs that can be directly attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each mechanism. The FCC will use the data to issue the universal service contribution factor for the first quarter of 2024. The Consumers’ Research group claims the USF “is an unconstitutional tax raised and spent by an unaccountable federal agency–which in turn has delegated almost all authority over this revenue-raising scheme to a private company registered in Delaware.”
Mergers & Acquisition: DISH Network Selling Spectrum & Prepaid Subscribers In Puerto Rico And U.S. Virgin Islands To Liberty Latin America
November 6, 2023 – Liberty Latin America Ltd. has entered into an agreement with DISH Network to acquire DISH spectrum assets in Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, as well as approximately 120,000 prepaid mobile subscribers in those markets in exchange for cash and international roaming credits. Liberty Latin America’s aggregate asset purchase price is $256 million, which will be paid in four annual installments. The transaction is subject to closing conditions and regulatory approvals, and is expected to close in 2024.
USAC Files First Quarter 2024 USF Size Projections
November 2, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed the fund size and administrative cost projections for the federal universal service support mechanisms for the first quarter of calendar year 2024. USAC’s filing shows the following total projected 1Q 2024 funding requirements for each federal Universal Service Fund (USF) support mechanism:
High Cost Support Mechanism – $1.09 billion
Low Income Support Mechanism – $225.47 million
Rural Health Care Support Mechanism – $168.60 million
Connected Care Pilot Program – There is no remaining collection requirement for the Connected Care Pilot Program. Based on 3Q2023 activity, there is a prior period adjustment for the Connected Care Pilot Program of ($0.51) million.
E-Rate Schools and Libraries Support Mechanism – $631.45 million
USAC projects a consolidated budget of $71.54 million for 1Q 2024. This breaks out into $34.19 million in direct costs for all USF support mechanisms, and $37.35 million in total joint and common costs which include costs associated with billing, collection, and disbursement of universal service funds. The FCC will use the of the quarterly funding requirements for the four USF support mechanisms, the projected administrative expenses, and the USF contribution base amount, to establish a quarterly USF contribution factor. Then, USAC will bill USF contributors on a monthly basis for their individual obligations based on the USF contribution factor, collect these owed amounts, and distribute USF support to eligible recipients.
FCC Issues Section 706 Broadband Availability Notice Of Inquiry – Proposes To Increase Definition Of Fixed Broadband To 100/20 Mbps
November 1, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released the Seventeenth Section 706 Report Notice Of Inquiry, initiating the FCC’s next annual assessment concerning the “availability of advanced telecommunications capability to all Americans.” Comments in response to the NOI are due on or before December 1, 2023. Reply comments are due December 18, 2023. In the NOI, the FCC proposes to increase the FCC’s definition for fixed broadband to 100 Mbps downstream and 20 Mbps upstream. It currently stands at 25/3 Mbps. This year’s inquiry will be the first to use the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection (BDC) data. The FCC also has proposed to focus the broadband availability inquiry on the universal service goals of Section 706 – universal deployment, affordability, adoption, availability, and equitable access to broadband throughout the country.
Section 706(b) of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 requires the FCC to annually inquire whether advanced telecommunications capability is being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion. In the statute, the term “advanced telecommunications capability” is defined, without regard to any transmission media or technology, as high-speed, switched, broadband telecommunications capability that enables users to originate and receive high-quality voice, data, graphics, and video telecommunications using any technology. If the FCC determines that broadband is not being deployed in a reasonable and timely fashion, Section 706(b) requires the FCC to take immediate action to accelerate broadband deployment by removing barriers to infrastructure investment and promoting competition.
USAD Announces $274 Million In Broadband Funding Awards – 14 ReConnect Awards & 1 Telecommunications Infrastructure Award
November 1, 2023 – The U.S. President Biden and U.S. Department of Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack have announced nearly $274 million in grants and loans under the ReConnect Program and the Telecommunications Infrastructure Program. A total of 14 projects have received ReConnect awards, and one project received a Telecommunications Infrastructure award. Total funding is $273,620,959, which breaks down to $45,443,175 in loans and $228,177,784 in grants. The awarded broadband projects will benefit 35,886 people and will cover the following states: Alaska, Arizona, Illinois, Michigan, Missouri, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Disney Purchasing Remaining Stake In Hulu From Comcast
November 1, 2023 – The Walt Disney Company has announced it will acquire the remaining 33% stake in Hulu, LLC held by Comcast Corporation. Comcast triggered the deal following its “November 1 exercise of its right under the put/call arrangement between the two companies.” Disney expects to pay at least $8.61 billion to gain full control of Hulu. Disney provided the following details in its announcement of the acquisition:
Under the terms of the put/call arrangement, by December 1, Disney expects it will pay NBCU approximately $8.61 billion, representing NBCU’s percentage of the $27.5 billion guaranteed floor value for Hulu that was set when the companies entered into their agreement in 2019 minus the anticipated outstanding capital call contributions payable by NBCU to Disney. Under the appraisal process agreed to by Disney and Comcast, Hulu’s equity fair value will be assessed as of September 30, 2023, and if the value is ultimately determined to be greater than the guaranteed floor value, Disney will pay NBCU its percentage of the difference between the equity fair value and the guaranteed floor value. While the timing of the appraisal process is uncertain, we anticipate it should be completed during the 2024 calendar year.
October 2023
FCC Authorizes 368 Rate-Of-Return Companies To Receive Enhanced A-CAM Support
October 30, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has authorized 368 rate-of-return carriers to receive model-based Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (Enhanced A-CAM) support. Carriers that have elected Enhanced A-CAM will receive a 15-year period of support beginning January 1, 2024, in exchange for deploying broadband service of at least 100/20 Mbps speeds to over 700,000 unserved locations across the U.S., and maintaining or improve existing 100/20 Mbps broadband service to approximately 2 million locations. Authorized Enhanced A-CAM support totals $18,281,852,513 over the 15-year term. Along with the Public Notice, the Bureau has released Authorization Report 1, which shows each carrier’s authorization amount and initial deployment obligations. Additional information, including each carrier’s election letter, are available from the FCC’s rate-of-return resources website.
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For November 15 Open Meeting
October 25, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Wednesday, November 15, 2023:
Preventing Digital Discrimination – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to establish a framework to facilitate equal access to broadband internet access service by preventing digital discrimination of access and seek additional comment on matters pertaining to the Commission’s administration of Section 60506 of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and our efforts to facilitate equal access. (GN Docket No. 22-69)
Empowering Survivors of Domestic Violence – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would adopt rules to implement the Safe Connections Act of 2022 to help survivors of domestic violence and similar crimes separate lines from shared mobile accounts that include their abusers, protect the privacy of calls made by survivors to domestic abuse hotlines, and support survivors who face financial hardship through the Commission’s affordability programs. (WC Docket Nos. 22-238, 11-42, 21-450)
Understanding Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Robocalls and Robotexts – The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry seeking to better understand the implications of Artificial Intelligence technologies as part of the Commission’s ongoing efforts to protect consumers from unwanted and illegal telephone calls and text messages under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA). (CG Docket No. 23-362)
Protecting Consumers from SIM Swapping and Port-Out Fraud – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would adopt rules to protect consumers from SIM swap and port-out fraud, two fraudulent practices that bad actors use to take control of consumers’ cell phones, and would also seek comment on whether to harmonize the Commission’s existing requirements governing customer access to customer proprietary network information with the new SIM change authentication and protection measures in the Report and Order. (WC Docket No. 21-341)
Amending Amateur Radio Rules for Greater Flexibility in Data Communications – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would eliminate the symbol rate (also known as baud rate) limitation and establish a bandwidth limitation that would provide flexibility to use modern digital emissions, thereby promoting innovation and experimentation in the amateur service. The item would also propose the removal the baud rate limitation in several additional bands. (WT Docket No. 16-239)
Reducing Regulatory Requirements for Rural Provider of Long-Distance Access Service – The Commission will consider a Declaratory Ruling and Memorandum Opinion and Order that would grant the Minnesota Independent Equal Access Corporation (MIEAC) relief from dominant carrier regulation with respect to its provision of centralized equal access (CEA) service, and regulate MIEAC as a non-dominant competitive LEC for this service going forward. In light of declining demand, intervening exchange access service regulatory reforms, and technological changes in the voice services marketplace generally, dominant carrier regulation of MIEAC’s CEA service is no longer necessary to serve the public interest. (WC Docket No. 22-407)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
President Biden Requests Supplemental Funding For Affordable Connectivity Program And Rip & Replace Program
October 25, 2023 – President Biden has called for Congress to appropriate supplemental funding to support the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program and Rip & Replace Program. The requests for supplemental funding for the two FCC programs are part of a larger set of funding requests for what the Biden Administration calls critical domestic priorities and urgent needs.
Affordable Connectivity Program – $6 Billion – For the FCC to extend free and discounted high-speed internet through the Affordable Connectivity Program for tens of millions of low-income households through December 2024.
Rip & Replace Program – $3.1 Billion – For the FCC to reimburse communications providers for the ongoing removal of insecure equipment and software from U.S. communications infrastructure.
FCC Approves E-Rate Funding For Wi-Fi On School Buses
October 25, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Declaratory Ruling “clarifying that the use of Wi-Fi, or other similar technologies that act as an access point, on school buses is an educational purpose as defined by E-Rate program rules and, therefore, the provision of such service is eligible for E-Rate funding.”
The schools and libraries universal service support mechanism – E-Rate Program – provides universal service fund support for the provision of broadband services to schools and libraries. The FCC’s E-Rate rules require schools and libraries to use E-Rate-supported services “primarily for educational purposes.” For schools, “educational purposes” are defined as “activities that are integral, immediate, and proximate to the education of students.” The E-Rate program does not provide support for most off-campus services. However, the FCC has allowed E-Rate support for off-campus services when those services are “integral, immediate, and proximate to the education of students or the provision of library services to library patrons, and thus, would be considered to be an educational purpose.”
In the Declaratory Ruling, the FCC concludes that “the use of Wi-Fi, or other similar access point technologies, on school buses serves an educational purpose,” and the use of Wi-Fi on school buses “is integral, immediate, and proximate to the education of students.” Accordingly, Wi-Fi or other similar access point services and equipment that enable them are eligible for E-Rate Program funding.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Shentel Acquiring Horizon Companies Of Ohio
October 24, 2023 – Shenandoah Telecommunications Company has announced it has entered into an agreement to acquire 100% of the equity interests in Horizon Acquisition Parent LLC for $385 million, which consists of $305 million in cash and $80 million of Shentel common stock. Horizon Acquisition Parent LLC is the parent company of two wholly-owned subsidiaries that hold domestic Section 214 authorizations: The Chillicothe Telephone Company and Horizon Technology, Inc. The press release announcing the transaction provides the following information on Horizon’s operations:
Horizon is a leading commercial fiber provider in Ohio and adjacent states serving national wireless providers, carriers, enterprises, and government, education and healthcare customers. Horizon’s unique 7,200 route-mile fiber network is the largest and most dense network across its footprint with over 9,000 on-net locations. Approximately 64% of Horizon’s revenues are derived from their commercial customers. Based in Chillicothe, Ohio, Horizon was founded in 1895 as the incumbent local exchange carrier (“ILEC”) in Ross County, Ohio and rapidly expanded its fiber network over the past 14 years. Most recently, Horizon has pursued a strategy of investing in Fiber-to-the-Home (“FTTH”) in tier 3 & 4 markets in Ohio and currently passes 14,000 homes and businesses with fiber in its ILEC market and 18,000 homes in new, greenfield markets adjacent to its commercial fiber network.
FCC Begins Net Neutrality Rulemaking Proceeding
October 20, 2023 – By a vote of 3-2, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has approved a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) which aims to reclassify broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service under Title II of the Communications Act. If ultimately approved, the NPRM would reestablish the FCC’s authority over broadband services and apply net neutrality rules to internet service providers. The proposed net neutrality rules would prohibit ISPs “from blocking legal content, throttling speeds, and creating fast lanes that favor those who can pay for access.” Comments in response to the NPRM are due on or before December 14, 2023. Reply comments are due January 17, 2024.
FCC Fines Lumen $867,000 For Two 911 Outages
October 17, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture against Lumen Technologies, Inc. for “apparently willfully and repeatedly failing to reasonably design and operate its network to ‘transmit all 911 calls,’ and to ‘notify, as soon as possible’ Public Safety Answering Points (PSAPs) for two 911 outages that occurred in February 2022.” For violating Sections 4.9 and 9.4 of the FCC’s rules and deploying an insufficient 911 system, Lumen has been assessed a penalty of $867,000. Lumen’s two 911 outages are summarized in the Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture:
On February 17, 2022, Lumen experienced an outage affecting 911 calls in South Dakota that lasted for almost five hours (First 911 Outage). Because of flaws in its system to notify PSAPs, Lumen did not notify the two affected PSAPs until days after the outage had ended. On February 22, 2022, Lumen experienced another 911 outage, this time related to its Bismarck, North Dakota switch (Second 911 Outage). This outage disrupted 911 service for more than seven hours in North Dakota. Similarly, because of flaws in its PSAP notification system, Lumen managed to notify only two of eleven affected PSAPs in a timely manner. This outage resulted in hundreds of calls failing to reach 911 emergency call centers.
FCC Chairwoman Circulates NPRMs That Propose Customer Rebates For TV Blackouts
October 11, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced she has circulated two Notices of Proposed Rulemaking that will seek comment on “rebates for consumers and requiring notifications to the Commission of blackouts lasting more than 24 hours.” The FCC News Release announcing the items includes the following high-level summaries of the NPRMs:
A Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that seeks comment on whether and how to require cable and satellite providers to issue rebates to subscribers in the event of a blackout due to a failure to reach a retransmission consent agreement with broadcast station(s)/group owners.
A Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that seeks comment on a proposal to require Multichannel Video Program Distributors (MVPDs) to notify the Commission via an online public portal when there is a blackout of 24 hours or more of broadcast programming due to a failure to reach a retransmission consent agreement.
FCC Announces Compliance Dates For Broadband Consumer Label Rules
October 10, 2023 – The FCC’s Consumer And Governmental Affairs Bureau has announced the compliance dates for the FCC’s broadband consumer label rules. Broadband providers with 100,000 or fewer subscribers must comply with the requirements to display broadband labels as of October 10, 2024. All other broadband providers must display broadband labels as of April 10, 2024. Compliance with the requirement in Section 8.1(a)(2) to make labels accessible in online account portals is required for all broadband providers as of October 10, 2024. Compliance with the requirement in Section 8.1(a)(3) to make information in broadband labels available in a machine-readable format is required for all providers as of October 10, 2024.
FCC Announces Carriers That Elected Enhanced A-CAM Support
October 4, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has announced carriers that have accepted offers of model-based Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) support. Also, the Bureau has confirmed that the number of acceptances has exceeded the minimum carrier participation threshold set by the FCC in the Enhanced A-CAM Order, which means the Enhanced A-CAM program will proceed. Carriers were required to elect support on a state-by-state basis. A complete list of carriers that selected Enhanced A-CAM is available here.
FCC Fines DISH $150,000 For Space Junk
October 2, 2023 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has entered into a Consent Decree with DISH Operating L.L.C. to resolve an “investigation into whether DISH failed to move its direct broadcast satellite (DBS) service EchoStar-7 satellite to the proper disposal orbit at the satellite’s end-of-life as required by DISH’s license terms and conditions.” As a result of the investigation, the Enforcement Bureau determined “DISH disposed of the EchoStar-7 satellite at 122 kilometers (km) above its operational geostationary orbit, short of the 300 km above its operational geostationary orbit specified in its orbital debris mitigation plan in DISH’s license.” Pursuant to the terms of the Consent Decree, “DISH admits that it failed to operate the EchoStar 7 satellite in accordance with its authorization, will implement a compliance plan, and will pay a $150,000 civil penalty.” The Consent Decree is the first space debris enforcement action by the FCC.
September 2023
TDS Accepts Enhanced A-CAM Support In 24 States
September 28, 2023 – TDS Telecommunications LLC has announced it has elected to receive Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) support from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in 24 states that it serves. Carriers that opt in to the Enhanced A-CAM program will receive model-based funding for a 15-year term beginning in 2024 in exchange for deploying 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband service and voice service to all locations in their service areas by the end of 2028. TDS has been part of the A-CAM program since 2016. Under the Enhanced A-CAM support program, TDS will be required to “deploy high-speed internet to more than 270,000 locations.” TDS Senior Vice President of Corporate Affairs Drew Petersen included the following remarks in the press release announcing the Enhanced A-CAM election:
“It is a landmark day for TDS and our customers. With this program, TDS and the federal government are ensuring quality, high-speed internet in our rural service areas. We are grateful for the support from Chairwoman Rosenworcel and all the commissioners. Together we are taking a crucial step forward in closing the digital divide in America.”
Tentative Agenda For FCC Open Meeting On October 19th
September 28, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, October 19, 2023:
Open Internet NPRM – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that proposes to reestablish the Commission’s authority over broadband Internet access service by classifying it as a telecommunications service under Title II of the Communications Act, which would allow the Commission to protect consumers by issuing straightforward, clear rules to prevent Internet service providers from engaging in practices harmful to consumers, competition, and public safety; establish a uniform, national regulatory approach rather than disparate requirements that vary state-by-state; strengthen the Commission’s ability to secure communications networks and critical infrastructure against national security threats; and enable the Commission to protect public safety during natural disasters and other emergencies. (WC Docket No. 23-320)
School Bus Wi-Fi Declaratory Ruling – The Commission will consider a Declaratory Ruling that would clarify that the use of Wi-Fi on school buses is an educational purpose and the provision of such service is therefore eligible for E-Rate funding. (WC Docket No. 13-184)
Broadband Connectivity and Maternal Health; Updating the Mapping Platform – The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry that will seek comment on its proposed plan to improve and enhance maternal health data in the Mapping Broadband Health in America platform, in order to ensure that future updates to the platform reflect input from stakeholders and other interested parties and improves the user experience. The platform was updated in June 2023 to incorporate publicly available data on maternal mortality and severe maternal morbidity pursuant to the Data Mapping to Save Moms’ Lives Act. (GN Docket No. 23-309)
Unlicensed Use of the 6 GHz Band – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order that would expand unlicensed use of the 6 GHz band by permitting very low power devices to operate in two sub-bands, a Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to expand very low power device operations to the remainder of the band, and a Memorandum Opinion and Order that would address a remand from a court challenge of a previous decision in the docket. (ET Docket No. 18-295; GN Docket No. 17-183)
Support for Alaska Connectivity – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking seeking comment on the use of high-cost program funding to continue supporting fixed and mobile services in Alaska. The accompanying Report and Order makes administrative changes to streamline high-cost program rules. (WC Docket Nos. 10-90, 16-271, WT Docket No. 10-208)
Improving Wireless Emergency Alerts – The Commission will consider a Report and Order that would improve Wireless Emergency Alerts by making WEA messages available in additional languages, including American Sign Language (ASL); supporting maps that show the location of an emergency; making it easier to conduct public-facing WEA performance and public awareness tests; and providing alert originators and members of the public with access to information about where and how WEA is available within their communities. (PS Docket Nos. 15-91, 15-94)
Accessible Video Programming – The Commission will consider a Second Report and Order that will enhance support for individuals who are blind or visually impaired by expanding audio description requirements to additional market areas. The Order would help ensure that a greater number of individuals who are blind or visually impaired can be connected, informed, and entertained by television programming. (MB Docket No. 11-43)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC Chair Announces NPRM To Restore Net Neutrality Rules
September 26, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Rosenworcel has announced she has circulated a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that proposes to restore net neutrality rules that apply to internet service providers. The full FCC will vote on the NPRM at its October 19th open meeting, and if approved, the FCC will open a net neutrality rulemaking and take public comment and reply comments on the proposed rules. Chairwoman Rosenworcel also gave a speech announcing the NPRM and explaining the reasons for restoring net neutrality rules. A fact sheet accompanying the announcement includes the following high-level description of the NPRM and proposed rules:
Openness – Establish basic rules for Internet Service Providers that prevent them from blocking legal content, throttling your speeds, and creating fast lanes that favor those who can pay for access.
Security – Reclassify broadband internet access to give the FCC and its national security partners the tools needed to defend our networks from potential security threats.
Safety – Allow the FCC to enhance the resiliency of broadband networks and bolster efforts to require providers to notify the FCC and consumers of internet outages.
Nationwide Standard – Establish a uniform national standard rather than a patchwork of state-by state approaches, benefiting consumers and Internet Service Providers.
FCC Seeks Further Comment On 5G Fund For Rural America
September 21, 2023 – The FCC has issued a Further Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking (FNPRM) on implementing the 5G Fund for Rural America (5G Fund) to support the deployment of high-speed, 5G mobile services. The new 5G Fund was first established in 2020 to distribute up to $9 billion to bring voice and 5G mobile broadband service to rural areas of the country unlikely to otherwise see unsubsidized deployment of 5G-capable networks. By releasing the FNPRM, the FCC seeks to refresh the record on expanding the deployment of 5G service and requests public comment on the following key issues and questions:
Whether to modify the $9 billion 5G Fund budget;
How to best aggregate areas eligible for support to minimum geographic areas for bidding;
Whether to make 5G Fund support available to areas in Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands
that meet the eligible areas definition;
Whether to require 5G Fund support recipients to implement cybersecurity and supply chain risk management plans; and
Whether the 5G Fund should be used to encourage the deployment of Open Radio Access Networks.
FCC Announces Corrected Enhanced A-CAM Support Offers For 82 Companies
September 21, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau (Bureau) has announced corrected Enhanced Alternative Connect America Model (Enhanced A-CAM) offers for 82 companies. The corrected offers, along with five illustrative reports are available here. The new offers are based on corrections that were made to two errors contained in the original Enhanced A-CAM offers:
First, some locations to which competitors provide 100/20 Mbps or faster service were not identified as “competitor-served” because the competitors were not identified as providing qualifying voice service in the state, despite having reported doing so. This error was caused by some carriers making recent changes to their BDC Provider IDs which resulted in a mismatch between the voice and broadband deployment data. As a result, some locations served by a competitor with 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband were not counted as competitively served in the initial offers. Correcting this error reduces the number of required locations—to which the electing Enhanced A-CAM carrier must deploy 100/20 Mbps or faster service—by 27,841 locations. The vast majority of these locations are below the funding threshold, however, and do not affect the amount of the Enhanced A-CAM offer. In addition, some locations that were treated as ILEC-only served in the original offer are now identified as ILEC and competitor-served in the corrected offer and will therefore receive 33% of the existing support amount, rather than 60%.
Second, due to a coding error in the support calculations, 10,354 locations to which an ILEC provides 100/20 Mbps or faster that were also subject to an enforceable commitment to serve by a competitor were identified as “competitor-only served,” rather than “ILEC and competitor served.” As a result, those locations received no support in the initial Enhanced A-CAM calculations, when they should have been assigned 33% of their existing support. This correction has no effect on the number of required locations.
Additionally, in the Public Notice, the Bureau has provided preliminary guidance regarding the assignment to carriers, in the Enhanced A-CAM offers, of locations outside their study area boundaries or in areas with overlapping study area boundaries. Carriers have until Friday, September 29, 2023 to indicate, on a state-by-state basis, whether they elect to receive Enhanced A-CAM support. Each Enhanced A-CAM offer is available here.
USF Contribution Factor For Fourth Quarter Of 2023: 34.5 Percent
September 13, 2023 – The FCC’s Office of Managing Director (OMD) has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the fourth quarter of 2023 will be 34.5 percent. If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. The 34.5 percent USF contribution factor for 4Q 202 is a significant increase from the 29.2 percent contribution factor from last quarter.
For the fourth quarter of 2023, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $8.172483 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected ($8.534206 billion was projected for 3Q 2023). USAC estimates that $2.078830 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms (revenue requirement) in the fourth quarter of 2023 (the 3Q 2023 demand was estimated at $1.912440 billion). Total fourth quarter 2023 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, which breaks out among the USF support mechanisms as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $652.04 million (3Q 2023 was $586.77 million)
Rural Health Care: $97.22 million (3Q 2023 was $66.17 million)
High-Cost: $1.06688 billion (3Q 2023 was $1.04415 billion )
Lifeline: $262.71 million (3Q 2023 was $206.97 million)
Connected Care: $(0.02) million (3Q 2023 was $8.38 million)
Anna Gomez Confirmed As FCC Commissioner
September 7, 2023 – By a vote of 55-43, the U.S. Senate has confirmed Anna Gomez to be a Commissioner on the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Gomez’s confirmation fills the fifth seat on the FCC which had been vacant since Joe Biden became president.
USAC Files Data On Fourth Quarter 2023 USF Contribution Base: $8,172,483,132
September 1, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed projected universal service fund (USF) contribution base data for the fourth quarter of calendar year 2023. The data will be used to determine the next USF contribution factor. For the fourth quarter of 2023, USAC has determined that the total projected collected interstate and international end user revenue base for the USF support mechanisms is $8,172,483,132. The 4Q contribution base data was calculated using projected revenue amounts for October - December 2023 reported by telecommunications service providers on their FCC Forms 499-Q which were due August 1, 2023. To provide a comparison, USAC’s total projected USF contribution base amounts for the first three quarters of 2023 and for the four quarters of 2022 were as follows:
Third Quarter 2023 – $8,534,205,926
Second Quarter 2023 – $8,761,742,607
First Quarter 2023 – $8,749,749,511
Fourth Quarter 2022 – $8,624,083,282
Third Quarter 2022 – $8,285,056,307
Second Quarter 2022 – $8,751,403,396
First Quarter 2022 – $9,235,845,776
For the fourth quarter of 2023, USAC received projected revenue data from 3,256 USF contributors who filed the Form 499-Q. USAC estimated revenue data for 185 non-de minimis service providers that had previously submitted Form 499-Q information to USAC, but failed to make the latest filing. After the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approves the total USF contribution base, the quarterly funding requirements for USF support mechanisms, and projected USF administrative costs, the FCC will establish a USF contribution factor for the fourth quarter of 2023. The new contribution factor will be announced by an FCC Public Notice. USAC will then bill USF contributors on a monthly basis for their individual obligations based on the approved contribution factor.
August 2023
FCC Announces Tentative Agenda For September 21st Open Meeting
August 31, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, September 21, 2023:
Satellite Application Processing – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on facilitating and expediting application processing for satellite and earth station operators in order to advance opportunities for innovation in the new space age. (IB Docket Nos. 22-411, 22-271)
Updating the 5G Fund for Rural America – The Commission will consider a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on the implementation of the 5G Fund for Rural America in light of new, precise, and verified mobile coverage data gathered through the Broadband Data Collection. (GN Docket No. 20-32)
Direct Access to Phone Numbers – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to strengthen the Commission’s direct access rules in order to stem the tide of illegal robocalls, protect the nation’s numbering resources from abuse by foreign bad actors, and advance other important public policy objectives tied to the use of numbering resources. The accompanying Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking would seek comment on the duties of existing direct access authorization holders. (WC Docket Nos. 13-97, 07-243, 20-67; IB Docket No. 16-155)
Updating Obsolete TV Broadcasting Rules – The Commission will consider a Report and Order which would amend Part 73 of the Commission’s Rules to update Television and Class A Television Broadcast Station Rules as well as certain rules applicable to all broadcast stations. This would ensure the FCC’s rules better reflect the current broadcast TV operating environment including changes related to major developments like the transition from analog to digital-only operations and the post-incentive auction transition to a smaller television band with fewer channels. (MB Docket No. 22-227)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC Releases Enhanced A-CAM Offers – Decisions Due September 29th
August 30, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released the offers of model-based Enhanced A-CAM support to existing A-CAM carriers and rate-of-return carriers receiving legacy support. Carriers have until Friday, September 29, 2023 to indicate, on a state-by-state basis, whether they elect to receive Enhanced A-CAM support. Each Enhanced A-CAM offer is available here.
The Enhanced A-CAM offer amounts are “predicated upon carriers receiving support for Enhanced A-CAM required locations calculated using a monthly funding threshold of $63.69, a funding cap per location of $350, and an alternative funding percentage of 80%, except that required locations in Tribal lands are subject to a funding threshold of $47.76 and a funding cap of $365.93.” The calculation of each offer is also based on the following:
Each offer includes 60% of the carrier’s current A-CAM support level for existing ILEC-only served locations, including those locations for which the ILEC may have received a loan or grant to deploy broadband, but excluding locations for which an unsubsidized competitor is receiving funding (e.g., a loan or grant).
Each offer includes 33% of the carrier’s current support level for (a) ILEC-only served locations for which a competitor is receiving funding to deploy 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband service, and (b) locations currently served by both the ILEC and a competitor with 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband.
The locations included in the initial offers are based on location data from the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric v.2 and account for broadband coverage data from the National Broadband Map, as well as federal broadband funding data from the Broadband Funding Map.
The Bureau also released four reports which provide data on support amounts and broadband locations. Report 1.1 shows the state-level offer of model-based support for each carrier that is eligible to elect Enhanced A-CAM support. Report 1.2 shows the number of required locations – both above and below the support threshold – to which an electing carrier will be required to deploy 100/20 Mbps service, in total. Report 1.3 shows the amount of support, by year, that a CAF BLS recipient electing Enhanced A-CAM will receive over the term of Enhanced A-CAM. Report 1.4 shows a list of known mixed support carriers (mixed support carriers that elect to participate in the Enhanced A-CAM mechanism, must elect for both their A-CAM and CAF BLS components).
Carriers must email their election letters to the Bureau at ConnectAmerica@fcc.gov on or before September 29, 2023. The Bureau provided the following information on the election process:
If a carrier fails to submit any final election letter by the September 29, 2023 deadline, the carrier will be deemed to have declined the Enhanced A-CAM offer and will continue to receive support under its existing program and be subject to its existing A-CAM I, Revised A-CAM I, A-CAM II, or CAF BLS deployment obligations. Carriers submitting election letters will receive an e mail confirming that their letters have been received and reviewed for completeness and should contact the Bureau no later than 4:00 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time on October 2, 2023 if they do not receive such confirmation. Confirmation of receipt does not constitute authorization to receive Enhanced A-CAM support pursuant to the terms of the offer. Carriers electing the Enhanced A-CAM support will not begin receiving such support until the Bureau issues a public notice authorizing the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) to disburse the appropriate amounts.
FCC Order On Reconsideration Clarifies Certain Broadband Label Rules
August 29, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has released an Order on Reconsideration that addresses three petitions that requested clarification and reconsideration of the FCC’s new broadband label rules. For the most part, the Order on Reconsideration affirms the rules, while making a few minor clarifications and changes.
First, the FCC affirmed its determination that “enterprise service offerings or special access services are not ‘mass-market retail services,’ and therefore, not covered by [the] label requirement.” The FCC has clarified that, “regardless of how the provider names or defines its offering, the manner in which the service is offered is dispositive of whether the labeling requirements apply.” The enterprise/special access “exemption” typically applies when the broadband service offering “is customized for the beneficiary through individually negotiated agreements.” Accordingly, “a broadband label is only required in E-Rate and Rural Health Care (RHC) Program competitive bids for standard mass-market broadband Internet services requested by a school, library, or health care provider, and that E-Rate and RHC service providers need not include a label for enterprise and special access services provided through those programs.”
Second, the FCC has reconsidered “the requirement that a provider must document each instance when it directs a consumer to a label at an alternative sales channel (e.g., retail stores, kiosks, and over the phone) and retain such documentation for two years.” Accordingly, the FCC has revised Section 8.1(a)(2) of its rules to clarify that the requirement will be deemed satisfied if the broadband provider: (1) establishes the business practices and processes it will follow in distributing the label through alternative sales channels; (2) retains training materials and related business practice documentation for two years; and (3) provides such information to the FCC upon request, within 30 days.
Finally, the has clarified that wireless providers have the flexibility to state “taxes included” or add similar language to the broadband label template when the provider has chosen to include taxes as part of its base price. Providers may only add this language when they have included all taxes in their monthly base price, and may not rely on general statements that taxes may apply if such taxes are not included in the base price.
The FCC has made the compliance dates for the amended rules in the Order on Reconsideration consistent with those for the other broadband label rules. Broadband providers with 100,000 or fewer subscribers have a compliance deadline of one year, and all other providers have a compliance deadline of six months. The FCC’s Consumer and Governmental Affairs Bureau will release a future Public Notice announcing all compliance dates for the broadband label rules.
Kansas Submits BEAD Program 5-Year Action Plan To NTIA
August 24, 2023 – Kansas Governor Laura Kelly has announced that the Kansas Office of Broadband Development (KOBD) has submitted the state’s comprehensive Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) Program Five-Year Action Plan (FYAP) to the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA). Kansas’ 5-year action plan details how the state plans to use the $451 million in BEAD funding NTIA has allocated to the state. The plan outlines KOBD’s “vision to provide universal access to quality broadband, with specific goals and objectives aimed at broadband coverage, adoption rates, and economic growth,” and “identifies existing programs and assets to reduce overlap and to leverage resources.” Additionally, Kansas’ plan “identifies challenges such as supply chain constraints, labor shortages, digital skill gaps, and how to overcome these obstacles,” and includes “a projected timeline, costs and strategies to close gaps in broadband service and ways to ensure fair digital access.” More information on the 5-year plan is available here.
FCC Opens Permit-But-Disclose Ex Parte Docket For Challenge To Fox Broadcast License Renewal
August 23, 2023 – The FCC’s Media Bureau has announced it has opened a permit-but-disclose ex parte docket (MB Docket No. 23-293) for Fox Television Stations, LLC’s (FTS) application to renew the broadcast license of station WTXF-TV, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (Facility ID No. 51568). In July 2023, the Media and Democracy Project filed a petition to deny the license, arguing that Fox’s “broadcasting of knowingly false narratives about the 2020 election” violated its obligations to “broadcast in the public interest, convenience, and necessity.” Applications for renewal of broadcast licenses are typically subject to treatment as restricted proceedings for ex parte purposes under the FCC’s rules. The Media Bureau opened the docket after concluding that classifying the proceeding “as permit-but-disclose would, in this case, permit broader public participation and thereby serve the public interest.”
UFC, NBA, & NFL Suggest Ways To Stop Illegal Live Streams Of Sporting Events
August 23, 2023 – The Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC), NBA, and NFL have submitted comments to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) suggesting ways to stop illegal live streams of sporting events. In May 2023, the USPTO solicited public comment from interested parties regarding their observations and insights into the future of anticounterfeiting and antipiracy strategies. In their joint comments, the three sporting leagues provided the following depiction of illegal live streams of sporting events:
Like so many purveyors of live content, however, UFC, NBAP and NFLP all face the growing and pervasive challenge of piracy. Specifically, bad actors create unauthorized and illegal livestreams of live UFC, NBA and NFL sports events, and distribute those streams on social media and other platforms for viewers to access at no or little cost, thereby depriving UFC, NBAP and NFL of significant revenue. Live piracy sometimes takes the form of rudimentary “screen-capturing” where someone uses their phone to record live content while it is playing on another screen, and livestreams it from their cell phone. In recent years, however, pirates have shown increasing sophistication in terms of the quality of their livestreams and now display livestreams in a way that often renders the final product indistinguishable from the legitimate feed. To garner maximum viewership of the pirated content, enterprising pirates will post “advertisements” on major social media platforms that drive traffic to off-platform sites where people can watch unlawful livestreams of live sports event content without paying a dime. Pirates will even target sports fans by setting up sophisticated websites dedicated to providing fans of a particular sport access to live sporting events featuring that sport, then generate revenue by charging a subscription fee and/or selling advertising.
When online service providers (OSPs) are notified of an illegal stream, the UFC, NBA and NFL claim “that many OSPs frequently take hours or even days to remove content in response to takedown notices—thus allowing infringing live content to remain online during the most anticipated moments, or even the entirety, of a UFC event or an NBA or NFL game.” Ultimately, the leagues want a revision to the Digital Millennium Copyright Act’s (DMCA) notice-and-takedown provisions “to establish that, in the case of live content, the requirement to ‘expeditiously’ remove infringing content means that content must be removed ‘instantaneously or near-instantaneously’ in response to a takedown request.” They provided the following in support of this suggestion:
This would be a relatively modest and non-controversial update to the DMCA that could be included in the broader reforms being considered by Congress or could be addressed separately. OSPs also should be required to impose particular verification measures before a user is permitted to livestream. Those include limiting livestream capabilities to users that have cleared certain verification measures; limiting the ability of newly created accounts to livestream; restricting viewership of livestreams posted by newly created accounts or accounts with few subscribers; and/or limiting livestream capabilities to users with a certain number of subscribers. Certain OSPs already impose measures like these, demonstrating that the measures are feasible, practical and important tools to reduce livestream piracy. Both of these reforms are needed.
NTCA Suggests NTIA Modify BEAD Program’s Letter Of Credit Requirement
August 23, 2023 – NTCA–The Rural Broadband Association has asked the National Telecommunications Information Administration (NTIA) to consider alternatives to the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program’s irrevocable standby Letter of Credit (LOC) requirements for subrecipients. Under BEAD, subrecipients must obtain a LOC issued by an FDIC-insured U.S. bank that has a Weiss rating of B- or better for 25% of the subaward amount. NTCA says that some of its members are concerned that the LOC requirement may hinder their ability to participate in the BEAD program. NTCA recommends two narrowly tailored alternatives to the LOC requirement:
Performance bond. Typically issued by a bank or an insurance company for construction projects, a performance bond is issued against the failure of one party to the contract to meet its contractual obligations. Bond issuers have every incentive to ensure that applicants are financially viable and qualified to perform their duties. Permitting grant subrecipients the ability to obtain performance bonds and/or leverage the performance bonds of their contractors and operators as an alternative to a LOC would protect the government’s interest, while allowing smaller qualified broadband providers greater opportunity to participate in the BEAD program.
Local government guarantee. Similar to a performance bond, a local government could guarantee the subrecipient’s obligation to fulfill its contract. A local government is likely to have, or to obtain, sufficient information about an applicant such that it can assess the applicant’s qualifications and determine its risk tolerance.
FCC Universal Service Notice Of Inquiry Comment Deadlines Announced – Comments Due October 23rd
August 23, 2023 – The FCC’s Notice Of Inquiry concerning high-cost universal service fund (USF) support has been published in the Federal Register. As a result, comments are due on or before October 23, 2023, and reply comments are due on or before November 21, 2023. The Notice Of Inquiry seeks comment on “methods for modifying the Universal Service Fund’s high-cost program to support ongoing expenses for broadband networks in light of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and other recent federal and state efforts.”
Department Of Commerce Proposes Limited Waiver Of Buy America Requirements For BEAD Program
August 22, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Commerce has released a proposed “limited, general applicability, nonavailability waiver of the Buy America Domestic Content Procurement Preference (Buy America Preference)” under the Build America, Buy America Act. The waiver would apply to awards made under the National Telecommunications and Information Administration’s (NTIA) Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program (BEAD Program). As summarized in the notice and request for comment, the waiver:
incentivizes the domestic production of specific manufactured products based on strategic prioritization criteria, including network and data security, which will directly expand American job opportunities;
promotes broad participation in the BEAD Program;
ensures that BEAD Program subrecipients will have access to the manufactured products necessary to fulfill their obligations under the program;
allows funding recipients to continue to provide economic opportunity through timely deployment of broadband infrastructure, which is recognized to expand job opportunities; and
supports the timely development of critical domestic infrastructure that delivers broadband internet services to all Americans.
There is a 30-day public comment period for the waiver. Comments must be received by September 21st, 2023. Electronic comment submissions can be emailed to BABA@ntia.gov with the subject “BEAD Program Nonavailability Waiver.” The Department of Commerce will determine whether to modify or finalize the proposed waiver after the comment period.
FCC 911 Reliability Certifications Due October 16th
August 22, 2023 – The FCC’s Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau has announced that the FCC’s 911 Reliability Certification System is now open for filing certifications for 2023. The FCC’s 911 Reliability Certifications are due annually on October 15. This year, the 15th falls on a Sunday, extending the due date to the next business day, which is October 16, 2023. Covered 911 service providers must file their certifications electronically using the FCC’s online portal at https://apps2.fcc.gov/rcs911/. The annual 911 Reliability Certification requirements – circuit auditing, backup power, and network monitoring – are found in Section 9.19(c) of the FCC’s rules.
FCC Announces Cuba City Telephone Exchange Co. & Cal-Ore Communications RDOF Defaults
August 22, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released a Public Notice announcing that Cuba City Telephone Exchange Co. (Cuba City) and Cal-Ore Communications, Inc. (Cal-Ore) have notified the FCC of their decisions to withdraw from the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) support program. Cuba City was authorized to receive $540,329 in RDOF support over a 10-year term to offer voice and broadband service to 302 locations in Wisconsin, and Cal-Ore was authorized to receive $1,063,513.10 in RDOF support over a 10-year term to offer voice and broadband service to 235 locations in California. Following a Cuba City and Cal-Ore letter notifying the FCC of the companies’ withdrawal from the RDOF program, the Bureau directed the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) to suspend future RDOF support payments. The Bureau has now directed USAC to recover RDOF support from Cuba City and Cal-Ore pursuant to the FCC’s rules.
RUS Announces $667 Million In ReConnect Program Awards
August 21, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Rural Utilities Service has announced it has awarded $667 million in grants and loans under the fourth round of the ReConnect Program. Funding will be used to cover the costs of construction, improvement, or acquisition of facilities and equipment needed to provide broadband service in rural areas. The $667 million has been awarded to 38 broadband projects in Alaska, Arkansas, Arizona, California, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, South Carolina, Texas, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin, and the Marshall Islands. Additionally, RUS announced that Hood Canal Telephone Co. Inc. will receive a $3.8 million loan through the Telecommunications Infrastructure Loan & Loan Guarantee Program to help construct 16 miles of fiber that will provide high-speed internet access to 800 households and 10 businesses in Union, Washington.
FCC Universal Service Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking Comment Deadlines Announced – Comments Due September 18th
August 18, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission’s Report And Order creating an Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) program has been published in the Federal Register. The accompanying Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking also has been published, which establishes the comment deadlines. Comments are due on or before September 18, 2023. Reply comments are due on or before October 2, 2023. The Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking seeks comment on further reforms to the legacy rate-of-return universal service system.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Communications Network, Inc. Acquiring Farmers & Merchants Mutual Telephone Company of Wayland, Iowa
August 17, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau is seeking comment on a Section 214 transfer of control application filed by The Farmers & Merchants Mutual Telephone Company of Wayland, Iowa (Farmers) and Communications Network, Inc. (CNI), requesting consent to transfer control of Farmers to CNI. Comments are due on or before August 31, 2023. Reply comments are due September 7, 2023.
Farmers is a privately held Iowa corporation that provides telecommunications services as an incumbent local exchange carrier in Iowa. Farmers receives high-cost universal service fund (USF) support through Connect American Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS), Connect America Fund Intercarrier Compensation (CAF-ICC) support, and High-Cost Loop Support (HCLS).
CNI is an Iowa corporation that provides wireless telecommunications services in Iowa. CNI is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Kalona Cooperative Telephone Company (KCTC), an Iowa cooperative association that provides local exchange service and other services in Iowa. CNI does not receive any USF high-cost support. CNI’s parent company, KCTC, receives CAF BLS, CAF-ICC support, and HCLS.
Pursuant to a reverse triangular merger, outstanding shares of Farmers stock will be converted into the right to receive a cash amount per share, and outstanding shares of Merger Sub, a wholly-owned subsidiary of CNI created for the purposes of the transaction, will be converted into shares of Farmers. Thereafter, Merger Sub will cease to exist and Farmers will remain in existence as a wholly-owned subsidiary of CNI.
Reid Consulting Files Evidence For Challenges To Fixed Wireless Broadband Coverage Claims In Missouri
August 15, 2023 – The Reid Consulting Group LLC has submitted evidence on behalf of the Missouri Association of Councils of Government for bulk challenges to broadband availability coverage by Licensed Fixed Wireless Access (LFWA) providers in Missouri. In the filing, submitted in the FCC’s Digital Opportunity Data Collection docket (WC Docket No. 19-195), Reid Consulting claims that LFWA broadband service is below 25/3 Mbps at 93,343 locations. At 63,848 of the locations, Reid Consulting claims the ISP has reported speeds of 100/20 Mbps or higher. It wants “the FCC to reverse the burden of proof, requiring that ISPs substantiate their claims rather than saddling communities with the near impossibility of proving a negative across such a wide geographic area.”
FCC Releases Additional Information For Enhanced A-CAM Illustrative Results
August 14, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released additional location information for the illustrative results for the new Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) program. The Wireline Bureau has also released an informational document describing the methodology and data sources that FCC staff used to calculate Enhanced A-CAM) illustrative offers. The illustrative results are available for download in PDF format.
FCC Releases Funding Data For New Enhanced A-CAM Program
August 7, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released the illustrative results for the new Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) program. These results utilize three different combinations of per-location funding caps for unserved locations and funding percentages for locations already deployed by the incumbent local exchange carrier (ILEC), and are based on Version 2 of the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric which incorporates currently served locations from Version 2 of the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection. The illustrative results are available for download in an excel spreadsheet format. Information on the data sources and funding calculations used to produce the illustrative results are available here.
On July 24, 2023, the FCC released a Report And Order creating an Enhanced A-CAM program. Rural rate-of-return carriers that opt in to the Enhanced A-CAM program will receive model based funding for a 15-year term in exchange for deploying 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband service and voice service to all locations in their service areas by the end of 2028. Current A-CAM I and A-CAM II participants, as well as rate-of-return carriers receiving legacy support are eligible to enter the Enhanced A-CAM program. The 15-year term of support will begin in 2024. Accompanying the Report And Order is a Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking that seeks comment on further reforms to the legacy rate-of-return universal service system. Also included is a Notice Of Inquiry that seeks comment on “methods for modifying the Universal Service Fund’s high cost program to support ongoing expenses for broadband networks in light of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and other recent federal and state efforts.”
Biden-Harris Administration Announces Actions To Strengthen Cybersecurity In K-12 Schools
August 7, 2023 – The Biden-Harris Administration has announced new actions and private commitments intended to strengthen cybersecurity at K-12 schools. The new Federal government cybersecurity actions include the following:
The U.S. Department of Education will establish a Government Coordinating Council (GCC) that will coordinate activities, policy, and communications between, and amongst, federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial education leaders to strengthen the cyber defenses and resilience of K-12 schools.
The U.S. Department of Education and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) jointly released K-12 Digital Infrastructure Brief: Defensible & Resilient, the second in a series of guidance documents to assist educational leaders in building and sustaining core digital infrastructure for learning. Additional briefs released by the U.S. Department of Education include Adequate and Future-Proof and Privacy-Enhancing, Interoperable and Useful.
CISA is committing to providing tailored assessments, facilitating exercises, and delivering cybersecurity training for 300 new K-12 entities over the coming school year.
The FBI and the National Guard Bureau are releasing updated resource guides to ensure state government and education officials know how to report cybersecurity incidents and can leverage the federal government’s cyber defense capabilities.
As for private industry actions, the White House has announced that technology companies are committing the following free and low-cost resources to school districts:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is committing the following: $20 million for a K-12 cyber grant program available to all school districts and state departments of education; free security training offerings tailored to K-12 IT staff delivered through AWS Skill Builder; and no-cost cyber incident response assistance through its Customer Incident Response Team in the event a school district experiences a cyberattack. AWS will also provide free well-architected security reviews to U.S. education technology companies providing mission-critical applications to the K-12 community.
Cloudflare, through its Project Cybersafe Schools, will offer a suite of free Zero Trust cybersecurity solutions to public school districts under 2,500 students, to give small school districts faster, safer Internet browsing and email security.
PowerSchool, a provider of cloud-based K-12 software in the United States for 80% of school districts, will provide new free and subsidized “security as a service” courses, training, tools and resources to all U.S. schools and districts.
Google released an updated “K-12 Cybersecurity Guidebook” for schools on the most effective and impactful steps education systems can take to ensure the security of their Google hardware and software applications.
D2L, a learning platform company, is committing to: providing access to new cybersecurity courses in collaboration with trusted third-parties; extending its information security review for the core D2L integration partners; and pursuing additional third-party validation of D2L compliance with security standards.
FCC Approves Up-To-$75 Monthly ACP Broadband Benefit In High-Cost Areas
August 4, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has approved new rules that establish enhanced discounts – an up-to-$75 monthly broadband benefit – for broadband services provided in high-cost areas by participants in the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP). The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act directed the FCC to establish the increase because “the $75 monthly benefit would support providers that can demonstrate that the standard $30 monthly benefit would cause them to experience ‘particularized economic hardship’ such that they would be unable to maintain part or all of their broadband network in a high-cost area.” In the Sixth Report And Order, the FCC takes the following actions to implement the increased ACP benefit:
Adopts rules to implement the up-to-$75 monthly ACP benefit in high-cost areas, as defined by NTIA and as required by the Infrastructure Act;
Defines “particularized economic hardship” and establishes the showing that ACP providers must make to demonstrate they are experiencing a particularized economic hardship in a high-cost area;
Sets the processes for reviewing and making determinations on providers’ economic hardship submissions, and appealing those determinations;
Creates a requirement for providers that are approved to offer the high-cost area benefit to annually resubmit an economic hardship showing to continue offering the high-cost area benefit; and
Outlines the steps providers must take to provide advance notice and a transition path for ACP consumers if the provider no longer qualifies to offer the high-cost area benefit.
FCC Issues $300 Million Robocall Fine Against International Network Of Companies
August 3, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has issued a Forfeiture Order against Sumco Panama SA, Sumco Panama USA, Virtual Telecom kft, Virtual Telecom Inc., Davis Telecom Inc., Geist Telecom LLC, Fugle Telecom LLC, Tech Direct LLC, Mobi Telecom LLC, and Posting Express Inc. jointly and severally, for placing “over five billion auto warranty robocalls to consumers between January 2021 and March 2021 in violation of the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) and Truth in Caller ID Act.” The international network of companies was involved in the largest illegal robocall operation the FCC has ever investigated. The Forfeiture Order imposes a penalty of $299,997,000 against the companies. Payment of the forfeiture is due within 30 days. If it is not paid within 30 days, the case may be referred to the U.S. Department of Justice for enforcement of the forfeiture pursuant to Section 504(a) of the Communications Act.
Consumers’ Research Files Comments And Objections To USAC’s 4Q 2023 USF Fund Size Projections
August 3, 2023 – Consumers’ Research, Cause Based Commerce, Inc., and 12 individual consumers have filed comments and objections in response to the Universal Service Administrative Company’s (USAC) Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections for the fourth quarter of 2023. USAC’s filing details the USF’s total projected funding requirements for 4Q 2023, which includes costs that can be directly attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each mechanism. The FCC will use the data in its calculation of the quarterly USF contribution factor. The Consumers’ Research group claims the universal service fund (USF) “is an unconstitutional tax raised and spent by an unaccountable federal agency.”
USAC Submits Estimated Fourth Quarter 2023 Universal Service Funding Requirements
August 2, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed the Federal Universal Service Support Mechanisms Fund Size Projections for the fourth quarter of 2023. The filing details the universal service fund’s (USF) total projected funding requirements for 4Q 2023, which includes costs that can be directly attributed to the High Cost, Low Income, Rural Health Care, and Schools and Libraries Support Mechanisms, as well as Connected Care Pilot Program costs, and projected administrative expenditures of each mechanism. All of USAC’s filings to the FCC are available here. USAC’s data shows the following total projected 4Q 2023 funding requirements for each USF support mechanism:
High Cost Support Mechanism – $1.06688 billion (the 3Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $1.044 billion; 2Q 2023 was $972.91 million; 1Q 2023 was $1.152 billion). USAC initially calculated the high cost funding requirement as $1.06760 billion, but the amount was decreased by prior period adjustments of $18.86 million, and increased by administrative costs of $18.14 million.
Low Income Support Mechanism – $262.71 million (the 3Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $206.97 million; 2Q 2023 was $202.05 million; 1Q 2023 was $201.21 million). USAC initially estimated funding requirements of 302.14 million for Lifeline and $0.06 million for Link-Up, resulting in a total funding requirement of $302.20 million. This amount was decreased by prior period adjustment of $63.57 million, and increased by $24.08 million for administrative costs.
Rural Health Care Support Mechanism – $170.98 million (the 3Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $170.57 million; 2Q 2023 was $159.36 million; 1Q 2023 was $70.79 million).
Connected Care Pilot Program – -$0.02 million (the 3Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $8.38 million; 2Q 2023 was $8.43 million; 1Q 2023 was $8.5 million). Based on collections of $8.33 million over the past 12 quarters, the remaining collection requirement for the Connected Care Pilot Program in 4Q2023 is $0.04 million. The collection requirement of $0.04 million was adjusted as follows: decreased by prior period adjustment of $0.14 million and increased by $0.08 million for administrative expenses, resulting in a 4Q2023 funding requirement of -$0.02 million.
E-Rate Schools and Libraries Support Mechanism – $652.04 million (the 3Q 2023 projected funding requirement was $586.77 million; 2Q 2023 was $609.15 million; 1Q 2023 was $697.13 million).
USAC projects a consolidated budget of $68.50 million for 4Q 2023. This breaks out to $35.29 million in direct costs for all four support mechanisms, and $33.21 million in joint and common costs which include costs associated with billing, collection, and disbursement of universal service funds. (USAC projected a consolidated budget of $68.04 million for 3Q 2023. It was $71.91 million for 2Q 2023, and $67.28 million for 1Q 2023.) The FCC will use the of the quarterly funding requirements for the four USF Support Mechanisms, the projected administrative expenses, and the USF contribution base amount to calculate the quarterly USF contribution factor. Copies of USAC’s historical USF filings are available on its website.
Mergers & Acquisitions: LICT To Spin Off Michigan Broadband
August 2, 2023 – LICT Corporation has announced the approval of its previous decision to spin off the company’s wholly-owned subsidiary Michigan Broadband. The separation will be effectuated through a pro-rata distribution of stock in the new company MachTen, Inc. Thereafter, “LICT and MachTen will be independent, publicly traded companies with distinct business operations, customers and geographic markets.”
So-Called Coalition Of RDOF Winners Ask FCC For More RDOF Support
August 1, 2023 – A group of communications providers that won Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) auction support have asked the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for supplementary RDOF support. The “Coalition of RDOF winners” say additional funding is needed “to address the massive and unprecedented increases in broadband deployment construction costs RDOF winners are facing.” They further claim these increased costs “could never have been anticipated at the time RDOF winners placed reverse bids during the RDOF auction.” In the ex parte filing, the group has laid out the following potential forms of relief that the FCC could provide:
Supplementary funding to RDOF winners that have affirmatively requested such funding;
A short “amnesty window” that allows RDOF winners to relinquish all or part of their RDOF winning areas without forfeitures or other penalties if the Commission chooses not to make supplemental funds available or if the amount of supplemental funds the Commission does make available does not cover an RDOF Winner’s costs that exceed reasonable inflation, so that such unserved areas are in included in the BEAD program;
RDOF payments in years 7-10 in earlier years;
An extra year of funding;
Relief from all, or certain aspects of, the letter of credit requirements on an expedited basis; and/or
Realignment of RDOF support provided to an RDOF winner that relinquishes certain areas pursuant to an amnesty window, so that RDOF funding in such areas is redirected to RDOF areas that the RDOF winner keeps so as to offset the significant broadband deployment construction cost increases in such areas.
July 2023
FCC Issues $20 Million Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture Against Q Link Wireless & Hello Mobile Telecom For Violating CPNI Rules
July 28, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has issued a Notice Of Apparent Liability For Forfeiture against Q Link Wireless LLC and Hello Mobile Telecom LLC for failing to safeguard customer proprietary network information (CPNI). The FCC found that there were at least 500 apparent violations of the FCC’s CPNI rules during the relevant time period of the violations, resulting in a proposed penalty of $20,000,000. Q Link and Hello Mobile are wholly owned by Quadrant Holdings Group LLC, which in turn is wholly owned by Quadrant’s Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Issa Asad. The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau’s opened an investigation into Q Link after the website Ars Technica published an article claiming that a security flaw in Q Link’s My Mobile Account app potentially exposed the private information of an unknown number of Q Link subscribers. The Enforcement Bureau then issued a Letter of Inquiry to Quadrant, directing Quadrant and Q Link and Hello Mobile to provide information and documents regarding their duty to protect CPNI and other proprietary information under Section 222 of the Communications Act and Section 64.2010 of the FCC’s rules. After the companies failed to respond, the Enforcement Bureau issued a Notice of Apparent Liability initially proposing a $100,000 forfeiture. Ultimately, the investigation led the FCC to conclude the following:
The companies’ methods for controlling access to CPNI apparently violate the requirement to “take reasonable measures to discover and protect against attempts to gain unauthorized access to CPNI” in Section 64.2010(a) of the FCC’s rules, as well as Section 222 of the Communications Act which requires carriers to protect customer information;
The companies’ practice of using customer readily available biographical information and account information as a default method to authenticate users apparently violates Section 64.2010(c) of the FCC’s CPNI rules; and
The method through which Q Link customers can access their accounts on the website, and reset their passwords, in the case of lost or forgotten login credentials apparently violates Section 64.2010(e) of the FCC’s CPNI rules.
Final Agenda For FCC Open Meeting On August 3, 2023
July 27, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the following final agenda for its next open meeting scheduled for 10:30 a.m. on Thursday, August 3, 2023:
Advancing Understanding of Non-Federal Spectrum Usage – The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry that would initiate a technical inquiry into how to obtain more sophisticated knowledge of real-time non-Federal spectrum usage—and how the Commission could take advantage of modern capabilities for doing so in a cost-effective, accurate, scalable, and actionable manner. The Notice of Inquiry would explore the potential to advance the Commission’s understanding of commercial spectrum usage by leveraging new data sources, methods, and technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in an increasingly congested radiofrequency environment. (Docket No. 23-232)
Updating Digital FM Radio Service – The Commission will consider an Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking seeking comment on proposed changes to the methodology used to determine maximum power levels for digital FM broadcast stations and to the process for authorizing digital transmissions at different power levels on the upper and lower digital sidebands. (MB Docket No. 22-405)
Affordable Connectivity Program High-Cost Benefit – The Commission will consider a Sixth Report and Order which would implement the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) high-cost area benefit, providing a discount of up to $75 per month for broadband services provided in qualifying high-cost areas, by participating ACP providers. (Docket No. 21-450)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC Chairwoman Circulates Section 706 Notice of Inquiry; Proposes New Definition Of Fixed Broadband: 100/20 Mbps
July 25, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has circulated a draft Notice of Inquiry (NOI) to initiate the FCC’s evaluation of the state of broadband deployment across the country, as required by Section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996. Generally, Section 706 directs the FCC to annually inquire whether advanced telecommunications capability is being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion. Advanced telecommunications capability is described as high speed, switched, broadband telecommunications capability that enables users to originate and receive high-quality voice, data, graphics, and video telecommunications using any technology. If the FCC determines that broadband is not being deployed in a timely manner, Section 706 requires the FCC to take immediate action to accelerate broadband deployment by removing barriers to infrastructure investment and promoting competition.
In the NOI, Chairwoman Rosenworcel proposes that the FCC “consider several crucial characteristics of broadband deployment, including affordability, adoption, availability, and equitable access.” Notably, the NOI proposes to increase the national fixed broadband standard to 100 megabits per second (Mbps) for download and 20 Mbps for upload. The FCC’s current definition of fixed broadband stands at 25/3 Mbps, which was set in 2015. The NOI proposes to set a separate national goal of 1 Gbps/500 Mbps for the future. As part of the announcement, Chairwoman Rosenworcel provided the following statement: “It’s time to connect everyone, everywhere. Anything short of 100% is just not good enough.”
FCC Releases Order Creating Enhanced A-CAM Program
July 24, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has approved and released a Report And Order creating an Enhanced Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM) program. Rural rate-of-return carriers that opt in to the Enhanced A-CAM program will receive model-based funding for a 15-year term in exchange for deploying 100/20 Mbps or faster broadband service and voice service to all locations in their service areas by the end of 2028. Current A-CAM I and A-CAM II participants, as well as rate-of-return carriers receiving legacy support are eligible to enter the Enhanced A-CAM program. The 15-year term of support will begin in 2024. Accompanying the Report And Order is a Notice Of Proposed Rulemaking that seeks comment on further reforms to the legacy rate-of-return universal service system. Also included is a Notice Of Inquiry that seeks comment on “methods for modifying the Universal Service Fund’s high-cost program to support ongoing expenses for broadband networks in light of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and other recent federal and state efforts.”
FCC Chairwoman Proposes New Voluntary Cybersecurity Labeling Program For Smart Devices
July 18, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has circulated a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) to create a voluntary cybersecurity labeling program for smart devices. If adopted, the proposed cybersecurity labeling program would provide consumers with clear information about the security of their Internet-enabled devices, more commonly referred to as “Internet of Things” or “smart” devices. According to the FCC news release announcement, the NPRM “outlines a voluntary cybersecurity labeling program that would be established under the FCC’s authority to regulate wireless communications devices based on cybersecurity criteria developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). If the proposal is adopted by a vote of the Commission, it would be issued for public comment, and could be up and running by late 2024.”
Wavelength Defaults On RDOF Winning Bids In California
July 18, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau and Office of Economics and Analytics have announced that Wavelength LLC has defaulted on five winning Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) bids in California. Wavelength was unable to receive designation as an eligible telecommunications carrier (ETC) by the California Public Utilities Commission, and thereafter, Wavelength’s petition for waiver of the RDOF ETC designation documentation deadline was denied by the FCC. Accordingly, the FCC has determined Wavelength to be in default on its RDOF bids, and subject to forfeiture. In the same Public Notice, the FCC has dismissed LTD Broadband’s request for waiver of the RDOF deadline to submit ETC designation documentation for its RDOF winning bids in South Dakota.
FCC Issues Tentative Agenda For August 3rd Open Meeting
July 13, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, August 3, 2023:
Advancing Understanding of Non-Federal Spectrum Usage – The Commission will consider a Notice of Inquiry that would initiate a technical inquiry into how to obtain more sophisticated knowledge of real-time non-Federal spectrum usage—and how the Commission could take advantage of modern capabilities for doing so in a cost-effective, accurate, scalable, and actionable manner. The Notice of Inquiry would explore the potential to advance the Commission’s understanding of commercial spectrum usage by leveraging new data sources, methods, and technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in an increasingly congested radiofrequency environment. (Docket No. 23-232)
Updating Digital FM Radio Service – The Commission will consider an Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking seeking comment on proposed changes to the methodology used to determine maximum power levels for digital FM broadcast stations and to the process for authorizing digital transmissions at different power levels on the upper and lower digital sidebands. (MB Docket No. 22-405)
Affordable Connectivity Program High-Cost Benefit – The Commission will consider a Sixth Report and Order which would implement the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) high-cost area benefit, providing a discount of up to $75 per month for broadband services provided in qualifying high-cost areas, by participating ACP providers. (Docket No. 21-450)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Final Agenda For FCC’s July 20th Open Meeting
July 13, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the final agenda for its open meeting on Thursday, July 20, 2023 at 10:30 am:
E-Rate: Enhancing Support for Connectivity in Tribal Communities – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which would adopt rules to enhance Tribal communities’ access to the E-Rate program by streamlining certain program rules, making Tribal college and university libraries eligible for E-Rate support, and reducing administrative burdens in the program. The Commission will also seek comment on ways to further improve and simplify program rules for all E-Rate applicants. (CC Docket Nos. 02-6, 96-45, 97-21)
Ensuring the Reliability and Resiliency of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to ensure that when there is a communications service outage that potentially affects people’s ability to reach the 988 Lifeline, the Commission and those who provide life-saving 988 crisis intervention services receive timely and actionable information. (PS Docket Nos. 23-5, 15-80; WC Docket No. 18-336)
Preserving Local Radio Programming – The Commission will consider a Report and Order allowing a limited group of existing channel 6 low power television stations to continue to provide analog FM radio service as an ancillary or supplementary service under specified rules. (MB Docket No. 03-185)
FCC Chairwoman Proposes E-Rate Pilot Program To Support Cybersecurity And Advanced Firewall-Related Services For Eligible K-12 Schools & Libraries
July 12, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced a proposal to create a pilot program that would provide E-Rate support for cybersecurity and advanced firewall-related services for eligible K-12 schools and libraries. Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel shared high-level details of the proposal in a speech before the School Superintendents Association and the Association of School Business officers. She said the proposed pilot program would work in tandem with federal agency partners to invest up to $200 million over three years to harden the cyber defenses and determine the most effective methods to protect schools and libraries. According to the FCC news release announcement, the pilot program would be established “within the Universal Service Fund, but separate from the E-Rate program, to ensure gains in enhanced cybersecurity don’t come at a cost of undermining E-Rate’s success in promoting digital equity.” In a December 2022 Public Notice, the FCC sought comment on using E-Rate funds to support next-generation firewalls and services, as well as numerous related issues.
USAC Files E-Rate Cost & Funding Data On Firewall Protection
July 12, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has filed two reports on E-Rate funding requests for firewall protection and services. The first report provides high-level data on firewall protection as part of total category one funding requests from 2016 to 2022. The second report provides high-level data on firewall services and components as part of total category two funding requests from 2016 to 2022. USAC filed the information upon a request from FCC staff.
FCC Chairwoman Circulates New Rules To Prevent SIM Swapping
July 11, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has circulated a Report and Order that would revise the FCC’s Customer Proprietary Network Information (CPNI) and Local Number Portability rules to prevent SIM Swapping. A SIM swap occurs when a new SIM card is registered with a phone number – swap out the old SIM for the new. A SIM card – subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module – is a small, removable chip in a mobile device that allows it to connect to a wireless provider’s network. A fraudulent SIM swap occurs when criminals link a new SIM to a victim’s phone number, typically through the use of social engineering. Sometimes, however, criminals work with an employee of a wireless provider to make it happen. The FCC’s new rules, if adopted, would “require wireless providers to adopt secure methods of authenticating a customer before redirecting a customer’s phone number to a new device or provider.” Wireless providers also would be required “to immediately notify customers whenever a SIM change or port-out request is made on customers’ accounts, and take additional steps to protect customers from SIM swap and port-out fraud.” The Report and Order is accompanied by a Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking which seeks comment on “ways to further harmonize the[] rules with existing CPNI rules and additional steps the Commission can take to harmonize government efforts to address SIM swap and port-out fraud.”
USAC Updates Connect America Fund Broadband Map
July 7, 2023 – The Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) has released an updated version of the Connect America Fund (CAF) Broadband map that reflects broadband deployment data as of December 31, 2022. The CAF map is an interactive online map that shows the impact of high-cost universal service fund support on broadband expansion in rural America. Information in the CAF map comes directly from broadband providers who submit broadband deployment data annually through USAC’s High Cost Universal Broadband (HUBB) portal. The dataset underpinning the map is available online here. The new map shows geographic areas that are eligible for CAF support, as well as the specific fixed locations where broadband providers have built out broadband service using the following types of CAF support:
Connect America Fund Phase II Model (CAF II Model Support)
Connect America Fund Phase II Auction (CAF II Auction Support)
Alternative Connect America Cost Model (ACAM Support)
Alternative Connect America Cost Model II (ACAM II Support)
Connect America Fund Broadband Loop Support (CAF BLS Support)
Rural Broadband Experiments (RBE Support)
Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF Support)
Alaska Plan (AK Plan Support)
Bringing Puerto Rico Together (Uniendo a Puerto Rico) Fund and the Connect the USVI Fund (PR Fixed Support)
FCC Extends Pause Of Phase-Out Of Lifeline Support For Voice-Only Services & Increase In Lifeline Minimum Mobile Broadband Data Capacity
July 7, 2023 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has extended, for an additional year, the waiver pausing both the phase-out of Lifeline support for voice-only services and the increase in Lifeline minimum service standards for mobile broadband data capacity. The pause will extend until December 1, 2024. As a result, the Lifeline program maintains $5.25 per month support for services that meet only the voice minimum service standard, and the 4.5 GB minimum service standard for mobile broadband data capacity. Without the extension, the $5.25 per month support for minimum voice service would be eliminated in most areas on December 1, 2023, and the mobile broadband data capacity minimum would rise to 20 GB per month.
Mergers & Acquisitions: GigFire Acquires Rural Comm In Illinois
July 7, 2023 – GigFire (formerly known as LTD Broadband) has announced it has acquired Rural Comm, a communications services provided located in Farina, IL. GigFire operates in ten states, primarily in the Midwest region of the U.S. With its acquisition of Rural Comm, “GigFire will build fiber to the home in over 150 towns and cities in Illinois and upgrade the existing network infrastructure to deliver gigabit speeds.” Terms of the deal were not disclosed.
FCC Announces Opening Of Next Broadband Data Collection Filing Window
July 3, 2023 – The FCC’s Broadband Data Task Force has announced that the next Broadband Data Collection (BDC) filing window opens Monday July 3, 2023. Specifically, starting July 2, 2023, facilities-based broadband service providers may begin to file in the BDC system data that reflects where their mass-market broadband internet access services are available as of June 30, 2023. Facilities-based broadband service providers, as well providers of fixed voice services, must also submit subscription data as of June 30, 2023 required under Form 477 in the BDC system. All mass-market broadband internet access service availability data and subscription data must be submitted no later than September 1, 2023.
FCC Chairwoman Sends Letter On RDOF Implementation To Senator Cindy Hyde-Smith
July 1, 2023 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has sent a letter to Senator Cindy Hyde-Smith (MS-R) which provides an update on the implementation of the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF). Chairwoman Rosenworcel’s letter provides the following information:
When the RDOF auction concluded, a total of 180 bidders were preliminarily awarded funding. After bidding consortia were allowed to distribute winning bids among their members, a total of 417 providers ultimately filed long-form applications with the FCC.
To date, the RDOF program has authorized over $6 billion in funding to bring primarily gigabit broadband service to over 3.4 million locations in 47 states. Hundreds of RDOF winners have begun deploying broadband networks to connect unserved areas.
The FCC sent letters to 197 RDOF applicants where data suggested certain RDOF locations were already served by an existing carrier or should not have been included in the auction. This resulted in the removal of nearly 5,000 census blocks from the program.
The RDOF auction allocated $9.2 billion of the RDOF budget to winning bidders, and, after long-form review, the FCC authorized just over $6 billion.
The FCC will collect only enough RDOF funding through the USF contribution process to match the approximately $6 billion committed. The FCC does not have support in reserve readily available for reallocation to the extent that the total amount authorized for RDOF fell below the projected budget.
June 2023
FCC Robocall Response Team Reminds All IP-Based Voice Service Providers Of June 30, 2023 STIR/SHAKEN Deadline
June 30, 2023 – The Federal Communications Commission’s Robocall Response Team has issued a News Release announcing that all IP-based voice service provider networks are required to implement STIR/SHAKEN to defend against spoofed robocalls. STIR/SHAKEN is defined as caller ID authentication standards that “serve as a common digital language used by phone networks, allowing valid information about a call to pass from provider to provider which, among other things, informs blocking tools of possible suspicious calls by making it easier to detect spoofed calls.” The FCC has applied the following deadlines to U.S. voice communications networks for implementing the STIR/SHAKEN standards:
Largest Voice Service Providers – by June 30, 2021.
Non-Facilities-Based Small Providers – by June 30, 2022.
Facilities-Based Small Providers – by June 30, 2023.
Gateway Providers – by June 30, 2023.
Intermediate Providers – under FCC rules passed in March, intermediate providers that receive unauthenticated IP calls directly from domestic originating providers must use STIR/SHAKEN to authenticate those calls by December 31, 2023.
Non-IP Networks – the FCC opened a proceeding to consider ways to implement caller ID authentication on non-IP networks, which cannot implement STIR/SHAKEN.